Abstract
Background: The results of animal studies suggest that superselective intra-arterial infusion allows the permeation of a high concentration of chemotherapeutic agents within intracranial neoplasms. In the present report, we review our clinical experience with the 100 intra-arterial infusions of carboplatin in intracranial neoplasms not responsive to other treatment modalities.
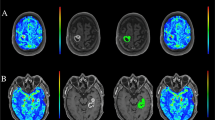
Methods: Carboplatin was infused in 100 separate sessions (24 patients) as a mean dose of 286 ± 60 mg/m2 (range 34–377 mg/m2). RMP-7, a bradykinin analog, was used as an adjunct in 28 sessions (6 patients). The infusions were performed through superselective microcatheterization of the following arteries: internal carotid (n = 39), middle cerebral (n = 61), posterior cerebral (n = 21) and anterior cerebral (n = 10). The frequency of neurological and non-neurological complications, and survival were recorded. In a subset of 10 patients, tumor volume was measured by serial magnetic resonance images to assess therapeutic response to therapy.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 44.5 years (range 26–67 years); 13 were men. The tumors were classified as glioblastoma multiforme (n = 12), metastatic tumor (n = 1), high-grade astrocytoma (n = 6), and anaplastic mixed glioma (n = 5). Follow-up was available for 23 patients (mean 22 months, range 2–69 months). Survival beyond 1 year after initiation of intra-arterial carboplatin therapy was documented in 12 of the 23 patients. A total of 13 neurological complications including seizures (n = 7), transient neurological deficits (n = 5), and ischemic stroke (n = 1) were observed in 100 procedures. A lower frequency of complications occurred in men and in patients who received adjunctive RMP-7. Volumetric analysis of serial magnetic resonance images demonstrated tumor mass reduction in 3 out of 10 patients. An increase in tumor mass ranging from 23% to 230% was observed in the other 7 patients over a period ranging from 2.3 to 37.7 months since initiation of carboplatin therapy.
Conclusions: Superselective intra-arterial administration of carboplatin appears feasible and was associated with predominantly transient neurological complications. The addition of RMP-7 to carboplatin therapy appears to be at least as safe as the administration of carboplatin alone and requires further investigation as a means of chemotherapeutic dose intensification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakashima M, Shibata S, Tokunaga Y, Fujita H, Anda T, Arizono K, Tomiyama N, Sasaki H, Ichikawa M: In-vivo microdialysis study of the distribution of cisplatin into brain tumour tissue after intracarotid infusion in rats with 9L malignant glioma. J Pharm Pharmacol 49: 777–780, 1997
Takeda N, Diksic M: Relationship between drug delivery and the intra-arterial infusion rate of SarCNU in C6 rat brain tumor model. J Neuro-Oncol 41: 235–246, 1999
Defer G, Fauchon F, Schaison M, Chiras J, Brunet P: Visual toxicity following intra-arterial chemotherapy with hydroxyethyl-CNU in patients with malignant gliomas. A prospective study with statistical analysis. Neuroradiology 33: 432–437, 1991
Shapiro WR, Green SB, Burger PC, Selker RG, VanGilder JC, Robertson JT, Mealey J Jr, Ransohff J, Mahaley MS Jr: A randomized comparison of intra-arterial versus intravenous BCNU, with or without intravenous 5-fluorouracil, for newly diagnosed patients with malignant glioma. J Neurosurg 76: 772–781, 1992
Stewart DJ, Grahovac Z, Russel NA, Hugenholtz H, Gupta S, Benoit BC, Richard MT, Maroun JA, Hopkins HS, Locke L: Phase I study of intracarotid PCNU. J Neuro-Oncol 5: 245–250, 1987
Maiese K, Walker RW, Gargan R, Victor JD: Intra-arterial cisplatin – associated optic and otic toxicity. Arch Neurol 49: 83–86, 1992
Tfayli A, Hentschel P, Madajewicz S, Manzione J, Chowhan N, Davis R, Roche P, Iliya A, Roque C, Meek A, Shady M: Toxicities related to intraarterial infusion of 158 cisplatin and etoposide in patients with brain tumors. J Neuro-Oncol 42: 73–77, 1999
Newton HB, Page MA, Junck L, Greenberg HS: Intraarterial cisplatin for the treatment of malignant gliomas. J Neuro-Oncol 7: 39–45, 1989
Stewart DJ, Wallace S, Feun L, Leavens M, Young SE, Handel S, Mavligit G, Benjamin RS: A phase I study of intracarotid artery infusion of cisdiamminedichloroplatinum(II) in patients with recurrent malignant intracerebral tumors. Cancer Res 42: 2059–2062, 1982
Go RS, Adjei AA: Review of the comparative pharmacology and clinical activity of cisplatin and carboplatin. J Clin Oncol 17: 409–422, 1999
Murry DJ: Comparative clinical pharmacology of cisplatin and carboplatin. Pharmacotherapy 17: 140S–145S, 1997
Ruckdeschel JC: The future role of carboplatin. Semin Oncol 21: 114–118, 1994
Alberts DS: Carboplatin versus cisplatin in ovarian cancer. Semin Oncol 22: 88–90, 1995
Cloughesy TF, Gobin YP, Black KL, Vinuela F, Taft F, Kadkhoda B, Kabbinavar F: Intra-arterial carboplatin chemotherapy for brain tumors: a dose escalation study based on cerebral blood flow. J Neuro-Oncol 35: 121–131, 1997
Follezou JY, Fauchon F, Chiras J: Intraarterial infusion of carboplatin in the treatment of malignant gliomas: a phase II study. Neoplasma 36: 349–352, 1989
Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M, Winkler A: Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer 47: 207–214, 1981
Stewart DJ, Belanger JM, Grahovac Z, Curuvija S, Gionet LR, Aitken SE, Hugenholtz H, Benoit BG, DaSilva VF: Phase I study of intracarotid administration of carboplatin. Neurosurgery 30: 512–516, 1992
Bonstelle CT, Kori SH, Rekate H: Intracarotid chemotherapy of glioblastoma after induced blood–brain barrier disruption. Am J Neuroradiol 4: 810–812, 1983
Fenstermacher J, Gazendam J: Intra-arterial infusions of drugs and hyperosmotic solutions asways of enhancingCNS chemotherapy. Cancer Treat Rep 65 (Suppl 2): 27–37, 1981
Inamura T, Nomura T, Bartus RT, Black KL: Intracarotid infusion of RMP-7, a bradykinin analog: a method for selective drug delivery to brain tumors. J Neurosurg 81: 752–758, 1994
Matsukado K, Inamura T, Nakano S, Fukui M, Bartus RT, Black KL: Enhanced tumor uptake of carboplatin and survival in glioma-bearing rats by intracarotid infusion of bradykinin analog, RMP-7. Neurosurgery 39: 125–133, 1996
Cloughesy TF, Black KL, Gobin YP, Farahani K, Nelson G, Villablanca P, Kabbinavar F, Vineula F, Wortel CH: Intraarterial Cereport (RMP-7) and carboplatin: a dose escalation study for recurrent malignant gliomas. Neurosurgery 44: 270–278, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qureshi, A.I., Fareed, M., Suri, K. et al. Superselective Intra-arterial Carboplatin for Treatment of Intracranial Neoplasms: Experience in 100 Procedures. J Neurooncol 51, 151–158 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010683128853
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010683128853