Abstract
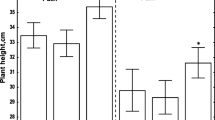
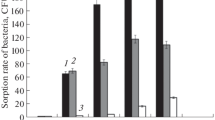
Changes in some physiological and biochemical characteristics of cabbage (cv. Slava) seedling roots in response to inoculation with the phytopathogen Xanthomonas campestrisand its surface and extracellular substances were evaluated. Seven days after the inoculation, the growth of the roots was slightly suppressed and they contained increased amounts of peroxidase. The effect of the lipopolysaccharides stripped from the cell surface or isolated from the culture liquid of X. campestriswas similar to that of the whole cells of the phytopathogen. The bacterial lectin isolated from the cell surface material did not induce any defense response in cabbage plants but, presumably, could play a role in the contact interactions between bacteria and plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kosenko, L.V., Kovalevskaya, T.M., Zakharova, I.Ya., Novikova, A.G., and Berestetskii, O.A., Interaction of the Legume Root-Nodule Bacterial Polysaccharides with the Host Plant Lectins, Mikrobiologiya, 1988, vol. 57, no. 4, pp. 675–679.
Nikitina, V.E., Alen'kina, S.A., Ponomareva, E.G., and Savenkova, N.N., Role of the Surface Lectins of Azospirillas in Interactions with the Wheat Roots, Mikrobiologiya, 1996, vol. 65, no. 2, pp. 165–170.
Grasser-Regallet, F., Scheftel, J.M., and Monteil, H., Isolation of Heat-Labile Enterotoxin Produced by a Human Strain of Escherichia coli by Wheat-Germ Agglutinin Affinity Chromatography, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1986, vol. 35, nos. 2-3, pp. 239–243.
Serra, T.M., Castresana, M.C., and Trjerina, G., Hemagglutinating Activity in Phytopathogenic Bacteria Surface Compounds, J. Basic Microbiol., 1987, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 147–153.
Holzworth, G. and Prestrige, E.B., Multistranded Helix in Xanthan Polysaccharide, Science, 1977, vol. 197, pp. 757–759.
Ramirez, M.E., Fucikovsky, L., Garcia-Jimenez, F., Quintero, R., and Galindo, E., Xanthan Gum Production by Altered Pathogenicity Variants of Xanthomonas campestris, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 1988, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 5–10.
Gvozdyak, R.I., Matyshevskaya, M.S., Grigor'eva, E.F., and Latvinchuk, O.A., Mikrobnyi polisakharid ksantan (The Microbial Polysaccharide Xanthan), Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1989.
Yakovleva, L.M., Role of Bacterial Glycopolymers in the Pathogenesis of Plant Bacterioses, Mikrobiol. Zh. (Kiev), 1992, vol. 54, no. 3, pp. 87–98.
Volk, W.A., Quantitative Assay of Polysaccharide Components Obtained from Cell Wall Lipopolysaccharides of Xanthomonas Species, J. Bacteriol., 1968, vol. 95, no. 3, pp. 980–982.
Shchegolev, S.Yu. and Khlebtsov, N.G., Primenenie mikro-i mini-EVM pri opredelenii parametrov dispersionnykh sistem spektroturbidimetricheskim metodom (Application of Computers in Spectro-and Turbidimetry), Saratov, 1984.
Laemmli, U.K., Cleavage of Structural Protein during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4, Nature, 1970, vol. 227, pp. 680–685.
Bradford, M., A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding, Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, no. 1, pp. 248–254.
Lutsik, M.D., Panasyuk, E.N., Antonyuk, V.A., and Lutsik, A.D., Metody poiska lektinov i opredeleniya ikh immunokhimicheskoi spetsifichnosti: Metodicheskie rekomendatsii dlya biokhimikov i immunologov (Methods for Analysis of Lectins and Determination of Their Immunochemical Specificity: Manual for Biochemists and Immunologists). L'viv: L'viv. Med. Inst., 1980.
Westphal, O. and Jann, K., Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides, Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry, Whistler, R.L. and Wolfrom, M.L., Eds., New York: Academic, 1962- 1965, vols. I-V. Translated under the title Metody khimii uglevodov, Moscow: Mir, 1967, pp. 325-332.
Konnova, S.A., Baberdina, I.V., Makarov, O.E., Skvortsov, I.M., and Ignatov, V.V., Polysaccharide-Lipid Complex on the Cell Surface and in the Culture Liquid of the S Variant of Azospirillum brasilense Sp7: Complex Degradation and Its Sugar Composition, Mikrobiol. Zh. (Kiev), 1990, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 40–46.
Rumshinskii, L.S., Matematicheskaya obrabotka rezul'tatov eksperimenta (Statistical Analysis of Experimental Results), Moscow: Nauka, 1971, p. 15.
Andreeva, V.A., Ferment peroksidaza: uchastie v zashchitnom mekhanizme rasteniya (Peroxidase: Involvement in the Defense Mechanisms of Plants), Moscow: Nauka, 1988.
Bukharov, A.V., Skvortsov, I.M., Ignatov, V.V., Shashkov, A.S., Knirel, Yu.A., and Dabrowski, J., Structure of O-Specific Polysaccharide of Xanthomonas campestris NCPPB 45 Lipopolysaccharide, Carbohydr. Res., 1993, vol. 241, pp. 309–316.
Zdorovenko, G.M., Extracellular Lipopolysaccharide of Gram-Negative Bacteria, Mikrobiol. Zh. (Kiev), 1988, vol. 50, no. 4, pp. 98–107.
Knirel', Yu.A. and Kochetkov, N.K., Structure of Gram-Negative Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides: General Characterization and the Structure of Lipid A, Biokhimiya, 1993, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 166–181.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stadnik, G.I., Kalashnikova, E.E., Konnova, S.A. et al. Role of the Surface and Extracellular Substances of the Phytopathogenic Bacterium Xanthomonas campestris in Its Interactions with Cabbage Plants. Microbiology 70, 228–231 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010493916899
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010493916899