Abstract
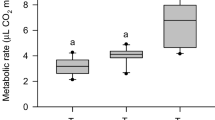
Two geographical subspecies of the honeybee Apis mellifera, the European bee A. m. carnica and the Egyptian bee A. m. lamarckii, were investigated by direct calorimetry. Maximum, mean and minimum heat production rates were determined for groups of 6 bees as a function of temperature and daytime. Smaller Egyptian subspecies showed significantly higher mass specific metabolic rates than the European one. Maximum and mean heat production rates decreased exponentially with growing temperatures while the minimum values remained constant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. S. Abou Zeid, Untersuchungen zur Biologie der Ägyptischen Biene, Apis mellifera lamarckii Cock., PhD-Thesis, Faculty of Biology, Free University Berlin 1989.
M. D. Allen, J. Exp. Biol., 36 (1959) 92.
G. A. Bartholomew, In: Insect Thermoregulation, ed. by B. Heinrich, Wiley, New York 1981.
K. Cahill and S. Lustick, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 55A (1976) 355.
L. Fahrenholz, I. Lamprecht and B. Schricker, J. Comp. Physiol. B, 159 (1989) 551.
L. Fahrenholz, I. Lamprecht and B. Schricker, J. Comp. Physiol. B, 162 (1992) 119.
J. B. Free and Y. Spencer-Booth, J. Exp. Biol., 35 (1958) 930.
J. F. Harrison and H. G. Hall, Nature, 363 (1993) 258.
B. Heinrich, J. Exp. Biol., 80 (1979) 217.
B. Heinrich, The Hot Blooded Insect. Strategies and Mechanisms of Thermoregulation, Springer Verlag, Berlin 1993.
A. Heusner and M. Roth, C. R. Acad. Sc. Paris, 256 (1963) 284.
F. Kronenberg and H. C. Heller, J. Comp. Physiol., 148 (1982) 65.
I. Lamprecht, F.-R. Matuschka and B. Schaarschmidt, J. Exp. Biol., 156 (1991) 375.
M. L. May, J. Comp. Physiol. B, 111 (1976) 55.
T. E. Rinderer, A. B. Bolten, A. M. Collins and J. R. Harbo, J. Apic. Res., 23 (1984) 70.
M. Roth, C. R. Acad. Sc. Paris, 258 (1964) 5534.
U. Rothe and W. Nachtigall, J. Comp. Physiol. B, 158 (1989) 739.
F. Ruttner, Biogeography and Taxonomy of Honeybees, Springer Verlag, Heidelberg 1988.
F. Ruttner, Naturgeschichte der Honigbiene, Ehrenwirth Verlag, München 1992.
E. Schmolz, I. Lamprecht and B. Schricker, Thermochim. Acta, 251 (1995) 293.
J. Simpson, Science, 133 (1961) 1327.
E. E. Southwick, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 71A (1982) 277.
E. E. Southwick, D. W. Roubik and J. M. Williams, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 97A (1990) 1.
M. L. Winston, Killer Bees, The Africanized Honey Bee in the Americas, Harvard Univ. Press, Cambridge 1992.
M. L. Winston, O. R. Taylor and O. W. Otis, Bee World, 64 (1983) 12.
P. V. W. Worswick, S. Afr. Tydskr. Dierk, 23 (1988) 124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmolz, E., Dewitz, R., Schricker, B. et al. Energy Metabolism of European (Apis Mellifera Carnica) and Egyptian (A. M. Lamarckii) Honeybees. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 65, 131–140 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011528618884
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011528618884