Abstract
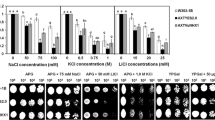
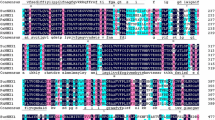
With a homologous gene region we successfully isolated a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from a halophytic plant, Atriplex gmelini, and named it AgNHX1. The isolated cDNA is 2607 bp in length and contains one open reading frame, which comprises 555 amino acid residues with a predicted molecular mass of 61.9 kDa. The amino acid sequence of the AgNHX1 gene showed more than 75% identity with those of the previously isolated NHX1 genes from glycophytes, Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa. The migration pattern of AgNHX1 was shown to correlate with H+-pyrophosphatase and not with P-type H+-ATPase, suggesting the localization of AgNHX1 in a vacuolar membrane. Induction of the AgNHX1 gene was observed by salt stress at both mRNA and protein levels. The expression of the AgNHX1 gene in the yeast mutant, which lacks the vacuolar-type Na+/H+ antiporter gene (NHX1) and has poor viability under the high-salt conditions, showed partial complementation of the NHX1 functions. These results suggest the important role of the AgNHX1 products for salt tolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Amtmann, A. and Sanders, D. 1999. Mechanisms of Na+ uptake by plant cells. Adv. Bot. Res. 29: 75–112.
Apse, M.P., Aharon, G.S., Snedden, W.A. and Blumwald, E. 1999. Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285: 1256–1258.
Barkla, B.J., Zingarelli, L., Blumwald, E. and Smith, J.A.C. 1995. Tonoplast Na+/H+ antiport activity and its energization by the vacuolar H+-ATPase in the halophytic plant Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. Plant Physiol. 109: 549–556.
Blum, A. 1993. The development of stress tolerant cultivars: from science to livelifood. In: T.J. Mabry, H.T. Nguyen, R.A. Dixon and M.S. Bonness (Eds.) Biotechnology for Aridland Plants, IC2 Institute, University of Texas, Austin, TX, pp. 1–10.
Blumwald, E. and Poole, R.T. 1985. Na+/H+ antiport in isolated tonoplast vesicles from storage tissue of Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 78: 163–167.
Bohnert, H.J., Nelson, D.E. and Jensen, R.G. 1995. Adaptation to environmental stresses. Plant Cell 7: 1099–1111.
Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principles of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Chomczynski, P. and Sacchi, N. 1987. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162: 156–159.
Counillon, L., Franchi, A. and Pouyssegur, J. 1993. A point mutation of the Na+/H+ exchanger gene (NHE1) and amplification of the mutated allele confer amiloride resistance upon chronic acidosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90: 4508–4512.
Dibrov, P. and Fliegel, L. 1998. Comparative molecular analysis of Na+/H+ exchangers: a unified model for Na+/H+ antiport? FEBS Lett. 424; 1–5.
Fukuda, A., Yazaki, Y., Ishikawa, T., Koike, S. and Tanaka, Y. 1998. Na+/H+ antiporter in tonoplast vesicles from rice roots. Plant Cell Physiol. 39: 196–201.
Fukuda, A., Nakamura, A. and Tanaka, Y. 1999. Molecular cloning and expression of the Na+/H+ exchanger gene in Oryza sativa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1446: 149–155.
Fukuda, Y., Ohme, M. and Shinshi, H. 1991. Gene structure and expression of a tobacco endochitinase gene in suspension-cultured cells. Plant Mol. Biol. 16: 1–10.
Garbarino, J. and DuPont, F.M. 1989. Rapid induction of Na+/H+ exchange activity in barley root tonoplast. Plant Physiol. 89: 1–4.
Gaxiola, R.A., Rao, R., 0Sherman, A., Grisafi, P., Alper, S.L. and Fink, G.R. 1999. The Arabiopsis thaliana proton transporters, AtNhx1 and Avp1, can function in cation detoxification in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 1480–1485.
Haro, R., Banuelos, M.A., Quintero, F.J., Rubio, F. and Rodriguez-Navarro, A. 1993. Genetic basis for sodium exclusion and sodium tolerance in yeast. A model for plants. Physiol. Plant 89: 868–874.
Hayakawa, T., Zhu, Y., Itoh, K., Kimura, Y., Izawa, T., Shimamoto, K. and Toriyama, S. 1992. Genetically engineered rice resistant to rice stripe virus, an insect-transmitted virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 9865–9869.
Kinoshita, T. and Shimazaki, K. 1999. Blue light activates the plasma membrane H+-ATPase by phosphorylation of the C-terminus in stomatal guard cells. EMBO J. 18: 5548–5558.
Matoh, T., Watanabe, J. and Takahashi, E. 1987. Sodium, potassium, chloride, and betaine concentrations in isolated vacuoles from salt-grown Atriplex gmelini leaves. Plant Physiol. 84: 173–177.
Mennen, H., Jacoby, B. and Marschner, H. 1990. Is sodium proton antiport ubiquitous in plant cells? J. Plant Physiol. 137: 180–183.
Nass, R., Cunningham, K.W. and Rao, R. 1997. Intracellular sequestration of sodium by a novel Na+/H+ exchanger in yeast is enhanced by mutations in the plasma membrane H+-ATPase: insights into mechanisms of sodium tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 26145–26152.
Nass, R. and Rao, R. 1998. Novel localization of a Na+/N+ exchanger in a late endosomal compartment of yeast: implications for vacuole biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 21054–21060.
Orlowski, J. and Grinstein, S. 1997. Na+/H+ exchangers of mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272; 22373–22376.
Prior, C., Potier, S., Souciet, J.L. and Sychrova, H. 1996. Characterization of the NHA1 gene encoding a Na+/H+-antiporter of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 387: 89–93.
Ratner, A. and Jacoby, B. 1976. Effect of K, its counter anion and pH on sodium efflux from barley roots. J. Exp. Bot. 27: 843–852.
Rausch, T., Kirsch, M., Low, R., Lehr, A., Viereck, R. and Zhigang, A. 1996. Salt stress responses of higher plants: the role of proton pumps and Na+/H+-antiporters. J. Plant Physiol. 148: 425–433.
Ros, R., Montesinos, C., Rimon, A., Padan, E. and Serrano, R. 1998. Altered Na+ and Li+ homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells expressing the bacterial cation antiporter NhaA. J. Bact. 180: 3131–3136.
Staal, M., Maathuis, F.J.M., Elzenga, J.T.M., Overbeek, J.H.M. and Prins, H.B.A. 1991. Na+/H+ antiport activity in tonoplast vesicles from roots of the salt-tolerant Plantago maritima and the salt-sensitive Plantago media. Physiol. Plant. 82: 179–184.
Takasu, A., Nakanishi, Y., Yamauchi, T. and Maeshima, M. 1997. Analysis of the substrate binding site and carboxyl terminal region of vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase of mung bean with peptide antibodies. J. Biochem. 122: 883–889.
Yun, C.H.C., Little, P.J., Nath, S.K., Levine, S.A., Pouyssegur, J., Tse, C.M. and Donowitz, M. 1993. Leu143 in the putative fourth membrane spanning domain is critical for amiloride inhibition of an epithelial Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-2). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 193: 532–539.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamada, A., Shono, M., Xia, T. et al. Isolation and characterization of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from the halophyte Atriplex gmelini. Plant Mol Biol 46, 35–42 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010603222673
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010603222673