Abstract
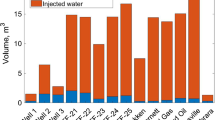
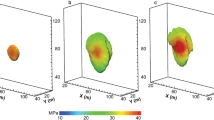
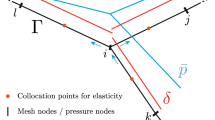
In this paper, we model water injection through a growing vertical hydrofracture penetrating a low-permeability reservoir. The results are useful in oilfield waterflood applications and in liquid waste disposal through reinjection. Using Duhamel's principle, we extend the Gordeyev and Entov (1997) self-similar 2D solution of pressure diffusion from a growing fracture to the case of variable injection pressure. The flow of water injected into a low-permeability rock is almost perpendicular to the fracture for a time sufficiently long to be of practical interest. We revisit Carter's model of 1D fluid injection (Howard and Fast, 1957) and extend it to the case of variable injection pressure. We express the cumulative injection through the injection pressure and effective fracture area. Maintaining fluid injection above a reasonable minimal value leads inevitably to fracture growth regardless of the injector design and the injection policy. The average rate of fracture growth can be predicted from early injection. A smart injection controller that can prevent rapid fracture growth is needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barenblatt, G. I.: 1959a, Concerning equilibrium cracks forming during brittle fracture. The stability of isolated cracks. Relationships with energetic theories, J. Appl. Math. Mech. 23(5), 1273-1282.
Barenblatt, G. I.: 1959b, Equilibrium cracks formed during brittle fracture. rectilinear cracks in plane plates. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 23(4), 1009-1029.
Barenblatt, G. I.: 1959c, The Formation of equilibrium cracks during brittle fracture. General ideas and hypotheses. Axially-symmetric cracks, J. Appl. Math. Mech. 23(3), 622-636.
Barenblatt, G. I.: 1961, On the finiteness of stresses at the leading edge of an arbitrary crack, J. Appl. Math. Mech. 25(4), 1112-1115.
Biot, M. A.: 1956, Theory of deformation of a porous viscoplastic anisotropic solid, J. Appl. Phys. 27, 459-467.
Biot, M. A.: 1972, Mechanics of finite deformation of porous solids, Indiana Uni. Math. J. 21, 597-620.
Carslaw, J. C. and Jaeger, J. C.: 1959, Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd edn, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
De, A. and Patzek, T.W.: 1999, Waterflood Analyzer, MatLab Software Package, Version, Lawrence Berkley National Lab, Berkeley, CA.
Gordeyev, Y. N. and Entov, V. M.: 1997, The pressure distribution around a growing crack, J. Appl. Maths. Mechs. 51(6), 1025-1029.
Gordeyev, Y. N. and Zazovsky, A. F.: 1992, Self-similar solution for deep-penetrating hydraulic fracture propagation, Transport in Porous Media 7, 283-304.
Hagoort, J., Weatherill, B. D. and Settari, A.: 1980, Modeling the propagation of waterflood-induced hydraulic fractures, SPEJ 8, 293-303.
Howard, G. C. and Fast, C. R.: 1957, Optimum fluid characteristics for fracture extension, Drill. Prod. Prac. API 261-270.
Ilderton, D., Patzek, T. E. et al.: 1996, Microseismic imaging of hydrofractures in the diatomite, SPE Form. Eval. 3, 46-54.
Koning, E. J. L.: 1985, Fractured water injection wells — analytical modeling of fracture propagation, SPE 14684, 1-27.
Kovscek, A. R., Johnston, R. M. and Patzek, T.W.: 1996a, Interpretation of hydrofracture geometry—During steam injection using temperature transients, I. Asymmetric hydrofractures, In Situ 20(3), 251-289.
Kovscek, A. R., Johnston, R. M. and Patzek, T. W.: 1996b, Interpretation of hydrofracture geometry during steam injection using temperature transients, II. Asymmetric hydrofractures, In Situ 20(3), 289-309.
Kuo, M. C. T., Hanson, H. G. and DesBrisay, C. L.: 1984, Prediction of fracture extension during waterflood, Paper SPE 12769, (Long Beach, (SPE)), 377-385.
Muskat, M.: 1946, The Flow of Homogeneous Fluids through Porous Media, J. W. Edwards, Ann Arbor, MI.
Ovens, J. E. V., Larsen, F. P. and Cowie, D. R.: 1998, Making sense of water injection fractures in the Dan field, SPE Reser. Eval. Engng 1(6), 556-566.
Patzek, T.W.: 1992, Surveillance of South Belridge Diatomite, SPE Western Regional Meeting Paper SPE 24040, SPE, Bakersfield.
Patzek, T. W.: 2000, Verification of a complete pore network model of drainage and imbibition, Twelfth SPE/DOE Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, SPE Paper 59312, Tulsa, SPE, OK; SPEJ, July 2001.
Patzek, T. W. and Silin, D. B.: 1998, Fluid injection into a low-permeability rock — 1. Hydrofrature growth, SPE/DOE Eleventh Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, SPE, Tulsa, Oklahoma.
Rapoport, L. A. and Leas, W. J.: 1953, Properties of linear waterfloods, Trans. AIME 216, 139-148.
Tikhonov, A. N. and Samarskii, A. A.: 1963, Equations of Mathematical Physics. International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Mathematics, Vol 39, Macmillan, New York.
Valko, P. and Economides, M. J.: 1995, Hydraulic Fracture Mechanics, Wiley, New York.
Vinegar, H. J. et al.: 1995, Active and passive seismic imaging of a hydraulic fracture in the diatomite, J. Petrol. Tech., 44, 28.
Warpinski, N. R.: 1996, Hydraulic fracture diagnostics, J. Petrol. Tech. 10.
Wright, C. A. and Conant, R. A.: 1995, Hydraulic fracture reorientation in primary and secondary recovery from low-permeability reservoirs, SPE Annual Technical Conference & Exhibition, SPE 30484, Dallas, TX.
Wright, C. A., Davis, E. J. et al.: 1997, Horizontal hydraulic fractures: Oddball occurrances or practical engineering concern? SPE Western Regional Meeting, SPE 38324, Long Beach, CA.
Zheltov, Y. P. and Khristianovich, S. A.: 1955, On hydraulic fracturing of an oil-bearing stratum, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR. Otdel Tekhn. Nuk 5, 3-41.
Zwahlen, E. D. and Patzek, T.W.: 1997a, Linear transient flow solution for primary oil recovery with infill and conversion to water injection, In Situ 21(4), 297-331.
Zwahlen, E. D. and Patzek, T.W.: 1997b, Linear transient flow solution for primary oil recovery with infill and conversion to water injection, 1997 SPE Western Regional Meeting, SPE 38280, SPE, Long Beach.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patzek, T.W., Silin, D.B. Water Injection into a Low-Permeability Rock - 1 Hydrofracture Growth. Transport in Porous Media 43, 537–555 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010689016442
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010689016442