Abstract
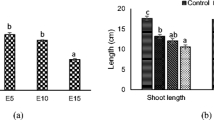
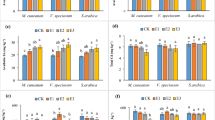
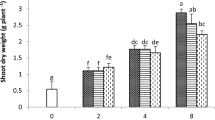
Synthetic chelates such as ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) have been shown to enhance phytoextraction of some heavy metals from contaminated soil. In a soil column study, we examined the effect of EDTA on the uptake of Pb, Zn and Cd by Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa), mobilization and leaching of heavy metals and the toxicity effects of EDTA additions on plants. The most effective was a single dose of 10 mmol EDTA kg−1 soil where we detected Pb, Zn and Cd concentrations that were 104.6, 3.2 and 2.3-times higher in the aboveground plant biomass compared to the control treatments. The same EDTA addition decreased the concentration of Pb, Zn and Cd in roots of tested plants by 41, 71 and 69%, respectively compared to concentrations in the roots of control plants. In columns treated with 10 mmol kg−1 EDTA, up to 37.9, 10.4 and 56.3% of initial total Pb, Zn and Cd in soil were leached down the soil profile, suggesting high solubility of heavy metals-EDTA complexes. EDTA treatment had a strong phytotoxic effect on the red clover (Trifolium pratense) in bioassay experiment. Moreover, the high dose EDTA additions inhibited the development of arbuscular mycorrhiza. The results of phospholipid fatty acid analyses indicated toxic effects of EDTA on soil fungi and increased environmental stress of soil microfauna.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berti R, Cunningham S C and Cooper E M 1998 Case studies in the field-in-place inactivation and phytorestoration of Pbcontaminated sites. In Metal-Contaminated Soils: In Situ Inactivation and Phytorestoration. Ed. W R Berti, Cunningham S C and Copper E M. pp 235–248. Landes Bioscience, Austin.
Blaylock M J, Salt D E, Dushenkov S, Zakharova O, Gussman C, Kapulnik Y, Ensley B D and Raskin I 1997 Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 860–865.
Brundrett M, Bougher N, Dell B, Grove T and Malajczuk N 1996 Working with Mycorrhizas in Forestry and Agriculture. ACAIR, Canberra, 374 p.
Cooper E M, Sims J T, Cunningham S D, Huang JW and Berti WR 1999 Chelate-assisted phytoextraction of lead from contaminated soils. J. Environ. Qual. 28, 1709–1719.
Council Directive 86/278/EEC 1986 On the Protection of the Environment, and In Particular of the Soil, When Sewage Sludge is Used in Agriculture. EC Official Journal L181, 4.7.1986, Brussels, 6 p.
Cunningham S C, Berti WR and Huang JW 1995Phytoremediation of contaminated soils. TIBtech. 13, 393–379.
Cunningham S C, Berti W R and Huang J W 1995 Remediation of contaminated soils and sludges by green plants. In Bioremediation of Inorganics. Ed. E Hinchee, J L Means and D Burris. pp 33–54. Batelle Press, Columbus-Richland.
Dahlin S, Witter E, Mĺlrtensson A, Turner A and Bĺlĺlth E 1997 Where's the limit? Changes in the microbiological properties of agricultural soils at low levels of metal contamination. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 29, 1405–1415.
Dirilgen N 1998 Effects of pH and chelator EDTA on Cr toxicity and accumulation in Lemma minor. Chemosphere v37, 771–783.
Ezawa T, Saito M and Yoshida T 1995 Comparison of phosphatase localization in the intraracial hyphae of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, Glomus spp. and Gigaspora spp. Plant and Soil 176, 57–63.
Epstein A L, Gussman C D, Blaylock M J, Yermiyahu U, Huang J W, Kapulnik Y, Orser C S 1999 EDTA and Pb-EDTA accumulation in Brassica juncea grown in Pb-amended soil. Plant and Soil 208, 87–94.
Flathman P E and Lanza G R 1998 Phytoremediation: current views on an emerging green technology. J. Soil Contamin. 7, 415–432.
Frostegard A and Bååth E 1996 The use of phospholipic fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 22, 59–65.
Frostegård A, Tunlid A and Bååth E 1991 Microbial biomass measured as a total lipid phosphate in soils of different organic content. J. Microb. Methods 14, 151–163.
Frostegård A, Tunlid A and Bååth E 1993 Phospholipid fatty acid composition, biomass, and activity of microbial communities from two soil types experimentally exposed to different heavy metals. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 3605–3617.
Godbold D L 1994 Aluminium and heavy metal stress: From the rhizosphere to the whole plant. In Effects of Acid Rain on Forest Processes. Ed. D L Godbold and A Hütterman. pp 232–264. Wiley-Liss, New York.
Guckert J B, Hood m A and White D C 1986 Phospholipid esterlinked fatty acid profile changes during nutrient deprivation of Vibrio cholerae: increase in the trans/cis ratio and proportions of cyclopropyl fatty acids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 52, 794–801.
Hamano T, Mitsuhashi Y, Kojima N and Aoki N 1993 Sensitive spectrophotometric method for the determination of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in foods. Analyst 118, 909–912.
Huang J W, Chen J, Berti W R and Cunningham S D 1997 Phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soils: role of synthetic chelates in lead phytoextraction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 3, 800–805.
Huang J W and Cunningham S D 1996 Lead phytoextraction: species variation in lead uptake and translocation. New Phytol. 134, 75–84.
Leyval C, Turnau K and Haselwandter K 1997 Effects of heavy metal pollution on mycorrhizal colonization and function: physiological, ecological and applied aspects. Mycorrhiza 7, 139–153.
Mark C S and Pichtel J 1998 Ex-situ remediation of a metalcontaminated superfund soil using selective extractants. J. Environ. Eng. 124, 639–645.
Nörtemann B 1999 Biodegradation of EDTA. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 51, 751–759.
Pawlowska T E, Chaney R L, Chin M and Charvat I 2000 Effects of metal phytoextraction practices on the indigenous community of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at a metal-contaminated landfill. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 2526–2530.
Phillips J M and Hayman D S 1970 Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 55, 58–160.
Postma J W M, Keltjens W G, Nelemans J A and van Tintelen W 2000 Interaction of Al(-EDTA) with the plant root: Plant growth and nutrient uptake. Plant Physiol. Biochem. Suppl. 38, 136–142.
Ringelberg D B, Sutton S and White D C 1997 Biomass, bioactivity and biodiversity: microbial ecology of the deep subsurface: analysis of ester-linked phospholipid fatty acids. FEMS Microb. Rev. 20, 371–377.
Ruby M V, Schoof R, Brattin W, Goldade M, Post G, Harnois M, Mosby D E, Casteel S W, Berti W, Carpenter M, Edwards D, Cragin D and Chappell W 1999 Advances in evaluating the oral bioavailability of inorganics in soil for use in human health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 3697–3705.
Salt D E, Blaylock M, Kumar P B A N, Dushenkov V, Ensley B D, Chet I and Raskin I 1995 Phytoremediation: a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Biotechnology 13, 468–474.
Sillanpaeae M and Oikari A 1996 Assessing the impact of complexation by EDTA and DTPA on heavy metal toxicity using Microtox bioassay. Chemosphere 32, 1485–1497.
Smith S E and Read D J 1997 Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. Academic Press, San Diego, London, 605 p.
Sommers L E and Lindsay W L 1979 Effect of pH and redox on predicted heavy metal-chelate equilibria in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J.43, 39–47.
Steele M C and Pichtel J 1998 Ex-situ remediation of metal contaminated superfund soil using selective extractants. J. Environ. Eng. 124, 639–645.
Thorn G 1997 The Fungi in Soil In Modern soil microbiology. Eds. J D Elsas, J T Trevors and EMH Wellington. pp 63–127. Marcel Dekker, Inc, New York.
Trouvelot A, Kongh J L and Gianinazzi-Pearson V 1986 Measure du taux de mycorrhization d'un systeme radiculaire. Recherche de methods d'estimation ayant une signification fonctionelle. In Physiological and Genetical Aspects of Mycorhizae. Eds. V Gianinazzi-Pearson and S Gianinazzi. pp 217–221. INRA, Dijon.
Vestal J R and White D C 1989 Lipid analysis and microbial ecology. BioSci. 39, 535–541.
White D C, Flemming C A, Leung K T and Macnaughton S J 1998 In situ microbial ecology for quantitative appraisal, monitoring and risk assessment of pollution remediation in soils, the subsurface, the rhizosphere and in biofilms. J. Microb. Meth. 32, 93–105.
Xian X 1989 Effect of chemical forms of cadmium, zinc, and lead in polluted soils on their uptake by cabbage plants. Plant Soil 113, 257–264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grčman, H., Velikonja-Bolta, Š., Vodnik, D. et al. EDTA enhanced heavy metal phytoextraction: metal accumulation, leaching and toxicity. Plant and Soil 235, 105–114 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011857303823
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011857303823