Abstract
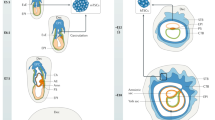
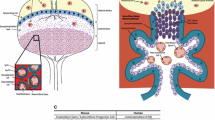
The mammalian embryo and fetus are unable to develop without a well-established, functional placenta. This transitory yet indispensable structure attaches the conceptus to the uterus and establishes the vascular connections necessary for nutrient and gaseous exchange between maternal and fetal compartments. Genetic targeting strategy allows the generation of mice lacking a specific gene. Such approaches reveal: (i) the high incidence of mutant embryonic or fetal death in utero, and (ii) the extraembryonic (placental) causes of these deaths. Due to the similarities presented between mouse and human placenta, we propose to use the potential of mouse targeting experiments as a model in order to understand human obstetrical pathologies. In this paper, we first review genes that have been demonstrated to be required in mice for implantation, choriovitelline and chorioallantoic placentation. Using examples (integrins, homeoboxs, hepatocyte growth factor or epidermal growth factor receptor...) we demonstrate the reality and efficiency of such an approach. Other candidate genes (receptor of leukemia inhibitory factor, Wnt2 or retinoic acid receptor α...) in order to understand, prevent and treat human obstetrical pathologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsohn PA and Zorn TM (1993) Implantation and decidualization in rodents. J Exp Zool 266: 603–628.
Adams RH, Porras A, Alonso G, Jones M, Vinterstein K, Panelli S, Valladares A, Perez L, Klein R and Nebreda AR (2000) Essential role of p38 alpha MAP, kianse in placental but not embryonic cardiovascular development. Mol Cell 6: 109–115.
Alsat E, Marcotty C, Gabriel R, Igout A, Frankenne F, Hennen G and Evain-Brion D (1995) Molecular approach to intrauterine growth retardation: an overview of recent data. Reprod Fertil Dev 7: 1457–1464.
Anson-Cartwright L, Dawson K, Holmyard D, Fisher SJ, Lazzarini RA and Cross JC (2000) The glial cells missing-1 protein is essential for branching morphogenesis in the chorioallantoic placenta. Nat Genet 25: 311–314.
Arthur HM, Ure J, Smith AJ, Renforth G, Wilson DI, Torsney E, Charlton R, Parums DV, Jowett T, Marchuk DA, Burn J and Diamond AG (2000) Endoglin, an ancillary TGFbeta receptor, is required for extraembryonic angiogenesis and plays a key role in heart development. Dev Biol 217: 42–53.
Baergen RN (1997) Gestational choriocarcinoma. Gen Diagn Pathol 143: 127–141.
Barak Y, Nelson MC, Ong ES, Jones YZ, Ruiz-Lozano P, Chien KR, Koder A and Evans RM (1999) PPAR gamma is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell 4: 585–595.
Bainbridge DR (2000) Evolution of mammalian pregnancy in the presence of the maternal immune system. Rev Reprod 5: 67–74.
Batten BE and Haat JL (1979) Fine structural differentiation of germ layers in the mouse at the time of mesoderm formation. Anat Res 194: 125–142.
Bilban M, Head S, Desoye G and Quaranta V (2000) DNA microarrays: a novel approach to investigate genomics in trophoblast invasion—a review. Placenta 21 Suppl A: S99–S105.
Bilinski P, Roopenian D and Gossler A (1998) Maternal IL-11Ralpha function is required for normal decidua and fetoplacental development in mice. Genes Dev 12: 2234–2243.
Bischoff FZ and Simpson JL (2000) Heritability and molecular genetic studies of endometriosis. Hum Reprod Update 6: 37–44.
Blackburn MR, Wakamiya M, Caskey CT and Kellems RE (1995) Tissue-specific rescue suggests that placental adenosine deaminase is important for fetal development in mice. J Biol Chem 270: 23891–23894.
Bladt F, Riethmacher D, Isenmann S, Aguzzi A and Birchmeier C (1995) Essential role for the c-met receptor in the migration of myogenic precursor cells into the limb bud. Nature 376: 768–771.
Bourdeau A, Dumont DJ and Letarte M (1999) A murine model of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Clin Invest 104: 1343–1351.
Bowen JA and Hunt JS (2000) The role of integrins in reproduction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 223: 331–343.
Bugge TH, Xiao Q, Kombrinck KW, Flick MJ, Holmback K, Danton MJ, Colbert MC, Witte DP, Fujikawa K, Davie EW and Degen JL (1996) Fatal embryonic bleeding events in mice lacking tissue factor, the cell-associated initiator of blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 6258–6263.
Capecchi MR (1989) Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science 244: 1288–1292.
Capecchi MR (1997) Hox genes and mammalian development. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 62: 273–281.
Carmeliet P, Mackman N, Moons L, Luther T, Gressens P, Van Vlaenderen I, Demunck H, Kasper M, Breier G, Evrard P, Muller M, Risau W, Edgington T and Collen D (1996) Role of tissue factor in embryonic blood vessel development. Nature 383: 73–75.
Chen JR, Cheng JG, Shatzer T, Sewell L, Hernandez L and Stewart CL (2000) Leukemia inhibitory factor can substitute for nidatory estrogen and is essential to inducing a receptive uterus for implantation but is not essential for subsequent embryogenesis. Endocrinology 141: 4365–4372.
Christiansen-Weber TA, Voland JR, Wu Y, Ngo K, Roland BL, Nguyen S, Peterson PA and Fung-Leung WP (2000) Functional loss of ABCA1 in mice causes severe placental malformation, aberrant lipid distribution, and kidney glomerulonephritis as well as high-density lipoprotein cholesterol deficiency. Am J Pathol 157: 1017–1029.
Clark DE, Smith SK, Sharkey AM, Sowter HM and Charnock-Jones DS (1996) Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and its receptor c-met: localisation and expression in the human placenta throughout pregnancy. J Endocrinol 151: 459–467.
Clark DE, Salvig JD, Smith SK and Charnock-Jones DS (1998) Hepatocyte growth factor levels during normal and intra-uterine growth-restricted pregnancies. Placenta 19: 671–673.
Connolly AJ, Ishihara H, Kahn ML, Farese RV Jr and Coughlin SR (1996) Role of the thrombin receptor in development and evidence for a second receptor. Nature 38: 516–519.
Cook CL and Pridham DD (1995) Recurrent pregnancy loss. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 7: 357–366.
Copp AJ (1995) Death before birth: clues from gene knockouts and mutations. Trends Genet 11: 87–93.
Coulam CB (1991) Epidemiology of recurrent spontaneous abortion. Am J Reprod Immunol 26: 23–27.
Cross JC, Werb Z and Fisher SJ (1994) Implantation and the placenta: key pieces of the development puzzle. Science 266: 1508–1518.
Cui J, O'Shea KS, Purkayastha A, Saunders TL and Ginsburg D (1996) Fatal haemorrhage and incomplete block to embryogenesis in mice lacking coagulation factor V. Nature 384: 66–68.
Cunningham DS and Tichenor JR (1995) Decay-accelerating factor protects human trophoblast from complement-mediated attack. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 74: 156–161.
Damsky CH, Fitzgerald ML and Fisher SJ (1992) Distribution patterns of extracellular matrix components and adhesion receptors are intricately modulated during first trimester cytotrophoblast differentiation along the invasive pathway, in vivo. J Clin Invest 89: 210–222.
Deligdish L (1992) Patholgy of the placenta. In: Pasqualini JR and Scholler R (eds) Hormones and Fetal Patho-physiology. 5th edn (pp. 203–249) Marcel Dekker, New York.
Dickson MC, Martin JS, Cousins FM, Kulkarni AB, Karlsson S and Akhurst RJ (1995) Defective haematopoiesis and vasculogenesis in transforming growth factor-beta 1 knock out mice. Development 121: 1845–1854.
Douglas GC, Hu J, Thirkill TL, Hovanes K, Sharma S and King BF (1994) Effect of cytokines and anti-adhesion molecule antibodies on the adhesion of lymphocytic cells to human syncytiotrophoblast. J Reprod Immunol 27: 49–62.
Edmonds DK, Lindsay KS, Miller JF, Williamson E and Wood PJ (1982) Early embryonic mortality in women. Fertil Steril 38: 447–453.
Ellish NJ, Saboda K, O'Connor J, Nasca PC, Stanek EJ and Boyle C (1996) A prospective study of early pregnancy loss. Hum Reprod 11: 406–412.
Enders AC (1965) A comparative study of the fine structure in several hemochorial placentas. Am J Anat 116: 29–67.
Enders AC and Blankenship TN (1999) Comparative placental structure. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 38: 3–15.
Farese RV Jr, Ruland SL, Flynn LM, Stokowski RP and Young SG (1995) Knockout of the mouse apolipoprotein B gene results in embryonic lethality in homozygotes and protection against dietinduced hypercholesterolemia in heterozygotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 1774–1778.
Favier B and Dollé P (1997) Developmental functions of mammalian Hox genes. Mol Hum Reprod 3: 115–131.
Faxen M, Nasiell J, Blanck A, Nisell H and Lunell NO (1997) Altered mRNA expression pattern of placnental epidermal growth factor receptor in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia and/or intrauterine growth retardation. Am J Perinatol 15: 9–13.
Fazel A, Vincenot A, Malassine A, Soncin F, Gaussem P, Alsat E and Evain-Brion D (1998) Increase in expression and activity of thrombomodulin in term human syncytiotrophoblast microvilli. Placenta 19: 261–268.
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O'Shea KS, Powell-Braxton L, Hillan KJ and Moore MW(1996) Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature 380: 439–442.
Firulli AB, McFadden DG, Lin Q, Srivastava D and Olson EN (1998) Heart and extra-embryonic mesodermal defects in mouse embryos lacking the bHLH transcription factor Hand1. Nat Genet 18: 266–270.
Fondacci C, Alsat E, Gabriel R, Blot P, Nessmann C and Evain-Brion D (1994) Alterations of human placental epidermal growth factor receptor in intrauterine growth retardation. J Clin Invest 93: 1149–1155.
Fong GH, Rossant J, Gertsenstein M and Breitman ML (1995) Role of the Flt-1 receptor tyrosine kinase in regulating the assembly of vascular endothelium. Nature 376: 66–70.
Fujiwara Y, Browne CP, Cunniff K, Goff SC and Orkin SH (1998) Arrested development of embryonic red cell precursors in mouse embryos lacking transcription factor GATA-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 12355–12358.
Gabriel HD, Jung D, Butzler C, Temme A, Traub O, Winterhager E and Willecke K (1998) Transplacental uptake of glucose is decreased in embryonic lethal connexin26-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 140: 1453–1461.
Gelb BD (2000) Recent advances in the understanding of genetic causes of congenital heart defects. Front Biosci 5: D321–D333.
Gendron RL, Paradis H, Hsieh-Li HM, Lee DW, Potter SS and Markoff E (1997) Abnormal uterine stromal and glandular function associated with maternal reproductive defects in Hoxa-11 null mice. Biol Reprod 56: 1097–1105.
George EL, Georges-Labouesse EN, Patel-King RS, Rayburn H and Hynes RO (1993) Defects in mesoderm, neural tube and vascular development in mouse embryos lacking fibronectin. Development 119: 1079–1091.
Giroux S, Tremblay M, Bernard D, Cardin-Girard JF, Aubry S, Larouche L, Rousseau S, Huot J, Landry J, Jeannotte L and Charron J (1999) Embryonic death of Mek1-deficient mice reveals a role for this kinase in angiogenesis in the labyrinthine region of the placenta. Curr Biol 9: 369–372.
Gnarra JR, Ward JM, Porter FD, Wagner JR, Devor DE, Grinberg A, Emmert-Buck MR, Westphal H, Klausner RD and Linehan WM (1997) Defective placental vasculogenesis causes embryonic lethality in VHL-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 9102–9107.
Goh KL, Yang JT and Hynes RO (1997) Mesodermal defects and cranial neural crest apoptosis in alpha5 integrin-null embryos. Development 124: 4309–4319.
Goumans MJ, Zwijsen A, van Rooijen MA, Huylebroeck D, Roelen BA and Mummery CL (1999) Transforming growth factor-beta signalling in extraembryonic mesoderm is required for yolk sac vasculogenesis in mice. Development 126: 3473–3483.
Guillemot F, Nagy A, Auerbach A, Rossant J and Joyner AL (1994) Essential role of Mash-2 in extraembryonic development. Nature 371: 333–336.
Gurtner GC, Davis V, Li H, McCoy MJ, Sharpe A and Cybulsky MI (1995) Targeted disruption of the murine VCAM1 gene: essential role of VCAM-1 in chorioallantoic fusion and placentation. Genes Dev 9: 1–14.
Han VK (1993) Pathophysiology, cellular and molecular mechanisms of foetal growth retardation. Equine Vet J Suppl 14: 12–16.
Harbers K, Muller U, Grams A, Li E, Jaenisch R and Franz T (1996) Provirus integration into a gene encoding a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme results in a placental defect and embryonic lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 12412–12417.
Healy AM, Rayburn HB, Rosenberg RD and Weiler H (1995) Absence of the blood-clotting regulator thrombomodulin causes embryonic lethality in mice before development of a functional cardiovascular system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 850–854.
Hess JL, Yu BD, Li B, Hanson R and Korsmeyer SJ (1997) Defects in yolk sac hematopoiesis in Mll-null embryos. Blood 90: 1799–1806.
Hill JA and Choi BC (2000) Maternal immunological aspects of pregancy success and failure. J Reprod Fertil Suppl 55: 91–97.
Hodivala-Dilke KM, McHugh KP, Tsakiris DA, Rayburn H, Crowley D, Ullman-Cullere M, Ross FP, Coller BS, Teitelbaum S and Hynes RO (1999) Beta3-integrin-deficient mice are a model for Glanzmann thrombasthenia showing placental defects and reduced survival. J Clin Invest 103: 229–238.
Hoffman JI (1995) Incidence of congenital heart disease: I. Postnatal incidence. Pediatr Cardiol 16: 103–113.
Hunter PJ, Swanson BJ, Haendel MA, Lyons GE and Cross JC (1999) Mrj encodes a DnaJ-related co-chaperone that is essential for murine placental development. Development 126: 1247–1258.
Igakura T, Kadomatsu K, Kaname T, Muramatsu H, Fan QW, Miyauchi T, Toyama Y, Kuno N, Yuasa S, Takahashi M, Senda T, Taguchi O, Yamamura K, Arimura K, Muramatsu T (1998) A null mutation in basigin, an immunoglobulin superfamily member, indicates its important roles in peri-implantation development and spermatogenesis. Dev Biol 194: 152–165.
Ishikawa T, Tamai Y, Zorn AM, Yoshida H, Seldin MF, Nishikawa S and Taketo MM (2001) MouseWnt receptor gene Fzd5 is essential for yolk sac and placental angiogenesis. Development 128: 25–33.
Itoh M, Yoshida Y, Nishida K, Narimatsu M, Hibi M and Hirano T (2000) Role of Gab1 in heart, placenta, and skin development and growth factor-and cytokine-induced extracellular signalregulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Mol Cell Biol 20: 3695–3704.
James RM, Klerkx AH, Keighren M, Flockhart JH and West JD (1995) Restricted distribution of tetraploid cells in mouse tetraploid-diploid chimaeras. Dev Biol 167: 213–226.
Janatpour MJ, Utset MF, Cross JC, Rossant J, Dong J, Israel MA and Fisher SJ (1999) A repertoire of differentially expressed transcription factors that offers insight into mechanisms of human cytotrophoblast differentiation. Dev Genet 25: 146–157.
Jollie WP (1985) Ultrastructure studies of protein transfer across rodent yolk sac. Placenta 7: 263–281.
Kaufmann P (1981) Functional anatomy of the non-primate placenta. Acta Anat Suppl I: 13–28.
Kaufmann P and Burton G (1994) Anatomy and genesis of the placenta. In: Knobil E and Neill D (eds) The Physiology of Reproduction. 2nd edn pp. (450–504) Raven Press, New York.
Kauma S, Hayes N and Weatherford S (1997) The differential expression of hepatocyte growth factor and met in human placenta. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82: 949–954.
Khong TY, Liddell HS and Robertson WB (1987) Defective haemochorial placentation as a cause of miscarriage: a preliminary study. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 94: 649–655.
Koutsourakis M, Langeveld A, Patient R, Beddington R and Grosveld F (1999) The transcription factor GATA6 is essential for early extraembryonic development. Development 126: 723–732.
Kozak KR, Abbott B and Hankinson O (1997) ARNT-deficient mice and placental differentiation. Dev Biol 191: 297–305.
Kraut N, Snider L, Chen CM, Tapscott SJ and Groudine M (1998) Requirement of the mouse I-mfa gene for placental development and skeletal patterning. EMBO J 17: 6276–6288.
Kutteh WH (1999) Recurrent pregnancy loss: an update. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 11: 435–439.
Laurini R, Laurin J and Marsal K (1994) Placental histology and fetal blood flow in intrauterine growth retardation. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 73: 529–534.
Li E, Bestor TH and Jaenisch R (1992) Targeted mutation of the DNA methyltransferase gene results in embryonic lethality. Cell 69: 915–926.
Li Y and Behringer RR (1998) Esx1 is an X-chromosome-imprinted regulator of placental development and fetal growth. Nat Genet 20: 309–311.
Li DY, Sorensen LK, Brooke BS, Urness LD, Davis EC, Taylor DG, Boak BB and Wendel DP (1999) Defective angiogenesis in mice lacking endoglin. Science 284: 1534–1537.
Lim KH, Zhou Y, Janatpour M, McMaster M, Bass K, Chun SH and Fisher SJ (1997) Human cytotrophoblast differentiation/invasion is abnormal in pre-eclampsia. Am J Pathol 151: 1809–1818.
Lim H, Ma L, Ma WG, Maas RL and Dey SK (1999) Hoxa-10 regulates uterine stromal cell responsiveness to progesterone during implantation and decidualization in the mouse. Mol Endocrinol 13: 1005–1017.
Lopez MF, Dikkes P, Zurakowski D and Villa-Komaroff L (1996) Insulin-like growth factor II affects the appearance and glycogen content of glycogen cells in the murine placenta. Endocrinology 137: 2100–2108.
Lu TY and Markert CL (1980) Manufacture of diploid/tetraploid chimeric mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 6012–6016.
Luo J, Sladek R, Bader JA, Matthyssen A, Rossant J and Giguere V (1997) Placental abnormalities in mouse embryos lacking the orphan nuclear receptor ERR-beta. Nature 388: 778–782.
Ma GT, Roth ME, Groskopf JC, Tsai FY, Orkin SH, Grosveld F, Engel JD and Linzer DI (1997) GATA-2 and GATA-3 regulate trophoblast-specific gene expression in vivo. Development 124: 907–914.
Ma L, Yao M and Maas RL (1999) Genetic control of uterine receptivity during implantation. Semin Reprod Endocrinol. 17: 205–216.
Maltepe E, Schmidt JV, Baunoch D, Bradfield CA and Simon MC (1997) Abnormal angiogenesis and responses to glucose and oxygen deprivation in mice lacking the protein ARNT. Nature 386: 403–407.
Mazur MT, Lurain JR and Brewer JI (1982) Fatal gestational choriocarcinoma. Clinicopathologic study of patients treated at a trophoblastic disease center. Cancer 50: 1833–1846.
Metzger D and Feil R (1999) Enginering the mouse genome by sitespecific recombination. Curr Opin Biotechnol 10: 470–476.
Miner JH, Cunningham J and Sanes JR (1998) Roles for laminin in embryogenesis: exencephaly, syndactyly, and placentopathy in mice lacking the laminin alpha5 chain. J Cell Biol 143: 1713–1723.
Mishell DR (1993) Recurrent abortion. J Reprod Med 38: 250–259.
Monkley SJ, Delaney SJ, Pennisi DJ, Christiansen JH and Wainwright BJ (1996) Targeted disruption of the Wnt2 gene results in placentation defects. Development 122: 3343–3353.
Morasso MI, Grinberg A, Robinson G, Sargent TD and Mahon KA (1999) Placental failure in mice lacking the homeobox gene Dlx3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 162–167.
Morriss Kay GM and Ward SJ (1999) Retinoids and mammalian development. Int Rev Cytol 188: 73–131.
Mudgett JS, Ding J, Guh-Siesel L, Chartrain NA, Yang L, Gopal S and Shen MM (2000) Essential role for p38alpha mitogenactivated protein kinase in placental angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 10454–10459.
Muntener M and Hsu YC (1977) Development of trophoblasts and placenta of the mouse. Acta Anat 98: 241–252.
Nagy A (2000) Cre recombinase: the universal reagent for genome tailoring. Genesis 26: 99–109.
O'Driscoll M, Macpherson P, Xu YZ and Karran P (1999) The cytotoxicity of DNA carboxymethylation and methylation by the model carboxymethylating agent azaserine in human cells. Carcinogenesis 20: 1855–1862.
Oike Y, Takakura N, Hata A, Kaname T, Akizuki M, Yamaguchi Y, Yasue H, Araki K, Yamamura K and Suda T (1999) Mice homozygous for a truncated form of CREB-binding protein exhibit defects in hematopoiesis and vasculo-angiogenesis. Blood 93: 2771–2779.
Oka C, Nakano T, Wakeham A, de la Pompa JL, Mori C, Sakai T, Okazaki S, Kawaichi M, Shiota K, Mak TW and Honjo T (1995) Disruption of the mouse RBP-J kappa gene results in early embryonic death. Development 121: 3291–3301.
Oshima M, Oshima H and Taketo MM (1996) TGF-beta receptor type II deficiency results in defects of yolk sac hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis. Dev Biol 179: 297–302.
Pardi G, Marconi AM and Cetin I (1997) Pathophysiology of intrauterine growth retardation: role of the placenta. Acta Paediatr Suppl 423: 170–172.
Patel Y, Kim H and Rappolee DA (2000) A role for hepatocyte growth factor during early postimplantation growth of the placental lineage in mice. Biol Reprod 62: 904–912.
Peel S and Bulmer D (1977) Proliferation and differentiation of trophoblast in the establishment of the rat chorio-allantoic placenta. J Anat 124: 675–687.
Qian X, Esteban L, Vass WC, Upadhyaya C, Papageorge AG, Yienger K, Ward JM, Lowy DR and Santos E (2000) The Sos1 and Sos2 Ras-specific exchange factors: differences in placental expression and signaling properties. EMBO J 19: 642–654.
Qu CK, Yu WM, Azzarelli B, Cooper S, Broxmeyer HE and Feng GS (1998) Biased suppression of hematopoiesis and multiple developmental defects in chimeric mice containing Shp-2 mutant cells. Mol Cell Biol 18: 6075–6082.
Raabe M, Flynn LM, Zlot CH, Wong JS, Veniant MM, Hamilton RL and Young SG (1998) Knockout of the abetalipoproteinemia gene in mice: reduced lipoprotein secretion in heterozygotes and embryonic lethality in homozygotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 8686–8691.
Radice GL, Rayburn H, Matsunami H, Knudsen KA, Takeichi M and Hynes RO (1997) Developmental defects in mouse embryos lacking N-cadherin. Dev Biol 181: 64–78.
Redline RW (1995) Placental pathology: a neglected link between basic disease mechanisms and untoward pregnancy outcome. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 7: 10–15.
Riley P, Anson-Cartwright L and Cross JC (1998) The Hand1 bHLH transcription factor is essential for placentation and cardiac morphogenesis. Nat Genet 18: 271–275.
Rinkenberger JL, Cross JC and Werb Z (1997) Molecular genetics of implantation in the mouse. Dev Genet 21: 6–20.
Rinkenberger JL, Horning S, Klocke B, Roth K and Korsmeyer SJ (2000) Mcl-1 deficiency results in peri-implantation embryonic lethality. Genes Dev 14: 23–27.
Rinkenberger J and Werb Z (2000) The labyrinthine placenta. Nat Genet 25: 248–250.
Robb L, Lyons I, Li R, Hartley L, Kontgen F, Harvey RP, Metcalf D and Begley CG (1995) Absence of yolk sac hematopoiesis from mice with a targeted disruption of the scl gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 7075–7079.
Roberts JM (2000) Preeclampsia: what we know and what we do not know. Semin Perinatol 24: 24–28.
Rossant J, Guillemot F, Tanaka M, Latham K, Gertenstein M and Nagy A (1998) Mash2 is expressed in oogenesis and preimplantation development but is not required for blastocyst formation. Mech Dev 73: 183–191.
Sapin V, Dolle P, Hindelang C, Kastner P and Chambon P (1997) Defects of the chorioallantoic placenta in mouse RXRalpha null fetuses. Dev Biol 191: 29–41.
Schmidt C, Bladt F, Goedecke S, Brinkmann V, Zschiesche W, Sharpe M, Gherardi E and Birchmeier C (1995) Scatter 397 factor/hepatocyte growth factor is essential for liver development. Nature 373: 699–702.
Schorpp-Kistner M, Wang ZQ, Angel P and Wagner EF (1999) JunB is essential for mammalian placentation. EMBO J 18: 934–948.
Schreiber J, Riethmacher-Sonnenberg E, Riethmacher D, Tuerk EE, Enderich J, Bosl MR and Wegner M (2000) Placental failure in mice lacking the mammalian homolog of glial cells missing, GCMa. Mol Cell Biol 20: 2466–2474.
Scott IC, Anson-Cartwright L, Riley P, Reda D and Cross JC (2000) The HAND1 basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor regulates trophoblast differentiation via multiple mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol 20: 530–541.
Shalaby F, Rossant J, Yamaguchi TP, Gertsenstein M, Wu XF, Breitman ML and Schuh AC (1995) Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice. Nature 376: 62–66.
Smith SK, Charnock-Jones DS and Sharkey AM (1998) The role of leukemia inhibitory factor and interleukin-6 in human reproduction. Hum Reprod 3: 237–246.
Somerset DA, Li XF, Afford S, Strain AJ, Ahmed A, Sangha RK, Whittle MJ and Kilby MD (1998) Ontogeny of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its receptor (c-met) in human placenta: reduced HGF expression in intrauterine growth restriction. J Pathol 153: 1139–1147.
Speroff L, Glass RH and Kase NG (1994) Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility. In: Williams and Wilkins (eds) 3rd edn (pp. 231–250) Baltimore.
Spyropoulos DD and Capecchi MR (1994) Targeted disruption of the even-skipped gene, evx1, causes early postimplantation lethality of the mouse conceptus. Genes Dev 8: 1949–1961.
Steingrimsson E, Tessarollo L, Reid SW, Jenkins NA and Copeland NG (1998) The bHLH-Zip transcription factor Tfeb is essential for placental vascularization. Development 125: 4607–4616.
Stephens LE, Sutherland AE, Klimanskaya IV, Andrieux A, Meneses J, Pedersen RA and Damsky CH (1995) Deletion of beta 1 integrins in mice results in inner cell mass failure and peri-implantation lethality. Genes Dev 9: 1883–1895.
Stewart CL, Kaspar P, Brunet LJ, Bhatt H, Gadi I, Kontgen F and Abbondanzo SJ (1992) Blastocyst implantation depends on maternal expression of leukaemia inhibitory factor. Nature 359: 76–79.
Stewart F (1996) Roles of mesenchymal-epithelial interactions and hepatocyte growth factor-scatter factor (HGF-SF) in placental development. Rev Reprod 1: 144–148.
Sun WY, Witte DP, Degen JL, Colbert MC, Burkart MC, Holmback K, Xiao Q, Bugge TH and Degen SJ (1998) Prothrombin deficiency results in embryonic and neonatal lethality in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 7597–7602.
Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL, Stambolic V, Elia AJ, Sasaki T, del Barco Barrantes I, Ho A, Wakeham A, Itie A, Khoo W, Fukumoto M and Mak TW (1998) High cancer susceptibility and embryonic lethality associated with mutation of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in mice. Curr Biol 8: 1169–1178.
Takayanagi T, Aoki Y and Tanaka K (2000) Expression of constitutively active c-met receptor in human choriocarcinoma. Gynecol Obstet Invest 50: 198–202.
Tallquist MD and Soriano P (2000) Epiblast-restricted Cre expression in MORE mice: a tool to distinguish embryonic vs. extra-embryonic gene function. Genesis 26: 113–115.
Tamai Y, Ishikawa To, Bosl MR, Mori M, Nozaki M, Baribault H, Oshima RG and Taketo MM (2000) Cytokeratins 8 and 19 in the mouse placental development. J Cell Biol 151: 563–572.
Taylor HS (2000) The role of HOX genes in human implantation. Hum Reprod Update 6: 75–79.
Threadgill DW, Dlugosz AA, Hansen LA, Tennenbaum T, Lichti U, Yee D, LaMantia C, Mourton T, Herrup K, Harris RC et al. (1995) Targeted disruption of mouse EGF receptor: effect of genetic background on mutant phenotype. Science 269: 230–234.
Toomey JR, Kratzer KE, Lasky NM, Stanton JJ and Broze GJ Jr (1996) Targeted disruption of the murine tissue factor gene results in embryonic lethality. Blood 88: 1583–1587.
Torchinsky A, Savion S, Gorivodsky M, Shepshelovich J, Zaslavsky Z, Fein A and Toder V (1995) Cyclophosphamide-induced teratogenesis in ICR mice: the role of apoptosis. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen 15: 179–190.
Tsai FY, Keller G, Kuo FC, Weiss M, Chen J, Rosenblatt M, Alt FW and Orkin SH (1994) An early haematopoietic defect in mice lacking the transcription factor GATA-2. Nature 371: 221–226.
Uehara Y, Minowa O, Mori C, Shiota K, Kuno J, Noda T and Kitamura N (1995) Placental defect and embryonic lethality in mice lacking hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. Nature 373: 702–705.
Voss AK, Thomas T and Gruss P (2000) Mice lacking HSP90beta fail to develop a placental labyrinth. Development 127: 1–11.
Wakamiya M, Blackburn MR, Jurecic R, McArthur MJ, Geske RS, Cartwright J Jr, Mitani K, Vaishnav S, Belmont JW, Kellems RE et al. (1995) Disruption of the adenosine deaminase gene causes hepatocellular impairment and perinatal lethality in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 3673–3677.
Wang LC, Kuo F, Fujiwara Y, Gilliland DG, Golub TR and Orkin SH (1997) Yolk sac angiogenic defect and intra-embryonic apoptosis in mice lacking the Ets-related factor TEL. EMBO J 1614: 4374–4383.
Wang ZQ, Kiefer F, Urbanek P and Wagner EF (1997) Generation of completely embryonic stem cell-derived mutant mice using tetraploid blastocyst injection. Mech Dev 62: 137–145.
Wang W, Van de Water T and Lufkin T (1998) Innear ear and maternal reproductive defects in mice lacking the Hmx3 homeobox gene. Development 125: 621–634.
Ware CB, Horowitz MC, Renshaw BR, Hunt JS, Liggitt D, Koblar SA, Gliniak BC, McKenna HJ, Papayannopoulou T, Thoma B et al. (1995) Targeted disruption of the low-affinity leukemia inhibitory factor receptor gene causes placental, skeletal, neural and metabolic defects and results in perinatal death. Development 121: 1283–1299.
Warren AJ, Colledge WH, Carlton MB, Evans MJ, Smith AJ and Rabbitts TH (1994) The oncogenic cysteine-rich LIM domain protein rbtn2 is essential for erythroid development. Cell 78: 45–57.
Wendling O, Chambon P and Mark M (1999) Retinoid X receptors are essential for early mouse development and placentogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 547–551.
Wilcox AJ, Baird DD and Weinberg CR (1999) Time of implantation of the conceptus and loss of pregnancy. N Engl J Med 340: 1796–1799.
Wilmut I, Sales DI and Ashworth CJ (1986) Maternal and embryonic factors associated with prenatal loss in mammals. J Reprod Fertil 76: 851–864.
Xiao X, Zuo X, Davis AA, McMillan DR, Curry BB, Richardson JA and Benjamin IJ (1999) HSF1 is required for extraembryonic development, postnatal growth and protection during inflammatory responses in mice. EMBO J 21: 5943–5952.
Xu X, Weinstein M, Li C, Naski M, Cohen RI, Ornitz DM, Leder P and Deng C (1998) Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2)-mediated reciprocal regulation loop between FGF8 and FGF10 is essential for limb induction. Development 125: 753–765.
Xu C, Mao D, Holers VM, Palanca B, Cheng AM and Molina H (2000) A critical role for murine complement regulator crry in fetomaternal tolerance. Science 287: 498–501.
Xue J, Wu Q, Westfield LA, Tuley EA, Lu D, Zhang Q, Shim K, Zheng X and Sadler JE (1998) Incomplete embryonic lethality and fatal neonatal hemorrhage caused by prothrombin deficiency in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 7603–7607.
Yamamoto H, Flannery M, Kupriyanov S, Pearce J, McKercher S, Henkel G, Maki R, werb Z and Oshima R (1998) Defective trophoblast function in mice with a targeted mutation of Ets2. Genes Dev 12: 1315–1326.
Yang JT, Rayburn H and Hynes RO (1993) Embryonic mesodermal defects in alpha 5 integrin-deficient mice. Development 119: 1093–1105.
Yang JT, Rayburn H and Hynes RO (1995) Cell adhesion events mediated by alpha 4 integrins are essential in placental and cardiac development. Development 121: 549–560.
Yang X, Castilla LH, Xu X, Li C, Gotay J, Weinstein M, Liu PP and Deng CX (1999) Angiogenesis defects and mesenchymal apoptosis in mice lacking SMAD5. Development 126: 1571–1580.
Zhou Y, Damsky CH and Fisher SJ (1997) Preeclampsia is associated with failure of human cytotrophoblasts to mimic a vascular adhesion phenotype? J Clin Invest 99: 2152–2164.
Zhu Y, Qi C, Jia Y, Nye JS, Rao MS and Reddy JK (2000) Deletion of PBP/PPARBP, the gene for nuclear receptor coactivator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-binding protein, results in embryonic lethality. J Biol Chem 275: 14779–14782.
Zinaman MJ, Clegg ED, Brown CC, O'Connor J and Selevan SG (1996) Estimates of human fertility and pregnancy loss. Fertil Steril 65: 503–509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sapin, V., Blanchon, L., Serre, AF. et al. Use of transgenic mice model for understanding the placentation: towards clinical applications in human obstetrical pathologies?. Transgenic Res 10, 377–398 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012085713898
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012085713898