Abstract
Recent advances in optical networking technologies are setting the foundation for the next-generation data-centric networking paradigm, an “Optical Internet”. This work addresses one of the most challenging issues facing today's service providers and data vendors; how will the SONET/SDH-based legacy infrastructure currently in place make a graceful transition to the next generation networking paradigm?
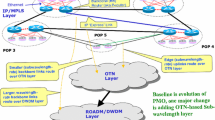
A simplified, two-tiered architecture that requires two types of sub-systems will set the stage for a truly optical internet: service delivery platforms that enforce service policies; and transport platforms that intelligently deliver the necessary bandwidth to these service platforms. If IP can be mapped directly onto the WDM layer, some of the unnecessary network layers can be eliminated, opening up new possibilities for the potential of collapsing today's vertically layered network architecture into a horizontal model where all network elements work as peers to dynamically establish optical paths through the network. This paper presents a balanced view of the vision of the next-generation optical internet
The work presented here builds on the IETF multi-protocol lambda switching (MPλS) initiative and addresses the implementation issues of the path selection component of the traffic-engineering problem in a hybrid IP-centric DWDM-based optical network. An overview of the methodologies and associated algorithms for dynamic lightpath computation is presented. Specifically, we show how the complex problem of real-time provisioning of optical channels can be simplified by using a simple dynamic constraint-based routing and wavelength assignment (RWA) algorithm that compute solutions to three sub-problems: (a) routing; (b) constrained-based shortest-route selection; (c) wavelength assignment.
We present two different schemes for dynamic provisioning of the optical channels. The two schemes use the same dynamic lightpath computation approach proposed here, except that the third component, that is the wavelength assignment algorithm and its implementation, is different for each of the two schemes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Awduche et al., Multiprotocol lambda switching, Internet Draft, work in progress (November 1999).
N. Chandhok et al., IP over optical networks: A summary of issues, Internet Draft, work in progress (July 2000).
N. Ghani, Lambda-Labeling: A framework for IP-over-WDM using MPLS, Optical Networks Magazine,, vol. 1, no. 2, (April 2000), pp. 45–58.
Y. Ye, S. Dixit, M. A. Ali, On joint protection/restoration in IP-centric DWDM-based optical transport networks, IEEE Communication Magazine,, vol. 38, no. 6, (June 2000), pp. 174–183.
B. Arnaud, Architectural and engineering issues for bulilding an optical Internet, SPIE Proceedings,, vol. 3531, (Nov. 1998), pp. 358–377.
D. Awduche, J. Malcolm, J. Agogbua, M. O'Dell, and J. MeManus, Requirements for Traffic Engineering Over MPLS, Internet draft, RFC-2702, (September 1999).
J. Bannister, J. Touch, A. Willner, S. Suryaputra, How many wavelengths do we really need? A study of the performance limits of packet over wavelengths, Optical Networks Magazine,, vol. 1, no. 2, (April 2000), pp. 17–28.
O. Gerstel, S. Kutten, Dynamic wavelength allocation in all-optical ring Networks, Proc. of IEEE ICC 97, Montreal, Quebec, Canada,, vol. 1, (June 1997), pp. 432–436.
S. Subramnian, R. A. Barry, Wavelength assignment in fixed routing WDM Networks, Proc. of ICC '97,, vol. 1, Montreal, Canada, (June 1997), pp. 406–410.
R. A. Barry, S. Subramanian. The MAX-SUM wavelength assignment algorithm for WDM ring networks, Proc. of OFC 97, Dallas, TX, (Feb. 1997), pp. 121–122.
G. Jeong, E. Ayanoglu, Comparison of wavelength-inter-changing and wavelength-selective cross-connects in multiwavelength all-Optical networks, Proc. IEEE INFOCOM '96, San Francisco, CA,, vol. 1, (March 1996), pp. 156–163.
E. Karasan, E. Ayanoglu, Effects of wavelength routing and selection algorithms on wavelength conversion gain in WDM optical Networks, IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, vol. 6, no. 2, (April 1998), pp. 186–196.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M.A., Shami, A., Assi, C. et al. Architectural Options for the Next-Generation Networking Paradigm: Is Optical Internet the Answer?. Photonic Network Communications 3, 7–21 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011475425915
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011475425915