Abstract
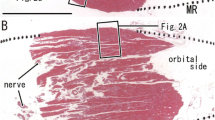
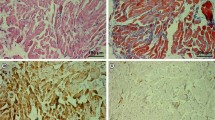
Myosin heavy chain (MHC) expression was determined immunohistochemically in individual muscle fibre types characterised by activities of ATPase and the key oxidative and glycolytic enzymes in rat ocular medial rectus (MR) muscles. In the global layer (GL), glycolytic activity of muscle fibres was higher and oxidative activity lower, than in the orbital layer (OL). Muscle fibres in the former displayed rosette-like organisation with a slow fibre surrounded by several fast fibres, which expressed either MHCIIa or MHCIIb, but many co-expressed both isoforms. In the OL some slow fibres co-expressed MHCIIa. Extraocular MHC isoform (MHCeom) could not be determined immunohistochemically and no pure MHCIIx/d containing fibres were found, suggesting that these isoforms, demonstrated electrophoretically, are co-expressed with others. Slow muscle fibres in both layers co-expressed MHCβ slow, MHCα cardiac and MHC-slow tonic. Neonatal isoform (MHCneo) was co-expressed in several fast and slow muscle fibres in the orbital, but not global layer. Slow fibres in the GL displayed very low oxidative activity. Electrophoretic analysis of ocular MR muscle homogenates revealed that about 50% of total MHC was MHCIIb, MHCeom was quite prominent (25%), and MHCIIa, MHCIIx/d and MHCI contributed each about 8%. MHCneo, MHCslow tonic and MHCα cardiac could not be identified as separate bands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asmussen G, Kiessling A and Wohlrab F (1971) Histochemische Charakterisierung der verschiedenen Muskelfasertypen in den a äusseren Augenmuskeln von Säugetieren. Acta Anat 79: 526–545.
Asmussen G (1979) Korrelation zwischen strukturellen und funktionellen Parametern der ausseren Augenmuskelfasern von Saugtieren. In: Drischel H and Kirmse W (eds). Das okulomotorische System. (pp. 156–178) Thieme, Leipzig.
Asmussen G, Traub I and Pette D (1993) Electrophoretic analysis of myosin heavy chain isoform patterns in extraocular muscles of the rat. FEBS Lett 335: 243–245.
Chiarandini DJ and Stefani E (1979) Electrophysiological identification of two types of fibers in rat extraocular muscles. J Physiol 290: 453–465.
Couly GF, Colty PM and Le Douarin NM (1992) The developmental fate of the cephalic mesoderm in quail-chick chimera. Development 114: 1–15.
Del Gaudio JM, Carroll WR, Sciote JJ and Esclamado RM (1995) A typical myosin heavy chain in rat laryngeal muscle. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 104: 237–245.
Demer JL, Oh SY and Poukens V (2000) Evidence for active control of rectus muscle pulleys. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41: 1280–1290.
Dubowitz V and Brooke MH (1985) Muscle biopsy–a practical approach. Bailliere Tindall, London.
Eržen I, Cvetko E, Obreza S and Angaut-Petit D (2000) Fibre types in the mouse levator auris longus muscle: a convenient preparation to study muscle and nerve plasticity. J Neurosci Res 59: 692–697.
Ezure K and Graf W (1984) A quantitative analysis of the spatial organization of the vestibulo-ocular reflexes in lateral and frontal-eyed animals. Neuroscience 12: 85–93.
Guth L and Samaha FJ (1970) Research note. Procedure for the histochemical demonstration of actomyosin ATPase. Experimental Neurology 28: 365–367.
Harker DW (1972) The structure and innervation of sheep superior rectus and levator palpebrae extraocular muscles. I Extrafusal muscle fibres. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 11: 956–969.
Jacoby J, Ko K, Weiss C and Rushbrook JI (1989) Systematic variation in myosin expression along extraocular muscle fibres of the adult rat. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 11: 25–40.
Jacoby J and Ko K (1993) Sarcoplasmic reticulum fast Ca2+ pump and myosin heavy chain expression in extraocular muscles. Invest Ophthalmol and Vis Sci 34: 2848–2858.
Kato T (1938) Ueber histologische Untersuchungen der Augenmuskeln von Menschen und Saugtieren. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 16: 131–145.
Kugler P (1991) Microphotometric determination of enzymes in brain section. Histochemistry 95: 579–583.
Lucas CA, Rughani A and Hoh JF (1995) Expression of extraocular myosin heavy chain in rabbit laryngeal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 16: 368–378.
Mayr R (1971) Structure and distribution of fiber types in the external eye muscles of the rat. Tissue Cell 3: 433–462.
McLoon LK, Rios L and Wirtschafter JD (1999) Complex three dimensional patterns of myosin isoform expression: differences between and within specific extraocular muscles. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 20: 771–783.
Morgan DL and Proske U (1984) Vertebrate slow muscle: its structure, pattern of innervation, and mechanical properties. Physiol Rev 64: 103–169.
Pachter BR (1982) Fiber composition of the superior rectus extraocular muscle of the Rhesus monkey. J Morphol 174: 237–250.
Pachter BR and Colbjù rnsen C (1983) Rat extraocular muscle I.Histochemical fibre types. J Anat 137: 161–170.
Pachter BR (1984) Rat extraocular muscle III. Histochemical variability along the length of multiply innervated fibers of the orbital surface layer. Histochemistry 80: 535–538.
Padykula HA and Herman E (1955) The specifity of the histochemical method for adenosine triphosphatase. J Histochem Cytochem 3: 170–195.
Peachey L (1971) The structure of the extraocular muscle fibers of mammals. In: Bach-Y-Rita P, Collins CC and Hyde JE (eds). The control of eye movements. (pp. 47–66) Academic Press, New York.
Pedrosa Domellőf F, Holmgren Y, Lucas A, Hoh JF and Thornell LE (2000) Human extraocular muscles: unique pattern of myosin heavy chain expression during myotube formation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41: 1608–1616.
Pernuš F, Bjelogrlič Z and Eržen I (1986) A computer aided method for muscle fibre type quantification. Acta Stereol 5: 49–54.
Pette D and Staron RS (1990) Cellular and molecular diversities of mammalian skeletal muscle fibers. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 116: 2–47.
Pette D and Staron RS (1997) Mammalian skeletal muscle fiber type transitions. Int Rev Cytol 170: 143–223.
Peuker H, Conjard A and Pette D (1998) α-Cardiac like myosin heavy chain as an inter-mediate between MHCIIa and MHCIβ in transforming rabbit muscle. Am Physiol Soc C595-C602.
Pilar G (1963) Further study of the electrical and mechanical responses of slow fibers in cat extraocular muscles. J Gen Physiol 50: 2289–3000.
Porter JD and Baker RS (1992) Prenatal morphogenesis of primate extraocular muscle: neuromuscular junction formation and fiber type differentiation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 33: 657–670.
Porter JD, Baker RS, Ragusa RJ and Brueckner JK (1995) Extraocular muscles: basic and clinical aspects of structure and function.Major review. Surv Ophthalmol 39: 451–484.
Reichmann H and Pette D (1991) Glycerophosphate oxidase succinate dehydrogenase activities in IIA and IIB fibres of mouse and rabit tibialis anterior muscles. Histochemistry 95: 429–433.
Reinach FC, Masaki T and Fischman DA (1983) Characterization of C protein from posterior latissimus dorsi muscle of the adult chicken. J Cell Biol 96: 297–300.
Ringel SP, Wilson WB, Barden MT and Kaiser KK (1978) Histo-chemistry of human extraocular muscle. Arch Ophthalmol 96: 1067–1072.
Rushbrook JI, Weiss C, Ko K, Feurman MH, Carleton S, Ing A and Jacoby J (1994) Identification of alpha cardiac myosin heavy chain mRNA and protein in extraocular muscle of the adult rabbit. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 15: 505–515.
Ruskell GL (1984) Spinal nerve endings in human extraocular muscles terminate in motor end plates. J Anat 139: 33–43.
Schiaffino S, Saggin I, Viel A et al (1986) Biochemical aspects of physical exercise. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Schiaffino S, Gorza L, Ausoni S, Bottinelli R, Reggiani C, Larson L, Edstrom L, Gundersen K and Lømo T (1990) Muscle fiber types expressing different myosin heavy chain isoforms. Their functional properties and adaptive capacity. In: Pette D (ed). The dynamic state of muscle fibers. (pp. 329–341) Walter de Gruyter & Co, Berlin-New York.
Spencer RF and Porter JD (1988) Innervation and structure of extraocular muscles in the monkey in comparison to those of the cat. J Comp Neurol 188: 649–653.
Spencer RF and Porter JD (1988) Structural organization of extraocular muscles. In: Buttner Ennever JA (ed.) Neuroanatomy of the oculomotor system. (pp. 33–79). Elsevier Science Publishers, New York.
Stirn Kranjc B and Vončina D (1990) Morphology and histochemistry of the human horizontal rectus eye muscles. Exp Eye Res 53 (Suppl VI): 120.
Stirn Kranjc B and Voncčina D (1992) Typisierung der horizontalen ausseren menschlichen Augenmuskeln. Spektrum Augenheilk 6: 114–118.
Talmadge RJ and Roy RR (1993) Electrophoretic separation of the rat skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain isoforms. J Appl Physiol 75: 2337–2340.
Wasicky R, Ziya-Ghazvini F, Blumer R, Lukas JR and Mayr R (2000) Muscle fiber types of human extraocular muscles: a histochemical and immunohistochemical study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41: 980–990.
Wieczorek DF, Periasamy M, Buttler Browne GS, Whalen RG and Nadal Ginard B (1985) Coexpression of multiple myosin heavy chain genes, in addition to tissue specific one, in extraocular muscle. J Cell Biol 101: 618–629.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kranjc, B.S., Sketelj, J., Albis, A.D. et al. Fibre types and Myosin heavy chain expression in the Ocular Medial Rectus Muscle of the Adult Rat. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 21, 753–761 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010362926221
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010362926221