Abstract
Purpose. Antigenic proteins encapsulated in biodegradable polyester microspheres (MS) can slowly denature or aggregate, which results in decreased antigenicity. In this study, we have evaluated the ability of co-encapsulated additives to protect against the loss of tetanus toxoid (TT) antigenicity.
Methods. Antibody responses were analyzed after immunization of mice with TT microencapsulated in the presence of additives (TT-MS-additive).
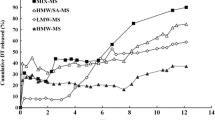
Results. Immunization with TT-MS-additives gave rise to higher responses than those obtained in the absence of additive. BSA, trehalose, -γ-hydroxypropylcyclodextrin and calcium salts preserved the immunogenicity of the incorporated antigen with the highest efficacy. Sustained responses were obtained with mixtures of fast and slowly releasing TT-MS containing BSA plus trehalose or calcium salts.
Conclusions. The selected additives may stabilize the antigen in MS during storage and rehydration in body fluids. Regulated antigen release from MS-based vaccines permits a reduction of the antigen dose and optimization of single-dose vaccine formulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
T. Aguado and P.-H. Lambert. Controlled release vaccines—biodegradable polylactide/polyglycolide (PL/PG) microspheres as antigen vehicles. Immunobiology 184:113–125 (1992).
R. Langer. New methods of drug delivery. Science 249:1527–1533 (1990).
G. E. Visscher, R. L. Robinson, H. V. Maulding, J. W. Fong, J. E. Pearson, and G. J. Argentieri. Biodegradation of and tissue reaction to 50:50 poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microcapsules. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 19:349–365 (1985).
C. Thomasin, G. Corradin, Y. Men, H. P. Merkle, and B. Gander. Tetanus toxoid and synthetic malaria antigen containing poly(lactide)/poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres: importance of polymer degradation and antigen release for immune response. J. Control. Release 41:131–145 (1996).
D. H. Jones, B. W. McBride, C. Thornton, D. T. O'Hagan, A. Robinson, and G. H. Farrar. Orally administered microencapsulated Bortella pertussis Fimbriae protect mice from B. pertussis respiratory infection. Infec. Immunity 64:489–494 (1996).
A. Moore, P. McGuirk, S. Adams, W. C. Jones, D. T. O'Hagan, and K. H. Mills. Immunization with a soluble recombinant HIV protein entrapped in biodegradable microparticles induces HIV-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes and CD4+ Th1 cells. Vaccine 13:1741–1749 (1995).
Y. Men, C. Thomasin, H. P. Merkle, B. Gander, and G. Corradin. A single administration of tetanus toxoid in biodegradable microspheres elicits T cell and antibody responses similar or superior to those obtained with aluminum hydroxide. Vaccine 13:683–689 (1995).
M. J. Alonso, R. K. Gupta, C. Min, G. R. Siber, and R. Langer. Biodegradable microspheres as controlled release tetanus toxoid delivery system. Vaccine 12:299–306 (1994).
K. J. Maloy, A. M. Donachie, D. T. O'Hagan, and A. M. Mowat. Induction of mucosal and systemic immune responses by immunization with ovalbumin entrapped in poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microparticles. Immunology 81:661–667 (1994).
J. H. Eldridge, J. K. Staas, J. A. Meulbroeck, J. R. MacGhee, T. R. Tice, and R. M. Gilley. Biodegradable and biocompatible poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres as an adjuvant for Staphylococcal enterotoxin B toxoid which enhances the level of toxin-neutralizing antibodies. Infec. Immunity 59:2978–2986 (1991).
M. Singh, A. Singh, and G. P. Talwar. Controlled delivery of diphtheria toxoid using biodegradable poly(D,L-lactide) microcapsules. Pharm. Res. 8:958–961 (1991).
D. T. O'Hagan, D. Rahman, J. P. McGee, Y. Jeffery, M. C. Davies, P. Williams, and S. S. Davis. Biodegradable microparticles as controlled release antigen delivery systems. Immunology 73:239–242 (1991).
Y. Men, B. Gander, H. P. Merkle, and G. Corradin. Induction of sustained and elevated immune responses to weakly immunogenic synthetic malarial peptides by encapsulation in biodegradable polymer microspheres. Vaccine 14:1442–1450 (1996).
D. F. Nixon, C. Hioe, P. Chen, Z. Bian, P. Kuebler, M.-L. Li, H. Qiu, X.-M. Li, M. Singh, J. Richardson, P. McGee, T. Zamb, W. Koff, C. Y. Wang, and D. T. O'Hagan. Synthetic peptides entrapped in microparticles can elicit cytotoxic cell activity. Vaccine 14:1523–1530 (1996).
C. D. Partidos, P. Vohra, D. H. Jones, G. H. Farrar, and M. W. Steward. Mucosal immunization with a measles virus CTL epitope encapsulated in biodegradable PLG microparticles. J. Immunol. Method. 195:135–138 (1996).
C. D. Partidos, P. Vohra, C. Anagnostopoulou, D. H. Jones, G. H. Farrar, and M. W. Steward. Biodegradable microparticles as a delivery system for measles virus cytotoxic T cell epitopes. Mol. Immunol. 33:485–491 (1996).
Y. Men, H. Tamber, R. Audran, B. Gander, and G. Corradin. Induction of a cytotoxic T lymphocyte response by immunization with a malaria specific CTL peptide based on biodegradable polymer microspheres. Vaccine 15:1405–1412 (1997).
T. E. Greenway, J. H. Eldridge, G. Ludwig, J. K. Staas, J. F. Smith, R. M. Gilley, and S. M. Michalek. Enhancement of protective immune responses to Venezuelan equine encephalitis (VEE) virus with microencapsulated vaccine. Vaccine 13:1411–1420 (1995).
P. A. Marx, R. W. Compans, A. Gettie, J. K. Staas, R. M. Gilley, M. J. Mulligan, G. V. Yamshchkov, D. Chen, and J. H. Eldridge. Protection against vaginal SIV transmission with microencapsulated vaccine. Science 260:1323–1326 (1993).
D. E. Rafferty, M. G. Elfaki, and P. C. Mongomery. Preparation and characterization of a biodegradable microparticle antigen/cytokine delivery system. Vaccine 14:532–538 (1996).
R. V. Nellore, P. G. Pande, D. Young, and H. R. Bhagat. Evaluation of biodegradable microspheres as vaccine adjuvant for hepatitis B surface antigen. J. Parenter. Sci. Technol. 46:176–180 (1992).
B. Gander, E. Wehrli, R. Alder, and H. P. Merkle. Quality improvement of spray-dried, protein-loaded D,L-PLA microspheres by appropriate polymer solvent selection. J. Microencapsulation 12:89–97 (1995).
G. Del Giudice, J. A. Cooper, J. Merino, A. S. Verdini, A. Pessi, A. R. Togna, H. D. Engers, G. Corradin, and P. Lambert. The antibody response in mice to carrier-free synthetic polymers of Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite repetitive epitope is I-Ab-restricted: possible implication for malaria vaccines. J. Immunol. 137:2952–2955 (1986).
S. P. Schwendeman, H. R. Costantino, R. K. Gupta, G. R. Siber, A. R. Klibanov, and R. Langer. Stabilization of tetanus and diphtheria toxoids against moisture-induced aggregation. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 92:11234–11238 (1995).
M. J. Alonso, S. Cohen, T. G. Park, R. K. Gupta, G. R. Siber, and R. Langer. Determinants of release rate of tetanus vaccine from polyester microspheres. Pharm. Res. 10:945–953 (1993).
A.-C. Chang and R. K. Gupta. Stabilization of tetanus toxoid in poly(DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres for the controlled release of antigen. J. Pharm. Sci. 85:129–132 (1996).
A. C. Allison and N. E. Byars. Immunological adjuvants: desirable properties and side-effects. Mol. Immunol. 28:279–284 (1991).
D. A. Howerton, R. L. Hunter, H. K. Ziegler, and I. J. Check. Induction of macrophage la expression in vivo by a synthetic block copolymer, L81. J. Immunol. 144:1578–1584 (1990).
A. F. M. Verheul and H. Snippe. Non-ionic block polymer surfactants as immunological adjuvants. Res. Immunol. 143:512–519 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Audran, R., Men, Y., Johansen, P. et al. Enhanced Immunogenicity of Microencapsulated Tetanus Toxoid with Stabilizing Agents. Pharm Res 15, 1111–1116 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011950732105
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011950732105