Abstract
Purpose. The main purpose of this study is to analyze the quantitative structure-activity relationship of two series of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors (leflunomide and quinoline carboxylic acid analogues), and to determine the structural requirements for optimum activity of these analogues.
Methods. A new CQSAR program was used in deriving regression equations and calculating the octanol/water partition coefficient and the molar refractivity values. The molecular modeling was performed using the HyperChem® program.
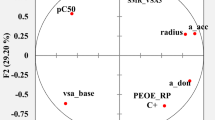
Results. Statistically significant correlations were obtained using a combination of 3−4 parameters. The structural requirements for optimum activity and critical regions for the inhibitory activity of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase were identified.
Conclusions. The quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis demonstrated that two series of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors may bind to different binding sites on the enzyme. These results provide a better understanding of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitor-enzyme interactions, and may be useful for further modification and improvement of inhibitors of this important enzyme.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. E. Jones. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 49:253–279 (1987).
L. Stryer. Biochemistry. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York, 1988, pp. 601–626.
G. Weber. Cancer Res. 43:3466–3492 (1983).
W. L. Elliott, D. P. Sawick, S. A. DeFrees, P. F. Heinstein, J. M. Cassady, and D. J. Morre. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 800:194–201 (1984).
M. Mahmoudian, A. H. Pakiari, and S. Khademi. Biochem. Pharmaco. 43:283–287 (1992).
S. Chen, L. M. Papp, R. J. Ardecky, G. V. Rao, D. P. Hesson, M. Forbes, and D. L. Dexter. Biochem. Pharmaco. 40:709–714 (1990).
E. A. Kuo, P. T. Hambleton, D. P. Kay, P. L. Evans, S. S. Matharu, E. Little, N. McDowall, C. B. Jones, C. J. R. Hedgecock, C. M. Yea, A. W. E. Chan, P. W. Hairsine, I. R. Ager, W. R. Tully, R. A. Williamson, and R. Westwood. J. Med. Chem. 39:4608–4621 (1996).
E. J. Lien. SAR side effects and drug design. Marcel Dekker, Inc. New York, 1987, pp. 135–154.
BioByte Corp. CQSAR data base. 201 West, 4th St., Suite 204, Claremont, CA 919711, 1997.
Hypercube, Inc. HyperChem ® for Windows, Vision 4.0. Publication MC40-00-02-01, 419 Phillip St. Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, 1994.
E. J. Lien. SAR side effects and drug design. Marcel Dekker, Inc. New York, 1987, pp. 50–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, S., Wu, S.K. & Lien, E.J. Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors: Quantitative Structure-activity Relationship Analysis. Pharm Res 15, 286–295 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011978904905
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011978904905