Abstract
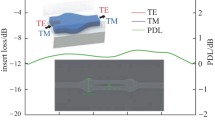
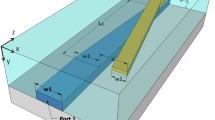
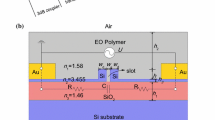
Passing across an abrupt junction from a thick vertically bimodal waveguide to a thinner single mode segment, guided light can undergo complete destructive interference, provided that the geometry and the phases of the modes in the initial segment are properly adjusted. We propose to employ this effect to realize a simple polarizer configuration, using a strip that is etched from a planar waveguide. A beam of light is made to pass the strip perpendicularly. The light enters from the single mode waveguide outside the strip into the strip segment, which is configured to support two modes. At the end of the strip, apart from reflections, the amount of power that is guided in the following lower segment depends on the local phases of the two modes. These phases are different for TE and TM light, hence we may expect a polarization dependent power transfer, resulting in polarizer performance for a properly selected geometry. The paper describes in detail the modeling of the device in terms of rigorous mode expansion. Design guidelines and tolerance requirements for geometric and material parameters are discussed. For typical Si3N4/SiO2 materials, our calculations predict a peak performance of 34 dB polarization discrimination and 0.3 dB insertion loss for a device with a total length of about 12 μm that selects TE polarization at a wavelength of 1.3 μm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bersiner, L., U. Hempelmann and E. Strake. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 8 422, 1991.
Bloemer, M.J. and J.W. Haus. Opt. Lett. 17 598, 1992a.
Bloemer, M.J. and J.W. Haus. Appl. Phys. Lett. 61 1619, 1992b.
Bloemer, M.J. and J.W. Haus. J. Lightwave Technol. 14 1534, 1996.
Brooke, G.H. and M.M.Z. Kharadly. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. MTT-30 760, 1982.
Findakly, T., B. Chen and D. Booher. Opt. Lett. 8 641, 1983.
Han, K.G., D.H. Kim, J.C. Jo and S.S. Choi. Opt. Lett. 16 1086, 1991.
Han, K.G., S. Kim and S.S. Choi. Opt. Lett. 15 108, 1990.
Hempelmann, U., H. Herrmann, G. Mrozynski, V. Reimann and W. Sohler. J. Lightwave Technol. 13 1750, 1995.
Johnstone, W., G. Stewart, T. Hart and B. Culshaw. J. Lightwave Technol. 8 538, 1990.
Lee, S.S., S. Garner, W.H. Steier and S.Y. Shin. Appl. Opt. 38 530, 1999.
Lohmeyer, M., N. Bahlmann and P. Hertel. Opt. Commun. 163 86, 1999a.
Lohmeyer, M., N. Bahlmann, O. Zhuromskyy and P. Hertel. Opt. Quantum Electr. 31 877, 1999b.
Nakano, T., K. Baba and M. Miyagi. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 11 2030, 1994.
Oh, M.-C., S.-Y. Shin, W.-Y. Hwang and J.-J. Kim. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 8 375, 1996.
Pérez, C.S., A. Morand, P. Benech, S. Tedjini, D. Bosc and A. Rousseau. Low cost integrated optical polarizer with an hybrid structure of birefringent polymer and ion-exchanged glass waveguide. In: Integrated Optics Devices III, eds. G.C. Righini and S.I. Najafi. SPIE Proceedings, Vol. 3620, p. 118, 1999.
Saini, M., E.K. Sharma and M. Singh. Opt. Lett. 20 365, 1995.
Shani, Y., C.H. Henry, R.C. Kistler and K.J. Orlowsky. Appl. Opt. 29 337, 1990.
Sletten, M.A. and S.R. Seshadri. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 7 1174, 1990.
Stoffer, R., H.J.W.M. Hoekstra, R.M. de Ridder, E. van Groesen and F.P.H. van Beckum. Opt. Quantum Electr. 32 947, 2000.
Sztefka, G. and H.P. Nolting. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 5 554, 1993.
Taflove, A. Computational Electrodynamics: The Finite Difference Time Domain Method. Norwood, MA, USA: Artech House Inc., 1995.
Thyagarajan, K., S. Diggavi, A.K. Ghatak, W. Johnstone, G. Stewart and B. Culshaw. Opt. Lett. 15 1041, 1990.
Thyagarajan, K. and S. Pilevar. J. Lightwave Technol. 10 1334, 1992.
Thyagarajan, K., S.D. Seshadri and A.K. Ghatak. J. Lightwave Technol. 9 315, 1991.
Trutschel, U., F. Ouelette, V. Delisle, M.A. Duguay, G. Fogarty and F. Lederer. J. Lightwave Technol. 13 239, 1995.
Vassallo, C. Optical Waveguide Concepts. Amsterdam, Elsevier, 1991.
Veasey, D.L., R.K. Hickernell, D.R. Larson and T.E. Batchman. Opt. Lett. 16 717, 1991.
Veasey, D.L., D.R. Larson and I. Veigl. Appl. Opt. 33 1242, 1994.
Willems, J., J. Haes and R. Baets. Opt. Quantum Electr. 27 995, 1995.
Wörhoff, K., P.V. Lambeck, H. Albers, O.F.J. Noordman, N.F. van Hulst and T.J.A. Popma. Optimization of LPCVD Silicon Oxynitride growth to large refractive index homogeneity and layer thickness uniformity. In: Micro-optical Technologies for Measurement, Sensors, and Microsystems II, eds. O.M. Parriaux, E.B. Kley, B. Culshaw and M. Breidne, SPIE Proceedings, Vol. 3099, p. 257, 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lohmeyer, M., Stoffer, R. Integrated optical cross strip polarizer concept. Optical and Quantum Electronics 33, 413–431 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010894801196
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010894801196