Abstract
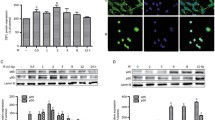
Malignant gliomas are highly resistant tumors against γ-irradiation and contained overexpression of p21WAF1/CIP1 (p21). Overexpression of p21 enhanced clonogenic survival and suppressed apoptosis after γ-irradiation in human brain tumor cell lines with or without p53 protein deficiency. The effect of antisense oligonucleotide to p21 against the γ-irradiation-induced apoptosis and cytotoxicity in malignant glioma cell lines was examined. Antennapedia homeodomain internalization peptide was used as an insertion vector. The high transfection efficiency of Antennapedia homeodomain internalization peptide joined with antisense oligonucleotide was observed. The pretreatment with antisense oligonucleotide enhanced the γ-irradiation-induced apoptosis and cytotoxicity in radioresistant glioma cells. p21 may represent an important new target for radiosensitization protocols, possibly involving antisense oligonucleotide directed against.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer E, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B: WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 75: 817–825, 1993
Chen YQ, Cipriano SC, Arenkiel JM, Miller F: Tumor suppression by p21WAF1. Cancer Res 55: 4536–4539, 1995
Luo Y, Hurwitz J, Massagu J: Cell-cycle inhibition by independent CDK and PCNA binding domains in p21 Cip1. Nature 375: 159–161, 1995
Waga S, Hannon GJ, Beach D, Stillman B: The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature 369: 574–578, 1994
Poluha W, Poluha DK, Chang B, Crosbie NE, Schonhoff CM, Kilpatrick DL, Ross AH: The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1 is required for survival of differentiating neuroblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 16: 1335–1341, 1996
Sheikh MS, Chen YQ, Smith ML, Fornance A: Role of p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1 in cell death and DNA repair as studied using a tetracycline-inducible system in p53-deficient cells. Oncogene 14: 1875–1882, 1997
McDonald III ER, Wu GS, Waldman T, El-Deiry S: Repair defect in p21WAF1/CIP1-/- human cancer cells. Cancer Res 56: 2250–2255, 1996
Bracey TS, Miller JC, Preece A, Paraskera C: γ-radiation-induced apoptosis in human colorectal adenoma and carcinoma cell lines can occur in the absence of wild type p53. Oncogene 10: 2391–2396, 1995
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Craig RW: Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res 51: 6304–6311, 1991
Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Tyler J, Jacks T, Housman DE: p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell 74: 957–967, 1993
Yount GL, Haas-Kogan DA, Vidair CA, Haas M, Dewey WC, Israel MA: Cell cycle synchrony unmasks the influence of p53 function on radiosensitivity of human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 56: 500–506, 1996
Waldman T, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B: Uncoupling of S phase and mitosis induced by anticancer agents in cells lacking p21. Nature 381: 713–716, 1996
Lu Y, Yamagishi N, Yagi T, Takebe H: Mutated p21WAF1/CIP1/SDI1 lacking CDK-inhibitory activity fails to prevent apoptosis in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncogene 16: 705–712, 1998
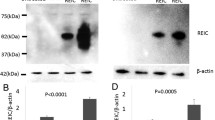
Kokunai T, Tamaki N: Relationship between expression of p21WAF1/CIP1 and radioresistance in human gliomas. Jap J Cancer Res 90: 638–646, 1999
Derossi D, Joliot AH, Chassaing G, Prochiantz A: The third helix of the Antennapedia homeodomain translocates through biological membranes. J Biol Chem 269: 10444–10450, 1994
Levine M, Rubin GM, Tjian R: Human DNA sequences homologous to a protein coding region conserved between homeotic genes of Drosophila. Cell 38: 663–673, 1984
Kokunai T, Sawa H, Tamaki N: Functional analysis of trk proto-oncogene product in medulloblastoma. Neurol Med Chir 36: 796–804, 1996
Kokunai T, Izawa I, Tamaki N: Overexpression of p21WAF1/CIP1 induces cell differentiation and growth inhibition in a human glioma cell line. Int J Cancer 75: 643–648, 1998
Van Meir EG, Kikuchi T, Tada M, Li H, Diserens A, Wojcik BE, Huang HS, Friedmann T, de Tribolet N, Cavenee WK: Analysis of the p53 gene and its expression in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 54: 649–652, 1994
Stewart N, Hicks GC, Paraskevas F, Mowat M: Evidence for a second cell cycle block at G2/M by p53. Oncogene 10: 109–115, 1995
MacPherson L, Montagnier I: Agar suspension culture for the selective assay of cells transformed by polyoma virus. Virology 23: 291–294, 1964
Hélène C, Toulmé JJ: Specific regulation of gene expression by antisense, sense and antigene nucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1049: 99–125, 1990
Wagner RW: Gene inhibition using antisense oligonucleotides. Nature 372: 333–335, 1994
Allinquant B, Hantraye P, Mailleux P, Moya K, Bouillot C, Prochiantz A: Downregulation of amyloid precursor protein inhibits neurite outgrowth in vitro. J Cell Biol 128: 919–927, 1995
Troy CM, Derossi D, Prochiantz A, Greene LA, Shelanski ML: Downregulation of Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase leads to cell death via the nitric oxide-peroxynitrite pathway. J Neurosci 16: 253–261, 1996
Milligan JJ, Matteucci MD, Martin JC: Current concepts in antisense drug design. J Med Chem 36: 1923–1937, 1993
Aigner L, Caroni P: Depletion of 43-kD growth-associated protein in primary sensory neurons leads to diminished formation and spreading of growth cones. J Cell Biol 123: 417–429, 1993
Ferreira A, Niclas J, Vale RD, Banker G, Kosik KS: Suppression of kinesin expression in cultured hippocampal neurons using antisense oligonucleotides. J Cell Biol 117: 595–606, 1992
Waldman T, Zhang Y, Dillehay L, Yu J, Kinzler K, Vogelstein B, Williams J: Cell-cycle arrest versus cell death in cancer therapy. Nature Med 3: 1034–1036, 1997
Schmidt EE, Ichimura K, Reifenberger G, Collins VP: CDKN2 (p16, MTS1) and gene deletion or CDK 4 amplification occurs in the majority of glioblastoma. Cancer Res 54: 6321–6324, 1994
Jung J-M, Bruner JM, Ruan S, Langford LA, Kyritsis AP, Kobayashi T, Kvein VA, Zang W: Increased levels of p21WAF1/CIP1in human brain tumors. Oncogene 11: 2021–2028, 1995
Deng C, Zhang P, Harper JW, Elledge SJ, Leder P: Mice lacking p21CIP1/WAF1undergo normal development, but are defective in G1 checkpoint control. Cell 82: 675–684, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kokunai, T., Urui, S., Tomita, H. et al. Overcoming of Radioresistance in Human Gliomas by p21WAF1/CIP1 Antisense Oligonucleotide. J Neurooncol 51, 111–119 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010645205169
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010645205169