Abstract
Purpose. Investigations into the kinetic assembly and dissociation of hexameric LysB28ProB29-human insulin (LysPro), a rapid-acting insulin analog produced by the sequence inversion of amino acids at positions B28 and B29, were designed to explain the impact that the sequence inversion has on the formulation and pharmacokinetics of the insulin analog.
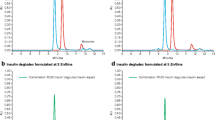
Methods. The kinetics of phenolic ligand binding to human insulin and LysPro were studied by stopped-flow spectroscopy. The kinetics of R6 hexamer disruption were studied by extraction of Co(II) with EDTA.
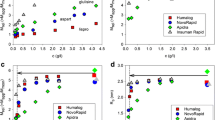
Results. Phenolic ligand binding to human insulin yielded rate constants for a fast and slow phase that increased with increasing ligand concentration and are attributed to the T6 → T3R3 and T3R3 → R6 transitions, respectively. However, the kinetics of phenolic ligand binding with LysPro was dominated by rates of hexamer assembly. The kinetic differences between the insulin species are attributed to alterations at the monomer-monomer interface in the dimer subunit of the LysPro analog. The extraction of Co(II) from both hexameric complexes by EDTA chelation is slow at pH 8.0 and highly dependent on ligand concentration. Cobalt extraction from LysPro was pH dependent. Of the various phenolic ligands tested, the relative affinities for binding to the human and LysPro hexamer are resorcinol > phenol > m-cresol.
Conclusions. The extraction data support the formation of an R6-type LysPro hexamer under formulation conditions, i.e., in the presence of divalent metal and phenolic ligand, that is similar in nature to that observed in insulin. However, the formation kinetics of LysPro identify a radically different monomeric assembly process that may help explain the more rapid pharmacokinetics observed with the hexameric formulation of LysPro insulin relative to human insulin.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. Brange and L. Langkjaer. Acta Pharm. Nord. 4:149–158 (1992).
U. Derewenda, Z. Derewenda, E. J. Dodson, G. G. Dodson, C. D. Reynolds, G. D. Smith, C. Sparks, and D. Swenson. Nature 338:594–596 (1989).
A. Wollmer, B. Rannefeld, B. R. Johansen, K. R. Hejnaes, P. Baldschmidt, and F. B. Hansen. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 368:903–911 (1987).
G. D. Smith and E. Ciszak. P.N.A.S. 91:8851–8855 (1994).
E. N. Baker, T. L. Blundell, J. F. Cutfield, S. M. Cutfield, E. J. Dodson, G. G. Dodson, D. M. C. Hodgkin, R. E. Hubbard, N. W. Isaacs, C. D. Reynolds, K. Sakabe, N. Sakabe, and N. M. Vijayan. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 319:369–456 (1988).
E. Ciszak, J. M. Beals, B. H. Frank, J. C. Baker, N. D. Carter, and G. D. Smith. Structure 3:615–622 (1995).
M. L. Brader and M. F. Dunn. TIBS 16:341–345 (1991).
M. Roy, M. L. Brader, R. W.-K. Lee, N. C. Kaarsholm, J. F. Hansen, and M. F. Dunn. J. Biol. Chem. 264:19081–19085 (1989).
P. Krüger, G. Gilge, Y. Çabuk, and A. Wollmer. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 371:669–673 (1990).
N. C. Kaarsholm, H.-C. Ko, and M. F. Dunn. Biochemistry 28:4427–4435 (1989).
N. C. Kaarsholm and M. F. Dunn. Biochemistry 26:883–890 (1987).
Y. Karatas, P. Krüger, and A. Wollmer. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 372:1035–1038 (1991).
M. C. Storm and M. F. Dunn. Biochemistry 24:1749–1756 (1985).
D. N. Brems, L. A. Alter, M. J. Beckage, R. E. Chance, R. D. DiMarchi, L. K. Green, H. B. Long, A. H. Pekar, J. E. Shields, and B. H. Frank. Protein Engineering 5:527–533 (1992).
D. L. Bakaysa, J. Radziuk, H. A. Havel, M. L. Brader, S. L. Edwards, S. W. Dodd, J. M. Beals, A. H. Pekar, and D. N. Brems. Physiochemical basis for the rapid time-action of LysB28ProB29-Insulin: Dissociation of a protein ligand complex. Protein Sci.: in press.
E. Ciszak, D. Langs, J. M. Beals, B. H. Frank, and G. D. Smith. A novel crystal form of LysPro insulin. In American Crystallographic Association Annual Meeting, Montreal, American Crystallographic Association, 1995.
D. C. Howey, R. R. Bowsher, R. L. Brunelle, and J. R. Woodworth. Diabetes 43:396–402 (1994).
J. Brange, D. R. Owens, S. Kang, and A. Volund. Diabetes Care 13:923–954 (1990).
B. H. Frank and A. J. Veros. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 32:155–160 (1968).
K. E. van Holde. Physical Biochemistry. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1985, pp. 110–136.
L. Gross and M. F. Dunn. Biochemistry 31:1295–1301 (1992).
P. Brzovic S., W. E. Choi, D. Borchardt, N. C. Kaarsholm, and M. F. Dunn. Biochemistry 33:13057–13069 (1994).
A. Wollmer, B. Rannefeld, J. Stahl, and S. G. Melberg. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 370:1045–1053 (1989).
E. Jacoby, P. Kruger, Y. Karatas, and A. Wollmer. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 374:877–885 (1993).
C. R. Bloom, W. E. Choi, P. S. Brzovic, J. J. Ha, S. T. Huang, N. C. Kaarsholm, and M. F. Dunn. J. Mol. Biol. 245:324–330 (1995).
A. D. Varshavsky, J. M. Beals, D. T. Birnbaum, S. W. Dodd, and B. E. Saxberg. A combined optimization strategy in mathematical modeling of phenolic ligand binding to the insulin hexamer. Math. Modeling and Sci. Computing: in press.
D. T. Birnbaum, S. W. Dodd, B. E. H. Saxberg, A. D. Varshavsky, and J. M. Beals. Biochemistry 35:5366–5378 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Birnbaum, D.T., Kilcomons, M.A., DeFelippis, M.R. et al. Assembly and Dissociation of Human Insulin and LysB28ProB29-Insulin Hexamers: A Comparison Study. Pharm Res 14, 25–36 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012095115151
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012095115151