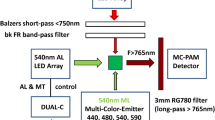
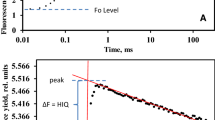
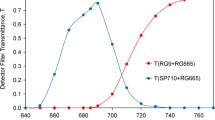
Abstract
Fluorescence clamp (FC) is a method of directly measuring the fluxes out of Photosystem II antenna. This is achieved by a feed-back loop which controls the light intensity of light emitting diodes in order to keep the amplitude of modulated chlorophyll fluorescence constant, and by taking the intensity or the current fed into the light emitting diodes as a measure of the fluxes. Saturating flashes serve to distinguish between fluxes into thermal deactivation and into the photosynthetic electron transfer chain (ETC). As FC is only active in the light period of the measuring light, the background signal (induced by actinic light) is compensated by a second feed-back loop in the dark period of the measuring light. Equations are provided for the interpretation of the FC signals. This includes the quenching parameters of chlorophyll fluorescence, the flux into the electron transfer chain and the redox state of QA. Experiments are presented which show that traditional fluorescence (LC) and FC measurements yield the same results. However, the FC method provides a better presentation of fluxes as the scaling factor (flux/signal) is constant for all states of Photosystem II. This leads to a simpler analysis of quenching mechanisms. Examples are given which show that the co-existing quenching mechanisms with different effects on photochemical and non-photochemical fluxes can be better identified by FC rather than by LC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bode HW (1964) Network Analysis and Feedback Amplifier Design. Von Nordstrand Comp, New York
Bilger W and Schreiber U (1986) Energy-dependent quenching of dark-level fluorescence in intact leaves. Photosynth Res 10: 303–308
Braun G, Driesenaar ARJ, Shalgi E and Malkin S (1992) Manipulation of the imbalance for linear electron flow activities between Photosystems I and II of photosynthesis by cyclic electron flow cofactors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1099: 57–66
Bruce D, Samson G and Carpenter C (1997) The origins of non-photochemical quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence in photosynthesis. Direct quenching by P680+ in Photosystem II enriched membranes at low pH. Biochemistry 36: 749–755
Dau H (1994) Molecular mechanisms and quantitative models of variable Photosystem II fluorescence. Photochem Photobiol 60: 1–23
Dau H (1998) Chlorophyll fluorescence measurements for assessment of primary production in aquatic ecosystems — the basics. Rostock Meeresbiol Beitr 6: 23–40
Dau H and Hansen UP (1988) The involvement of spillover changes in state 1-state 2 transitions in intact leaves at low light intensities. Biochim Biophys Acta 934: 156–159
Dau H and Hansen UP (1990) A study of the energy dependent quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence by means of photoacoustic measurements. Photosynth Res 25: 269–278
Genty B, Briantais J-M and Baker NR (1989) The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochim Biophys Acta 990: 87–92
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B and Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391: 85–100
Hansen UP, Dau H, Brüning B, Fritsch T and Moldaenke C (1991) Linear analysis applied to the comparative study of the I-D-P phase chlorophyll fluorescence as induced by actinic PS-II light, PS-I light and changes in CO2-concentration. Photosynth Res 28: 119–130
Hansen U-P, Moldaenke C, Tabrizi H and Ramm D (1993) The effect of transthylakoid proton uptake on cytosolic pH and the imbalance of ATP and NAPDH/H+ production as measured by CO2-and light-induced depolarisation of the plasmalemma. Plant Cell Physiol 34: 681–695
Havaux M, Strasser RJ and Greppin H (1991) A theoretical and experimental analysis of the qp and qN coefficients of chlorophyll fluorescence quenching and their relation to photochemical and nonphotochemical events. Photosynth Res 27: 41–55
Horton P (1996) Nonphotochemical quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. In: Jenings et al (eds) Light as a Source and Information Carrier in Plant Physiology, pp 99–111. Plenum Press, New York
Lavorel J and Joliot P (1972) A connected model of the photosynthetic unit. Biophys J 12: 815–831
Marmont G (1949) Studies on the axon membrane. J Cell Comp Physiol 34: 351–382
Moldaenke C, Vanselow KH and Hansen UP (1995) The 1-Hz-Fluorometer: A new approach to fast and sensitive long-term studies of algal density and environmental influences. Helgolander Meeresuntersuchungen 49: 785–796
Schreiber U and Krieger A (1996) Two fundamentally different types of variable chlorophyll fluorescence in vivo. FEBS Lett 397: 131–135
Schreiber U, Schliwa U and Bilger W (1986) Continuous recording of photochemical and non-photochemical chlorophyll fluorescence quenching with a new type of modulation fluorometer. Photosynth Res 10: 51–62
Tabrizi H, Schinner K, Spors J and Hansen UP 1998 Deconvolution of the three components of the photoacoustic signal by curve fitting and the relationship of CO2 uptake to proton fluxes. Photosynth Res 57: 101–115
Thiel G (1995) Dynamics of chloride and potassium currents during the action potential in Chara studied with action potential clamp. Eur Biophys J 24: 85–92
Van Kooten O and Snel JFH (1990) The use of chlorophyll fluorescence in plant stress physiology. Photosynth Res 25: 147–150
Voorthuysen TV, Bulychev AA, Dassen HHA, Snel JFH and Vredenberg WJ (1996) Suppression of flash-induced PS II-dependent electrogenesis caused by proton pumping in chloroplasts. Physiol Plant 98: 156–164
Walters RG and Horton P (1993) Theoretical assessment of alternative mechanisms for non-photochemical quenching of PS II fluorescence in barley leaves. Photosynth Res 36: 119–139
Zhu Z., Gerendás J, Bendixen R, Schinner K, Tabrizi H, Sattelmacher B and Hansen UP 2000. Different tolerance to light stress in NO3 −-and NH4 +-grown Phaseolus vulgaris L., Plant Biol 2: 558–570
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schinner, K., Giannikos, I. & Hansen, UP. Fluorescence clamp: A direct measure of fluxes into and out of the antenna pool of Photosystem II. Photosynthesis Research 66, 109–123 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010660030547
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010660030547