Abstract
Purpose. A new mathematical approach was developed to quantify convulsant interaction between pefloxacin and theophylline in rats.
Methods. Animals received each compound separately or in different combination ratios. Infusion was stopped at the onset of maximal seizures. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma samples were collected for HPLC drug determination. The nature and intensity of the pharmacodynamic (PD) interaction between drugs was assessed with a new modeling approach which includes (a) data transformation to create an essentially error-free X-variable and (b) estimation of an interaction parameter α by fitting a nonlinear hyperbolic model to the combination data with unweighted nonlinear regression.
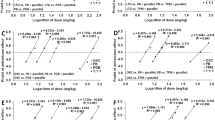
Results. Drug disposition to the biophase was linear within the range of administered doses. The estimates of α suggested a Loewe antagonistic interaction between pefloxacin and theophylline at the induction of maximal seizures in rats. Similar intensity of PD interaction was observed at the dose and biophase level (α was −0.415 ± 0.069 and −0.567 ± 0.079, respectively).
Conclusions. The suitability of the proposed model was assessed by Monte Carlo simulation. This new mathematical approach enabled the characterization of the Loewe antagonistic nature of the PD (convulsant) interaction between pefloxacin and theophylline, whereas previously used methodologies failed to do so.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. A. Upton. Pharmacokinetic interactions between theophylline and other medication, Part I. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 20:66–80 (1991).
I. M. Ramzan and G. Levy. Kinetics of drug action in disease states. XIV. Pharmacodynamics of theophylline-induced seizures in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 236:708–713 (1986).
J. Zhi and G. Levy. Isobolographic assessment of the convulsant interaction between theophylline and caffeine or pentylenetetrazol in rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 79:678–681 (1990).
A. Delon, F. Huguet, Ph. Courtois, J. M. Vierfond, S. Bouquet, and W. Couet. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic contributions to the convulsant activity of pefloxacin and norfloxacin in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 280:983–987 (1997).
U. Jachde, M. W. E Langemeijer, A. G. de Boer, and D. D. Breimer. Cerebrospinal fluid transport and disposition of the quinolones ciprofloxacin and pefloxacin in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 263:1140–1146 (1992).
L. Levasseur, H. Faessel, H. K. Slocum, and W. R. Greco. Precision and pattern in 96-well plate cell growth experiments, Proc. Biopharm. Sect. Am. Stat. Assoc. 227–232 (1995).
W. R. Greco, G. Bravo, and J. C. Parsons. The search for synergy: a critical review from a response surface perspective. Pharmacol. Rev. 47:331–385 (1995).
N. Draper and H. Smith. Applied Regression Analysis, 2nd edition. In John Wiley & Sons (eds.), New York, 1981.
M. C. Berenbaum. Synergy, additivism and antagonism in immunosuppression. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 25:1–18 (1977).
SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT User's Guide, Version 6, Fourth Edition, Volume 2, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, 1989.
M. L. Ralston and R. I. Jennrich. DUD, a derivative-free algorithm for nonlinear least squares. Technometrics 20:7–14 (1978).
A. Delon, C. Pariat, Ph. Courtois, S. Bouquet, and W. Couet. A new approach for early assessment of the epileptogenic potential of quinolone. (submitted).
P. K. Gessner. The isobolographic method applied to drug interaction. In P. L. Morselli, S. Garattini, and S. N. Cohen (eds.), Drug interactions, Raven Press, New York, 1974, pp. 349–362.
D. Z. D'Argenio and A. Schumitzky. ADAPT II User's guide: Pharmacokinetic / Pharmacodynamic systems analysis software. Biomedical Simulations Resource, Los Angeles, CA, 1997.
S. Segev, M. Rehavi, and E. Rubinstein. Quinolones, theophylline and diclofenac interactions with the γ-aminobutyric acid receptor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32:1624–1626 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levasseur, L.M., Delon, A., Greco, W.R. et al. Development of a New Quantitative Approach for the Isobolographic Assessment of the Convulsant Interaction Between Pefloxacin and Theophylline in Rats. Pharm Res 15, 1069–1076 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011938429379
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011938429379