Abstract
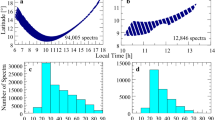
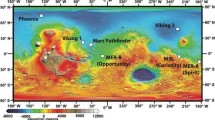
In addition to the Viking in-situ mass spectrometry measurements, our knowledge of the Martian atmosphere comes from remote sensing spectroscopy from the ground and from space. In particular, infrared measurements from the Mariner 9, Viking, Phobos and MGS orbiters have provided information upon the thermal profile, the chemical composition, the stratospheric winds, some isotopic ratios, and the properties of suspended dust. However, further remote sensing monitoring is still needed for a better understanding of the water cycle, a more accurate knowledge of the minor species and the aerosol composition, an improved measurement of the hydrogen and oxygen isotopic ratios, and for a full mapping of the middle altitude winds. Some of these information will be provided with the Mars Express mission.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atreya, S.K., and Blamont, J.: 1990, 'Stability of the Martian Atmosphere: Possible Role of Heterogeneous Chemistry', Geophys. Res. Lett. 17, 287-290.
Atreya, S.K., and Gu, Z.: 1994, 'Stability of the Martian Atmosphere: is Heterogeneous Chemistry Essential?', J. Geophys. Res. 99, 13,133-13145.
Barker, E.: 1972, 'Detection ofMolecular Oxygen in the Martian Atmosphere', Nature 238, 447-448.
Barker, E.: 1976, 'Martian AtmosphericWater Vapor Observations: 1972-74 Apparitions', Icarus 28, 247-268.
Barth, C.A., Hord, C.W., Stewart, A.I., Lane, A.L., Dick, M.L., and Anderson, G.P.: 1973, 'Mariner 9 Ultraviolet Spectrometer Experiment:S easonal Variation of Ozone on Mars', Science 179, 795-796.
Bézard, B., de Bergh, C., Crisp, D., and Maillard, J.P.: 1990, 'The Deep Atmosphere of Venus Revealed by High-resolution Night-side Spectra', Nature 345, 508-511.
Billebaud, F., Rosenqvist, J., Lellouch, E., Maillard, J.P., Encrenaz, Th., and Hourdin, F.: 1998, 'Observations of CO in the Atmosphere of Mars in the (2-0) Vibrational Band at 2.35 microns', Astron. Astrophys 333, 1092-1099.
Bjoraker, G.L., Mumma, M.J., and Larson, H.P.: 1989, 'Isotopic Abundance Ratios for Hydrogen and Oxygen in the Martian Atmosphere, Bull. Amer. Astron. Soc. 21, 990-990.
Bogard, D.D., Clayton, R.N., Marti, K., Owen, T., and Turner, G.: 2001, 'Martian Volatiles:Isotopic Composition, Origin, and Evolution', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Burgdorf, M.J., et al.: 2000, 'ISO Observations of Mars:an Estimate of the Water Vapor Vertical Distribution and the Surface Emissivity', Icarus 145, 79-90.
Carleton, N.P., and Traub, W.A.: 1972, 'Detection of Molecular Oxygen on Mars', Science 177, 988-992.
Clancy, R.T., Muhleman, D.O., and Berge, G.L.: 1990, 'Global Changes in the 0-70 km Thermal Structure of the Mars Atmosphere Derived from 1975-1989 Microwave CO Spectra', J. Geophys. Res. 95, 14,543-14554.
Clancy, R.T., Grossman, A.W., and Muhleman, D.O.: 1992, 'Mapping Mars Water Vapor with the Very Large Array', Icarus 100, 48-59.
Clancy, R.T., et al.: 1996, 'Water Vapor Saturation at low Altitudes Around Mars Aphelion: a Key to Martian Climate?', Icarus 122, 36-62.
Clark, R.N., Swayze, G.A., Singer, R.B., and Pollack, J.: 1990, 'High-resolution Reflectance Spectra of Mars in the 2.3 μm Region:Ev idence for Mineral Scapolite', J. Geophys. Res. 95, 14,463-14480.
Conrath, B.J., Pearl, J.C., Smith, M.D., and Christensen, P.R.: 1999, 'Mars Global Surveyor TES Results: Atmospheric Thermal Structure Retrieved from Limb Measurements', Bull. Amer. Astron. Soc. 31, 1150-1150.
Drossart, P., Rosenqvist, J., Erard, S., Langevin, Y., Bibring, J. P., and Combes, M.: 1991, 'Martian Aerosol Properties from the Phobos/ISM Experiment', Annales Geophysicae 9, 754-760.
Encrenaz, Th., et al.: 1991, 'The Atmospheric Composition of Mars: ISM and Ground-based Observational Data', Annales Geophysicae 9, 797-803.
Encrenaz, Th., Lellouch, E., Cernicharo, J., Paubert, G., and Gulkis, S.:1995a, 'A Tentative Detection of the 183-GHz Water Vapor Line in the Martian Atmosphere:C onstraints Upon the H2O Abundance and Vertical Distribution', Icarus 113, 110-118.
Encrenaz, Th., et al.:1995b, Detectability of Molecular Species in Planetary and Satellite Atmospheres from their Rotational Transitions', Plan. Space Sci. 43, 1485-1516.
Encrenaz, Th., et al.: 1998, 'A Study of the Water Vapor Vertical Distribution on Mars from ISO and IRAM Measurements', Annales Geophysicae 16, III, C1038-C1038.
Encrenaz, Th., Lellouch, E., Paubert, G., and Gulkis, S.: 1999, IAU Circ. 7186, June 4.
Espenak, F., Mumma, M., and Kostiuk, T.: 1991, 'Ground-based Infrared Measurements of the Global Distribution of Ozone in the Atmosphere of Mars', Icarus 92, 252-262.
Farmer, C.B., Davies, D.W., Holland, A.L., LaPorte, D.D., and Doms, P.E.: 1977, 'Mars:Water Vapor Observations from the Viking Orbiters', J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4225-4248.
Forget, F., et al.: 1999, 'Improved General Circulation Models of the Martian Atmosphere from the Surface to Above 80 km', J. Geophys. Res. 104, 24,155-24176.
Hanel, R.A., et al.: 1972, 'Investigation of the Martian Environment by Infrared Spectroscopy on Mariner 9', Icarus 17, 423-442.
Head, J.W., et al.: 2001, 'Geological Processes and Evolution', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Jakosky, B.M., and Haberle, R.M.: 1992, 'The Seasonal Behavior ofWater on Mars', in H.H. Kieffer, B.M. Jakosky, C.W. Snyder, and M.S. Matthews (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, pp. 969-1016.
Kahn, R.A., Martin, T.Z., Zurek, R.W., and Lee, S.W.: 1992, 'The Martian Dust Cycle', in H.H. Kieffer et al. (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, pp. 1017-1053.
Kaplan, L., Connes, P., and Connes, J.: 1969, 'Carbon Monoxide in the Martian Atmosphere', Astrophys. J. 157, L187-L192.
Kieffer, H.H., Martin, T.Z., Peterfreund, A.R., Jakosky, B.M., Miner, E.D., and Palluconi, F.D.: 1977, 'Thermal and Albedo Mapping of Mars during the Viking Primary Mission', J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4249-4291.
Kliore, A.J., Cain, D.L., Fjeldbo, G., Sidel, B.L., Sykes, M.J., and Rasool, S.I.: 1972, 'The Atmosphere of Mars from Mariner 9 Radio-occultation Measurements', Icarus 17, 484-516.
Korablev, O.I., et al.: 1993, 'Tentative Detetion of Formaldehyde in the Martian Atmosphere', Plan. Space Sci. 41, 441-451.
Krasnopolsky, V.A., Parshev, V.A., Krysko, A.A., and Rogachev, V.N.: 1979, 'Structure of the Mars Lower and Middle Atmosphere Based on Mars 5 Ultraviolet Photometry Data', Academy of Sciences (USSR), Moscow.
Krasnopolsky, V.A.: 1986, 'Photochemistry of the Atmospheres of Venus and Mars', Springer-Verlag.
Krasnopolsky, V.A.: 1997, 'High-resolution Spectroscopy of Mars at 3.7 and 8 μm:a Sensitive Search for H2O2, H2CO, HC1, and CH4, and Detection of HDO', J. Geophys. Res. 102, 6525-6534.
Lellouch, E., Goldstein, J.J., Bougher, S.W., Paubert, G., and Rosenqvist, J.:1991a, 'First Absolute Wind Measurements in the Middle Atmosphere of Mars', Astrophys. J. 383, 401-406.
Lellouch, E., Paubert, G., and Encrenaz, Th.:1991b, 'Mapping of CO Millimeter-wave Lines in Mars' Atmosphere:t he Spatial Distribution of Carbon Monoxide on Mars', Plan. Space Sci. 39, 219-224.
Lellouch, E., et al.: 2000, 'The 2.4-45 μm Spectrum of Mars Observed with the Infrared Space Observatory', Plan. Space Sci., in press.
Lindal, G.F., et al.: 1979, 'Viking Radio-occultation Measurements of the Atmosphere and Topography of Mars:Dat a Acquired during 1 Martian Year of Tracking', J. Geophys. Res. 84, 8443-8456.
Maguire, W.C.: 1977, 'Martian Isotopic Ratios and Upper Limits for Possible Minor Constituentns as Derived from the Mariner 9 Infrared Spectrometer Data', Icarus 32, 85-97.
Martin, T.Z.: 1981, 'Mean Thermal and Albedo Behavior of the Mars Surface and Atmosphere over a Martian Year', Icarus 45, 427-446.
Masson, P., Carr, M.H., Costard, F., Greeley, R., Hauber, E., and Jaumann, R.: 2001, 'Geomorphologic Evidence for Liquid Water', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
McElroy, M.B., and Donahue, T.M.: 1972, 'Stability of the Martian Atmosphere', Science 177, 986-988.
McElroy, M.B., Kong, T.Y., and Yung, Y.L.: 1977, 'Photochemistry and Evolution of Mars' Atmosphere: a Viking Perspective', J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4379-4388.
Nier, A.O., and McElroy, M.B.: 1977, 'Composition and Structure of Mars' Upper Atmosphere: Results from the Neutral Mass Spectrometers of Viking 1 and 2', J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4341-4349.
Owen, T.: 1992, 'The Composition and Early History of the Atmosphere of Mars', in H.H. Kieffer et al. (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, pp. 1017-1053.
Owen, T., Biemann, K., Rushneck, D.R., Biller, J.E., Howarth, D.W., and Lafleur, A.L.: 1977, 'The Composition of the Atmosphere at the Surface of Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4635-4639.
Owen, T., Maillard, J.P., de Bergh, C., and Lutz, B.L.: 1988, 'Deuterium on Mars: the Abundance of HDO and the Value of D/H', Science 240, 1767-1770.
Parkinson, T.D., and Hunten, D.M.: 1972, 'Spectroscopy and Aeronomy of O2 on Mars', J. Atmos. Sci. 29, 1380-1390.
Pollack, J.B., et al.: 1977, 'Properties of the Aerosols in the Martian Atmosphere, as Inferred from Viking Lander Imaging Data', J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4479-4496.
Pollack, J.B., et al.:1990a, 'Thermal Emission Spectra of Mars (5.4-10.5 μm):E vidence for Sulfates, Carbonates and Hydrates', J. Geophys. Res. 95, 14,595-14,628.
Pollack, J.B., Haberle, R.M., Schaeffer, J., and Lee, H.:1990b, Simulations of the General Circulation of the Martian Atmosphere, I. Polar processes', J. Geophys. Res. 95, 1447-1473.
Rizk, B., et al.: 1991, 'Meridional Martian Water Abundance Profiles during the 1988-1989 Season', Icarus 90, 205-213.
Rosenqvist, J., et al.: 1992, 'Minor Constituents in the Martian Atmosphere from the ISM/Phobos Experiment', Icarus 98, 254-270.
Rosenqvist, J., and Chassefière, E.: 1995, 'A Reexamination of the Relationship between Eddy Mixing and O2 in the Martian Middle Atmosphere', J. Geophys. Res. 100, 5541-5551.
Seiff, A., and Kirk, D.B.: 1977, 'Structure of the Atmosphere of Mars in Summer at Mid-latitudes', J. Geophys. Res. 82, 4364-4378.
Smith, P.H., et al.: 1997, 'Results of the Mars Pathfinder Camera', Science 278, 1758-1765.
Théodore, B., Lellouch, E., Chassefière, E., and Hauchecorne, A.: 1993, 'Solstitial Temperature Inversions in the Martian Middle Atmosphere:Obser vational Clues and 2-D Modeling', Icarus 105, 512-528.
Titov, D.V., et al.: 1994, 'Observations of Water Vapor Anomaly Above Tharsis Volcanoes on Mars in the ISM (Phobos 2) Experiment', Plan. Space Sci. 42, 1001-1010.
Titov, D.V., Rosenqvist, R., Moroz, V.I., Grigoriev, A.V., and Arnold, G.: 1995, 'Evidences of the Regolith-atmosphere Water Exchange on Mars from the ISM (Phobos 2) Infrared Spectrometer Observations', Adv. Space Res. 16, (6)23-(6)33.
Titov, D.V., et al.: 1998, 'Measurements of the Atmospheric Water Vapor on Mars by the Imager for Mars Pathfinder', J. Geophys. Res. 104, 9019-9026.
Titov, D.V., Fedorova, A.A., and Haus, R.: 2000, 'A new Method of Remote Sounding of theMartian Aerosols by Means of Spectroscopy in the 2.7 μm CO2 Band', Plan. Space Sci. 48, 67-74.
Toon, O.B., Pollack, J.B., and Sagan, C.: 1977, 'Physical Properties of the Particles Composing the Martian Dust Storm of 1971-1972', Icarus 30, 663-696.
Traub, W.A., Carleton, N.P., Connes, P., and Noxon, J.F.: 1979, 'The Latitude Variation of O2 Dayglow and O3 Abundance on Mars', Astrophys. J. 229, 846-850.
Trauger, J.T., and Lunine, J.I.: 1983, 'Spectroscopy of Molecular Oxygen in the Atmospheres of Venus and Mars', Icarus 55, 272-281.
Zurek, R.W.: 1992, 'Comparative Aspects of the Climate of Mars: an Introduction to the Current Atmosphere', in H.H. Kieffer et al. (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, pp. 799-817.
Zurek, R.W., and Martin, T.Z.: 1993, 'Interannual Variability of Planet-encircling Dust Storms on Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 98, 3247-3259.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Encrenaz, T. The Atmosphere of Mars as Constrained by Remote Sensing. Space Science Reviews 96, 411–424 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011922011532
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011922011532