Abstract
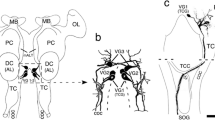
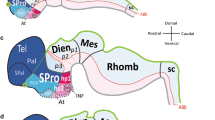
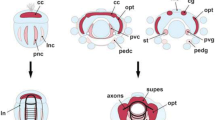
Contemporary study of molecular patterning in the vertebrate midbrain is handicapped by the lack of a complete topological map of the diverse neuronal complexes differentiated in this domain. The relatively less deformed reptilian midbrain was chosen for resolving this fundamental issue in a way that can be extrapolated to other tetrapods. The organization of midbrain centers was mapped topologically in terms of longitudinal columns and cellular strata on transverse, Nissl-stained sections in the lizard Gallotia galloti. Four columns extend along the whole length of the midbrain. In dorsoventral order: 1) the dorsal band contains the optic tectum, surrounded by three ventricularly prominent subdivisions, named griseum tectale, intermediate area and torus semicircularis, in rostrocaudal order; 2) a subjacent region is named here the lateral band, which forms the ventral margin of the alar plate and also shows three rostrocaudal divisions; 3) the basal band forms the basal plate or tegmentum proper; it appears subdivided into medial and lateral parts: the medial part contains the oculomotor and accessory efferent neurons and the medial basal part of the reticular formation, which includes the red nucleus rostrally; the lateral part contains the lateral basal reticular formation, and includes the substantia nigra caudally; 4) the median band contains the ventral tegmental area, representing the mesencephalic floor plate. The alar regions (dorsal and lateral) show an overall cellular stratification into periventricular, central and superficial strata, with characteristic cytoarchitecture for each part. The lateral band contains two well developed superficial nuclei, one of which is commonly misidentified as an isthmic formation. The basal longitudinal subdivisions are simpler and basically consist of periventricular and central strata.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ALVARADO-MALLART, R. M. (1993) Fate and potentialities of the avian mesencephalic/metencephalic neuroepithelium. Journal of Neurobiology 24, 1341–1355.
BASS, A. H. & BAKER, R. (1997) Phenotypic specification of hindbrain rhombomeres and the origins of rhythmic circuits in vertebrates. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 50, 3–16.
BELEKHOVA, M. G., ZHARSKAJA, V. D., KHACHUNTS, A. S., GAIDAENKO, G. V. & TUMANOVA, N. L. (1985) Connections of the mesencephalic, thalamic and telencephalic auditory centers in turtles. Some structural bases for audiosomatic interrelations. Journal für Hirnforschung 26, 127–152.
BERGQUIST, H. (1953) On the development of diencephalic nuclei and certain mesencephalic relations in Lepidochelys olivacea and other reptiles. Acta Zoologica (Stockholm) 34, 155–190.
BERGQUIST, H. (1954) Ontogenesis of diencephalic nuclei in vertebrates. A comparative study. Kungliska Fysiografiska Sällskapets (Lund) Handlingar 6, 1–34.
BERGQUIST, H. & KÄLLÉN, B. (1953a) Studies on topography of the migrations areas in the vertebrate brain. Acta Anatomica 17, 353–369.
BERGQUIST, H. & KÄLLÉN, B. (1953b) On the development of the neuromeres to migration areas in the vertebrate central tube. Acta Anatomica (Basel) 18, 65–73.
BERGQUIST, H. & KÄLLÉN, B. (1954) Notes on the early histogenesis and morphogenesis of the central nervous system in vertebrates. Journal of Comparative Neurology 100, 627–660.
BRUCE, L. L. & BUTLER, A. B. (1984) Telencephalic connections in lizards. I. Projections to cortex. Journal of Comparative Neurology 229, 585–601.
BULFONE, A., PUELLES, L., PORTEUS, M. H., FROHMAN, M. A., MARTÍN, G. R. & RUBENSTEIN, J. L. R. (1993) Spatially restricted expression of Dlx-1, Dlx-2 (Tes-1), Gbx-2, and Wnt-3 in the embryonic day 12.5 mouse forebrain defines potential transverse and longitudinal segmental boundaries. Journal of Neuroscience 13, 3155–3172.
BUTLER, A. B. & NORTHCUTT, R. G. (1973) Architectonic studies of the diencephalon of Iguana iguana (Linnaeus). Journal of Comparative Neurology 149, 439–462.
CABALLERO-BLEDA, M. (1988) Región alar del diencéfalo y mesencéfalo en el conejo: Quimioarquitectonía de AChE y NADH-diaforasa, como contribución a su neuroanatomía comparada. Ph.D. dissertation, Universidad de Murcia, Murcia, Spain.
CABALLERO-BLEDA, M., FERNáNDEZ, B. & PUELLES, L. (1992) The pretectal complex of the rabbit: Distribution of acetylcholinesterase and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide diaphorase activities. Acta Anatomica 144, 7–16.
CRUCE, W. L. R. & NIEUWENHUYS, R. (1974) The cell masses in the brain stem of the turtle Testudo hermanni; A topographical and topological analysis. Journal of Comparative Neurology 156, 277–306.
DACEY, D. M. & ULINSKI, P. S. (1986) Optic tectum of the eastern garter snake, Thamnophis sirtalis. V. Morphology of brainstem afferents and general discussion. Journal of Comparative Neurology 245, 423–453.
DE LANGE, S. J. (1913) Das Zwischenhirn und das Mittelhirn der Reptilien. Folia Neurobiologica 7, 67–138.
DÍAZ, C. (1991) Contribución al estudio de la conectividad intersegmental diencefálica: Algunas poblaciones del parencéfalo posterior en Gallotia galloti. Ph.D. dissertation, Universidad de La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain.
DÍAZ, C. & PUELLES, L. (1992a) In-vitro HRP-labeling of the fasciculus retroflexus in the lizard Gallotia galloti. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 39, 305–311.
DÍAZ, C. & PUELLES, L. (1992b) Afferent connections of the habenula complex in the lizard Gallotia galloti. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 39, 312–324.
DIAZ, C., PÉREZ-SANTANA, L., MARTÍNEZ-DE-LATORRE, M. & PUELLES, L. (1999) Diencephalic neuronal populations projecting axons into the basal plate in the lizard Gallotia galloti. European Journal of Morphology 37, 130–133.
EBBESSON, S. O. E. (1967) Ascending axon degeneration following hemisection of the spinal cordin the tegu lizard (Columba livia). Journal of Comparative Neurology 269, 18–46.
GARDNER, C. A. & BARALD, K. F. (1991) The cellular environment controls the expression of engrailed-like protein in the cranial neuroepithelium of quail-chick chimeric embryos. Development 113, 1037–1048.
GILLAND, E. & BAKER, R. (1993) Conservation of neuroepithelial and mesodermal segments in the embryonic veretebrate head. Acta Anatomica 148, 110–123.
HALLONET, M. R., TEILLET, M. & LEDOUARIN, N. M. (1990) A new approach to the development of the cerebellum provided by the quail-chick marker system. Development 108, 19–31.
HERRICK, J. C. (1910) The morphology of the forebrain in amphibia and reptilia. Journal of Comparative Neurology 20, 413–547.
HERRICK, J. C. (1917) The internal structure of the midbrain and thalamus of the Necturus. Journal of Comparative Neurology 28, 215–348.
HIS, W. (1893) Vorschlage zur Einteilung des Gehirns. Archiv für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte (Leipzig) 17, 172–179.
HIS, W. (1904) Die Entwicklung des menschlichen Gehirns während der ersten Monate. Leipizg: S. Hirzel Verlag.
HOOGLAND, P. V. (1982) Brainstem afferents to the thalamus in a lizard, Varanus exanthematicus. Journal of Comparative Neurology 210, 152–162.
HUBER, G. C. & CROSBY, E. C. (1926) The nuclei and fiber paths in the brain of the American alligator. Journal of Comparative Neurology 48, 1–225.
HUBER, G. C. & CROSBY, E. C. (1933) The reptilian optic tectum. Journal of Comparative Neurology 57, 57–163.
HYNES, M., PORTER, J. A., CHIANG, C., CHANG, D. & TESSIER-LAVIGNE, M. (1995a) Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons by Sonic hedgegog. Neuron 15, 35–44.
HYNES, M., POUSEL, K., TESSIER-LEVIGNE, M. & ROSENTHAL, A. (1995b) Control of neuronal diversity by the floor plate: Contact-mediated induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Cell 80, 95–102.
JOYNER, A. L. (1996) Engrailed, Wnt and Pax genes regulate midbrain-hindbrain development. Trends in Genetics 12, 15–20.
KARTEN, H. J. & HODOS, W. (1967) A Stereotaxic Atlas of the Brain of Pigeon (Columba livia). Baltimore: John Hopkins Press.
KEYSER, A. (1972) The development of the diencephalon of the Chinese hamster. An investigation of the vality of the criteria of subdivision of the brain. Acta Anatomica 83 (Suppl. 59), 1–178.
KINGSBURY, B. F. (1920) The extent of the floor-plate of His and its significance. Journal of Comparative Neurology 32, 113–135.
KINGSBURY, B. F. (1922) The fundamental plan of the vertebrate brain. Journal of Comparative Neurology 34, 461–491.
KINGSBURY, B. F. (1930) The developmental significance of the floor-plate of the brain and spinal cord. Journal of Comparative Neurology 50, 177–207.
KUHLENBECK, H. (1973) The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates, Vol. 3 (II). Berlin: S. Karger A.G.
KUHLENBECK, H. (1975) The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates, Vol. 4. Berlin: S. Karger A.G.
KüNZLE, H & WOODSON, W. (1982) Mesodiencephalic and other target regions of ascending spinal projections in the turtle, Pseudemys scripta elegans. Journal of Comparative Neurology 212, 349–364.
KüNZLE, H. & SCHNYDER, H. (1984) Doretinalandspinal projections overlap within the turtle thalamus?. Neuroscience 10, 161–168.
LIEM, K. F. JR., TREMML, G. & JESSEL, T. M. (1997) A role for the roof plate and its resident TGF beta-related proteins in neuronal patterning in the dorsal spinal cord. Cell 91, 127–138.
LIEM, K. F. JR., TREMML, G. ROELINK, H. & JESSEL, T. M. (1995) Dorsal differentation of neural plate cells induced by BMP-mediated signals from epidermal ectoderm. Cell 82, 969–979.
LUMSDEN, A. & KEYNES, R. (1989) Segmental patterns of neuronal development in the chick hindbrain. Nature 337, 424–428.
MACDONALD, R., XU, Q., BARTH, K. A., MIKKOLA, I., HOLDER, N., FJöSE, A., KRAUSS, S. & WILSON, S. W. (1994) Regulatory gene expression boundaries demarcate sites of neuronal differentiation in the embryonic zebrafish forebrain. Neuron 13, 1039–1053.
MARÍN, F. & PUELLES, L. (1994) Patterning of the embryonic avian midbrain after experimental inversions:Apolarizing activity from the isthmus. Developmental Biology 163, 19–37.
MARTI, E., BUMCROT, D. A., TAKADA, R. & MCMAHON, A. P. (1995) Requirement of 19K form of sonic hedgehog for induction of distinct ventral cell types in CNS explant. Nature 375, 322–325.
MARTÍNEZ, S. & PUELLES, L. (1989) Avian nucleus isthmi ventralis projects to the contralateral optic tectum. Brain Research 481, 181–184.
MARTÍNEZ, S. & ALVARADO-MALLART, R. M. (1989) Rostral cerebellum originates from the caudal portion of the so-called Ómesencephalicó vesicle: A study using chick-quail chimeras. European Journal of Neuroscience 1, 549–560.
MARTÍNEZ, S. & ALVARADO-MALLART, R. M. (1990) Expression of the homeobox chick-en gene in chick/quail chimeras with inverted mes-metencephalic grafts. Developmental Biology 139, 432–436.
MARTÍNEZ, S., PUELLES, L. & ALVARADO-MALLART, R. M. (1992) Tangential neuronal migration in the avian tectum: Cell type identification and mapping of regional differences with quail/chick homotopic transplants. Developmental Brain Research 66, 153–163.
MARTÍNEZ, S., WASSEF, M. & ALVARADO-MALLART, R. M. (1991) Induction of a mesencephalic phenotype in the 2 day-old chick prosencephalon is preceded by the early expression of the homeobox gene en. Neuron 6, 971–981.
MARTÍNEZ, S., MARÍN, F., NIETO, M. A. & PUELLES, L. (1995) Induction of ectopic engrailed expression and fate change in avian rhombomeres: Intersegmental boundaries as barrier. Mechanisms of Development 51, 289–303.
MARTÍNEZ-DE-LA-TORRE, M. (1985) Estructura del mesencéfalo y diencéfalo en aves y reptiles: Aportaciones a una síntesis en la búsqueda de homologías. Ph.D. dissertation, Universidad de Murcia, Murcia, Spain.
MASTICK, G. S., DAVIS, N. M., ANDREW, G. L. & EASTER, S. S. JR. (1997) Pax-6 functions in boundary formation and axon guidance in the embryonic mouse forebrain. Development 124, 1985–1997.
MATSUI, Y., ZSEBO, K. M. & HOGAN, B. L. M. (1990) Embryonic expression of a hematopoietic growth factor encoded by the SI locus and the ligand for c-kit. Nature 347, 667–669.
MEDINA, L. (1990) Est dio ontogenético e inmun h stoquímico de los centros visuales en el lagarto Gallotia galloti. Ph.D. dissertation, Universidad de La Laguna, Spain.
MEDINA, L. & SMEETS, W. J. A. J. (1992) Cholinergic, monoaminergic and peptidergic innervation of the primary visual centers in the brain of the lizards Gekko gecko and Gallotia galloti. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 40, 157–181.
MEDINA, L., PUELLES, L. & SMEETS, W. J. A. J. (1994) Development of catecholamine systems in the brain of the lizard Gallotia galloti. Journal of Comparative Neurology 350, 41–62.
MEDINA, L., SMEETS, W. J. A. J., HOOGLAND, P. V. & PUELLES, L. (1993) Distribution of cholinacetyltransferase immunoreactivity in the brain of the lizard Gallotia galloti. Journal of Comparative Neurology 331, 261–285.
MILáN, F. J. & PUELLES, L. (2000) Patterns of calretinin, calbindin and tyrosine-hydroxylase expression are consistent with the prosomeric map of the frog diencephalon. Journal of Comparative Neurology 419, 96–121.
MILLET, S., BLOCH-GALLEGO, E., SIMEONE, A. & ALVARADO-MALLART, R. M. (1996) The caudal limit of Otx-2 gene expression as a marker of the midbrain/ hindbrain boundary: A study using in situ hybridization and chick/quail homotopic grafts. Development 122, 3785–3797.
MüLLER, F. & O'RAHILLY, R. (1988) The development of the human brain, incluiding the longitudinal zoning in the diencephalon at stage 15. Anatomy and Embryology 179, 55–71.
NAKAMURA, H. & ITASAKI, N. (1992) Expression of en in the prosencephalon heterotopically transplanted into the mesencephalon. Development, Growth and Differentiation 34, 387–391.
NEWGREEN, D. F., ALLAN, I. J., YOUNG, H. M. & SOUTHWELL, B. R. (1981) Accumulation of exogenous catecholamines in the neural tube and non-neural tissue of the early fowl embryo. Correlation with morphogenetic movements. Roux's Archives 190, 320–330.
NEWMAN, D. B. & CRUCE, W. R. L. (1982) The organization of the reptilian brainstem reticular formation: A comparative study using Nissl and Golgi techniques. Journal of Morphology 173, 325–349.
NIEUWENHUYS, R. (1974) Topological analysis of the brain stem: A general introduction. Journal of Comparative Neurology 156, 255–276.
NIEUWENHUYS, R. (1998) Morphogenesis and general structure. In The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates, Vol. 1. (edited by NIEUWENHUYS, R., TEN DONKELAAR H. J. & NICHOLSON, C.) pp. 158–228. Berlin: Springer.
NIEUWENHUYS, R. & BODENHEIMER, T. S. (1966) The diencephalon of the primitive bony fish Polypterus in the light of the problem of homology. Journal of Morphology 118, 415–450.
NIEUWENHUYS, R., TEN DONKELAAR, H. J. & NICHOLSON, C. (1998) The meaning of it all. In The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates, Vol. 3. (edited by NIEUWENHUYS, R., TEN DONKELAAR, H. J & NICHOLSON, C.) pp. 2135–2195. Berlin: Springer.
NODEN, D. M. (1991) Vertebrate craniofacial development: The relation between ontogenetic process and morphological outcome. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 38, 190–225.
NORTHCUTT, R. G. (1984) Anatomical organization of the optic tectum of reptiles. In Comparative Neurology of the Optic Tectum (edited by VANEGAS, H.) pp. 547–600. New York: Plenum.
PALMGREN, A. (1921) Embryological and morphological studies on the midbrain and cerebellum of vertebrates. Acta Zoologica (Stockholm) 2, 1–94.
PAXINOS, G. & WATSON, C. (1986) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Sidney: Academic Press.
PAXINOS, G., TöRK, I., HALLIDAY, G. & MEHLER, W. R. (1990) Human homologues to brainstem nuclei identified in other animals as revealed by acetylcholinesterase activity. In The Human Nervous System (edited by PAXINOS, G.) pp. 149–202. San Diego: Academic Press.
PÉREZ-SANTANA, L. (1993) Aportaciones a la conectividad del techo óptico del lagarto Gallotia stehlini desde la perspectiva segmentaria. Ph.D. dissertation, Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Gran Canaria, Spain.
PÉREZ-SANTANA, L., MARTÍNEZ-DE-LA-TORRE, M., LORO, J. F. & PUELLES, L. (1996) Intertectal commissural projection in the lizard Gallotia stehlini: Origin and midline topography. Journal of Comparative Neurology 366, 360–369.
PLACZEK, M., JESSEL, T. M. & DODD, J. (1993) Induction of floor plate differentiation by contact-dependent, homeogenetic signals. Journal of Comparative Neurology 117, 205–218.
POMBAL, M. A. & PUELLES, L. (1999) A prosomeric map of the lamprey forebrain based on calretinin immunocytochemistry, Nissl stain and ancillary markers. Journal of Comparative Neurology 414, 391–422.
PRITZ, M. B. & STRITZEL, M. E. (1989) Reptilian somatosensory midbrain: Identification based on input from the spinal cord and dorsal column nucleus. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 33, 1–14.
PRITZ, M. B. & STRITZEL, M. E. (1990) Thalamic projections from a midbrain somatosensory area in a reptile, Caiman crocodilus. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 36, 1–13.
PUELLES, L. (1995) A segmental morphological paradigm for understanding vertebrate forebrains. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 46, 319–337.
PUELLES, L., AMAT, J. A. & MARTÍNEZ-DE-LA-TORRE, M. (1987) Segment-related, mosaic neurogenetic pattern in the forebrain and mesencephalon of early chick embryos: I. Topography of AchE-positive neuroblasts up to stage HH18. Journal of Comparative Neurology 266, 247–268.
PUELLES, L. & VERNEY, C. (1998) Early neuromeric distribution of tyrosine-hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons in human embryos. Journal of Comparative Neurology 394, 283–308.
PUELLES, L. & ZABALA, C. (1982) Evidence for a concealed neuromeric pattern in the disposition of retino recipient grisea in the avian diencephalon. Sixth European Neuroscience Congress. (Suppl), 10, 396.
PUELLES, L. & RUBENSTEIN, J. L. R. (1993) Expression patterns of homeobox and other putative regulatory genes in the embryonic mouse forebrain suggest a neuromeric organization. Trends in Neurosciences 16, 472–479.
PUELLES, L. & MARTÍNEZ-DE-LA-TORRE, M. (1987) Autoradiographic and Golgi study on the early development of n.isthmi principalis and adjacent grisea in the chick embryo: A tridimensional viewpoint. Anatomy and Embryology 176, 19–34.
PUELLES, L., KUWANA, E., PUELLES, E., BULFONE, A., SHIMAMURA, K., KELEHER, J., SMIGA, S. & RUBENSTEIN, J. L. R. (2000) Pallial and subpallial derivatives in the embryonic chick and mouse telencephalon, traced by the expression of the genes Dlx-2, Emx-1, Nkx-2.1, Pax-6 and Tbr. Journal of Comparative Neurology 424, 409–438.
PUELLES, L., MARTÍNEZ, S. & MARTÍNEZ-DE-LA-TORRE, M. (1988) The locus of optic nerve head representation in the retinotopic projection over nucleus geniculatus lateralis ventralis and nucleus griseum tectalis in the chick also lacks a retinal projection. Neuroscience Letters 85, 35–39.
PUELLES, L., MILáN, J. & MARTÍNEZ-DE-LA-TORRE, M. (1996a) A segmental map of architectonic subdivisions in the diencephalon of the frog Rana perezzi: A cetylcholinesterase-histochemical observations. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 8, 279–310.
PUELLES, L., MARÍN, F., MARTÍNEZ-DE-LA-TORRE, M. & MARTÍNEZ, S. (1996b) The midbrain-hindbrain junction: A model system for brain regionalization through morphogenetic neuroepithelial interactions. In Mammalian Development (edited by LONAI, P.) Amsterdam: Gordon&Breach/Harwood Academic Publishers.
PUELLES, L., ROBLES, C., MARTÍNEZ-DE-LA-TORRE, M. & MARTÍNEZ, S. (1994) New subdivision schema for the avian torus semicircularis: Neurochemical maps in the chick. Journal of Comparative Neurology 340, 98–125.
PUSCHEL, A. W., GRUSS, P. & WESTERFIELD, M. (1992) Sequence and expression pattern of pax-6 are highly conserved between zebrafish and mice. Development 114, 643–651.
RAMóN, P. (1896) Estructura del encéfalo del camaleón. Revista Trimestral Micrográfica 1, 46–82.
REINER, A., KRAUSE, J. E., KEYSER, K. T., ELDRED, W. D. & MCKELVY, J. F. (1984) The distribution of substance P in turtle nervous system: A radioimmunoassay and immunohistochemical study. Journal of Comparative Neurology 226, 50–75.
RENDAHL, H. (1924) Embryologische und morphologische Studien uber das Zwischenhirn beim Huhn. Acta Zoologica (Stockholm) 5, 241–344.
REPÉRANT, J. (1975) Nouvelles données sur les projections rétiniennes chez Caiman sclerops. Etude radioautographique. Comptes Rendus de l'Academie des Sciences (Paris) 280, 2881–2884.
REPÉRANT, J. & RIO, J. P. (1976) Retinal projections in Vipera aspis. A reinvestigation using light radioautographic and electron microscopic degeneration techniques. Brain Research 107, 603–609.
REPÉRANT, J., RIO, J. P., MICELI, D. & LEMIRE, M. (1978) A radioautographic study of retinal projections in type I and type II lizards. Brain Research 142, 401–411.
ROBLES, C. (1995) Estudio comparado de la subdivisión quimioarquitectónica del complejo toral del mesencéfalo en el pollo y en la Tarentola mauretanica. Ph.D. dissertation, Universidad de Murcia, Murcia, Spain.
RöTHIG, P. (1923) Beiträge zum Studien des Zentralnervensystems der Wirbeltiere. 8. über das Zwischenhirn der Amphibien. Archiv für Mikroskopische Anatomie 98, 616–645.
RUBENSTEIN, J. L. R. & PUELLES, L. (1994) Homeobox gene expression during development of the vertebrate brain. Current Topics in Developmental Biology 29, 1–63.
SCHWAB, M. E. (1979) Variation in the rhombencephalon. In Biology of the Reptilia, Vol. 10: Neurology B (edited by GANS, C., NORTHCUTT R, G. & ULINSKI, P. S.) pp. 201–246. London: Academic Press.
SCHWAB, M. E. (1979) Variations in the rombencephalon. In Biology of the Reptilia, Vol. 10: Neurology B (edited by GANS, G. C., NORTHCUTT, R. G. & ULINSKI, P. S.) pp. 201–246. London: Academic Press.
SENN, D. G. (1968) Bau und Ontogenese von Zwischen-und Mittelhirn bei Lacerta sicula (Rafinesque). Acta Anatomica 71, 1–150.
SENN, D. G. (1970) The stratification in the reptilian central nervous system. Acta Anatomica 75, 521–552.
SENN, D. G. (1979) Embryonic development of the central nervous system. In Biology of the Reptilia, Vol. 9: Neurology A (edited by GANS, C., NORTHCUTT, R. G. & ULINSKI, P. S.) pp. 173–244. London: Academic Press.
SERENO, M. I. (1985) Tectoreticular pathways in the turtle, Pseudemys scripta. I. Morphology of tectoreticular axons. Journal of Comparative Neurology 233, 48–90.
SERENO, M. I. & ULINSKI, P. S. (1987) Caudal topographic nucleus isthmi and the rostral nontropographic nucleus isthmi in the turtle, Pseudemys scripta. Journal of Comparative Neurology 261, 319–346.
SHIMAMURA, K., HARTIGAN, D. J., MARTÍNEZ, S., PUELLES, L. & RUBENSTEIN, J. R (1995) Longitudinal organization of the anterior neural plate and neural tube. Development 121, 3923–3933.
SMEETS, W. J. A. J. (1994) Catecholamine systems in the CNS of reptiles: Structure and functional correlations. In Phylogeny and Development of Catecholamine Systems in the CNS of Vertebrates (edited by SMEETS, W. J. A. J. & REINER, A.) Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 103–133.
SMEETS, W. J. A. J., HOOGLAND, P. V. & LOHMAN, A. H. M. (1986a) A forebrain atlas of the lizard Gekko gecko. Journal of Comparative Neurology 254, 1–19.
SMEETS, W. J. A. J., HOOGLAND, P. V. & VOORN, P. (1986b) The distribution of dopamine immunoreactivity in the forebrain and midbrain of the lizard Gekko gecko: An immunohistochemical study with antibodies against dopamine. Journal of Comparative Neurology 253, 46–60.
STOKES, T. M., LEONARD, C. M. & NOTTEBOHM, F. (1974) The telencephalon, diencephalon and mesencephalon of the canary, Serinus canaria, in stereotaxic coordinates. Journal of Comparative Neurology 156, 337–374.
STOYKOVA, A., FRITSCH, R., WALTHER, C. & GRUSS, P. (1996) Forebrain patterning defects in Small eye mutant mice. Development 122, 3453–3465.
TANABE, Y., ROELINK, H. & JESSEL, T. M. (1995) Induction of motor neurons by sonic hedgehog is independent of floor plate differentiation. Current Biology 5, 651–658.
TEITELMAN, G., JAEGER, C. B., ALBERT, U., JOHN, T. H. & REIS, D. J. (1983) Expression of amino acid decarboxylase in proliferating cells of the neural tube and notochord of developing rat embryo. Journal of Neuroscience 3, 1379–1388.
TEN DONKELAAR, H. J. (1998) Reptiles. In The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates, Vol. 2 (edited by NIEUWENHUYS, R., TEN DONKELAAR, H. J. & NICHOLSON, C.) pp. 1315–1524. Berlin: Springer.
TEN DONKELAAR, H. J. & NIEUWENHUYS, R. (1979) The brainstem. In Biology of the Reptilia, Vol. 10: Neurology B (edited by GANS, G. C., NORTHCUTT, R. G. & ULINSKI, P. S.) pp. 133–200. London: Academic Press.
TEN DONKELAAR, H. J., BANGMA, G. C., BARBASHENRY, H. A., DE BOER-VAN HUIZEN, R. & WOLTERS, J. G. (1987) The brain stem in a lizard, Varanus exanthematicus. Journal of Comparative Neurology 107, 1–167.
VAAGE, S. (1969) The segmentation of the primitive neural tube in chick embryos (Gallus domesticus) Ergebnisse der Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte 41, 1–88.
VAAGE, S. (1973) The histogenesis of the isthmic nuclei in chick embryos (Gallus domesticus). I. A morphological study. Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeshichte 142, 283–314.
VOOGD, J., NIEUWENHUYS, R., VAN DONGEN, P. A. M. & TEN DONKELAAR H. J. (1998) Mammals. In The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates, Vol. 3. (edited by NIEUWENHUYS, R., TEN DONKELAAR H. J. & NICHOLSON, C.) pp. 1637–2097. Berlin: Springer.
WALLACE, J. A. (1982) Monoamines in the early chick embryo. Demonstration of serotonin synthesis and the regional distribution of serotonin-concentrating cells during morphogenesis. American Journal of Anatomy 165, 261–276.
WANG, S.-R., YAN, K., WANG, Y.-T., JIANG, S.-Y. & WANG, X.-S. (1983) Neuroanatomy and electrophysiology of the lacertidian nucleus isthmi. Brain Research 275, 355–360.
WARREN, N. & PRICE, D. J. (1997) Roles of Pax-6 in murine diencephalic development. Development 124, 1573–1582.
WELKER, E., HOOGLAND, P. V. & LOHMAN, A. H. M. (1983) Tectal connections in Python reticulatus. Journal of Comparative Neurology 220, 347–354.
WOLTERS, J. G., TEN DONKELAAR, H. J. & DE BOER-VAN HUIZEN, R. (1985) The cell masses in the brain stem and caudal diencephalon of the lizard Varanus exanthematicus. Ch. 1. In On the Anatomy of Descending Pathways from the Brain Stem to the Spinal Cord in a Lizard, Varanus exanthematicus (edited by WOLTERS, J. G.); Ph.D. dissertation, University of Nijmegen. The Netherlands, pp. 17–41.
YAMADA, T., PFAFF, S. L., EDLUND, T. & JESSEL, T. M. (1993) Control and cell pattern in the neural tube: Motor neuron induction by diffusible factors from notochord and floor plate. Cell 73, 673–686.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz, C., Yanes, C., Trujillo, CM. et al. Cytoarchitectonic subdivisions in the subtectal midbrain of the lizard Gallotia galloti. J Neurocytol 29, 569–593 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011067918585
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011067918585