Abstract
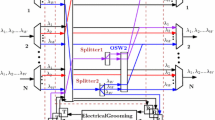
In this paper, we propose novel traffic grooming algorithms to reduce the cost of the entire system in WDM multi-ring networks. In order to achieve this goal, it is important to construct a virtual topology and groom the traffic in these networks. We consider four kinds of virtual topologies of WDM multi-ring networks according to the way in which traffic is transmitted among rings. Accordingly, we design four kinds of traffic grooming (TG) algorithms depending on the considered virtual topologies: mixed (MTG), partially mixed (PMTG), separate (STG), and independent (ITG) traffic grooming algorithms. Each algorithm consists of a separation, a connection-ring construction, and a grooming procedure. In the separation procedure, all traffic connections are classified into intra and inter-connections. The connection-ring construction procedure makes full connection-rings from traffic connections. The grooming procedure groups connection-rings onto a wavelength in order to reduce the number of SONET add/drop multiplexers (SADMs) and wavelengths and to improve the utilization of network resources. To analyze the performance of each algorithm, a circular multi-ring architecture with uniform traffic is considered. The simulation results show that ITG and PMTG are more efficient in terms of wavelengths. STG and PMTG require a smaller number of SADMs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chungpeng Fan, Optical networking—A paradigm shift of technology, WDM Forum, (June 1998).
O. Gerster, P. Lin, G. Sasaki, Wavelength assignment in a WDM ring to minimize cost of embedded SONET rings, Proceedings of INFOCOM'98, vol. 1, (San Francisco, CA, April 1998), pp. 94-101.
A. L. Chiu, E. H. Modian, Reducing electronic multiplexing costs in unidirectional SONET/WDM ring networks via efficient traffic grooming, Proceedings of GLOBECOM'98, vol. 1, (Sydney, Australia, Nov. 1998), pp. 322-327.
J. M. Simmons, E. L. Goldstein, A. M. Saleh, On the value of wavelength-add/drop in WDM rings with uniform traffic, in: Proceedings of OFC'98, (San Jose, CA, March 1998), pp. 361-362.
X. Zhang, C. Qiao, An effective and comprehensive solution to traffic grooming and wavelength assignment in SONET/WDM rings, SPIE Proc. of Conf. on All-Optical Networking, vol. 3531, (Nov. 1998), pp. 221-232.
L. Wuttisittikulij, M. J. O'Mahony, Design of a WDM network using a multiple ring approach, Proceedings of GLOBECOM '97, vol. 1, (Phoenix, AZ, Nov. 1997), pp. 551-555.
Jian Wang, Biswanath Mukherjee, Inter connected WDM ring networks: Strategies for interconnection and traffic grooming, Proceedings of Optical Network Workshop 2000, (UT Dallas, Jan. 2000).
T. Iamvasant, C. Baworntummarat, L. Wuttisittikulkij, A comparative study of mesh and multi-ring designs for survivable WDM networks, IFIP Proceedings of Networking 2000, (Paris, France, May 2000), pp. 189-200.
Seung-jin Yoon, Sun-sik Roh, Young-chon Kim, Traffic grooming algorithm for minimizing the number SONET ADM in WDM bi-directional ring networks, Proceedings of OECC 2000, (Chiba, Japan, July 2000), pp. 226-227.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roh, SS., So, WH. & Kim, YC. Design and Performance Evaluation of Traffic Grooming Algorithms in WDM Multi-Ring Networks. Photonic Network Communications 3, 335–348 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011955911519
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011955911519