Abstract
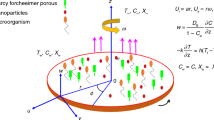
This paper considers, in the context of modeling the evolution of a protoplanetary cloud, the hydrodynamic aspects of the theory of concurrent processes of mass transfer and coagulation in a two-phase medium in the presence of shear turbulence in a differentially rotating gas–dust disk and of polydisperse solid particles suspended in a carrying flow of solid particles. The defining relations are derived for diffuse fluxes of particles of different sizes in the equations of turbulent diffusion in the gravitational field, which describe the convective transfer, turbulent mixing, and sedimentation of disperse dust grains onto the central plane of the disk, as well as their coagulation growth. A semiempirical method is developed for calculating the coefficients of turbulent viscosity and turbulent diffusion for particles of different kinds. This method takes into account the inverse effects of dust transfer on the turbulence evolution in the disk and the inertial differences between disperse solid particles. To solve rigorously the problem of the mutual influence of the turbulent mixing and coagulation kinetics in forming the gas–dust subdisk, the possible mechanisms of gravitational, turbulent, and electric coagulation in a protoplanetary disk are explored and the parametric method of moments for solving the Smoluchowski integro-differential coagulation equation for the particles' size distribution function is considered. This method takes into account the fact that this distribution belongs to a definite parametric class of distributions.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Alfven, H., in Protostars and Planets I, Gehrels, T., Ed., Tucson: Arizona Univ. Press, 1978, pp. 533-544.
Alfven, H. and Arrhenius, G., The Evolution of the Solar System, Washington: NASA, SP-345. Translated under the title Evolutsiya solnechnoi sistemy, Moscow: Mir, 1979.
Balbus, S.A. and Hawley, J.F., A Powerful Local Shear Instability in Weakly Magnetised Disks: 1. Linear Analysis, Astrophys. J., 1991, vol. 376, pp. 214-222.
Cuzzy, J.N., Dobrovolski, A.R., and Chapmen, J.M., Particle–Gas Dynamics in the Midplane of Protoplanetary Nebula, Icarus, 1993, vol. 106, pp. 102-134.
Davis, M.H. and Sartor, T.D., Theoretical Collision Efficiencies for Small Cloud Droplets in Stokes Flow, Nature, 1967, vol. 215, pp. 1371-1372.
Dominik, C. and Tielens, A.G.G.M., The Physics of Dust Coagulation and the Structure of Dust Aggregates in Space, Astrophys. J., 1997, vol. 480. p. 647.
Dubrulle, B., Differential Rotation as a Source of Angular Momentum Transfer in the Solar Nebula, Icarus, 1993, vol. 106, no. 1, pp. 59-77.
Fuks, N.A., Mekhanika aerozolei (Mechanics of Aerosols), Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1955.
Gor'kavyi, N.N. and Fridman, A.M., Fizika planetnykh kolets (Physics of Planetary Rings), Moscow: Nauka, 1994.
Hahn, G. and Shapiro, S., Statistical Models in Engineering, New York, 1967. Translated under the title Statisticheskie modeli v inzhenernykh zadachakh, Moscow: Mir, 1969.
Kolesnichenko, A.V., To the Theory of Turbulence in Planetary Atmospheres: Numerical Modeling of Structural Parameters, Astron. Vestn., 1995, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 133-154 [Sol. Syst. Res. (Engl. transl.), 1995, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 114-132].
Kolesnichenko, A.V., Stefan-Maxwell Relationships and Heat Flux for Turbulent Multicomponent Continuous Media, in Problemy sovremennoi mekhaniki: For the L.I. Sedov Jubilee, Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1998, pp. 52-76.
Kolesnichenko, A.V. and Marov, M.Ya., Turbulentnost' mnogokomponentnykh sred (Turbulence of Multicomponent Media), Moscow: MAIK “Nauka,” 1999.
Kolesnichenko, A.V., Modeling Turbulent Transfer Coefficients for Gas-Dust Accretion Disks, Astron. Vestn., 2000, vol. 34, no. 6, pp. 516-528 [Sol. Syst. Res., (Engl. transl.), 2000, vol. 34, no. 6].
Lee, K.W., Change of Particle Size Distribution during Brownian Coagulation, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1983, vol. 92, no. 2.
Levich, V.G., Fiziko-khimicheskaya gidrodinamika (Physicochemical Hydrodynamics), Moscow: Fiz.-Mat. Lit., 1959.
Lissauer, J.J. and Stewart, G.R., Growth of Planets from Planetesimals, in Protostars and Planets III, Levy, E.H. and Lunine, I.J., Eds., Tucson: Arizona of Univ. Press, 1993, pp. 1061-1088.
Loginov, V.I., Obezvozhivanie i obessolivanie neftei (Dehydration and Desalinization of Oil), Moscow: Khimiya, 1979.
Mazin, I.P., Teoreticheskaya otsenka koeffitsienta koagulyatsii kapel' v oblakakh (Theoretical Evaluation of the Coefficient of Coagulation of Droplets in Clouds), Tr. Spec. Astrophys. Obs., 1971, no. 95, pp. 12-25.
Makalkin, A.B. and Dorofeeva, V.A., The Structure of the Protoplanetary Accretion Disk around the Sun at the T Tauri Stage: II. Results of Model Calculations, Astron. Vestn., 1996, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 496-513 [Sol. Syst. Res. (Engl. transl.), 1996, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 440-455].
Marov, M.Ya. and Kolesnichenko, A.V., Vvedenie v planetarnuyu aeronomiyu (Introduction to Planetary Aeronomy), Moscow: Nauka, 1987.
Mednikov, E.P., Turbulentnyi perenos i osazhdenie aerozolei (Turbulent Transport and Sedimentation of Aerosols), Moscow: Nauka, 1981.
Monin, A.S. and Yaglom, A.M., Statisticheskaya gidromekhanika (Statistical Fluid Mechanics), Moscow: Nauka, 1965, vol. 1.
Morfill, G., Spruit, H., and Levy, E.H., Physical Processes and Conditions Associated with the Formation of Protoplanetary Disks, in Protostars and Planets III, Levy, E.H. and Lunine, I.J., Eds., Tucson: Univ. of Arizona Press, 1993, pp. 939-978.
Nakamura, R., Kitada, Y., and Mukai, T., Gas Drag Forces on Fractal Aggregates, Planet. Space Sci., 1994, vol. 42, no. 9, pp. 721-726.
Reist, P., Introduction to Aerosol Science, New York: Macmillan, 1984. Translated under the title Aerozoli. Vvedenie v teoriyu, Moscow: Mir, 1987.
Ruden, S.P. and Pollack, J.B., The Dynamical Evolution of the Protosolar Nebula, Astrophys. J., 1991, vol. 375, pp. 740-760.
Ruzmaikina, T.V. and Makalkin, A.B., Formation and Evolution of the Protoplanetary Disk, in Nauka o planetakh (Planetary Science), Trudy Sov.–Amer. Soveshchaniya po Fizike Planet (Proc. Sov.-Amer. Seminar on Planetary Physics), Sagdeev, R.Z., Mukhin, L.M., and Donahue, T., Eds., Moscow: IKI, Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1989, pp. 43-63.
Safronov, V.S., Evolutsiya protoplanetnogo oblaka i obrazovanie Zemli i planet (Evolution of the Protoplanetary Cloud and the Formation of the Earth and Planets), Moscow: Nauka, 1969 [NASA TTF-667 (Engl. transl.), 1972].
Safronov, V.S., Current State of the Theory of the Earth's Origin, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Fiz. Zemli, 1982, no. 6, pp. 5-24.
Safronov, V.S. and Ruzmaikina, T.V., Formation of the Solar Nebula and Planets, in Protostars and Planets II, Black, D.C. and Matthews, M.S., Eds., Tucson: Univ. of Arizona Press, 1985, pp. 958-980.
Safronov, V.S., Proiskhozhdenie Zemli (Origin of the Earth), Moscow: Znanie, 1987.
Shakura, N.I. and Syunyaev, R.A., Black Holes in Binary Systems: Observational Appearance, Astron. Astrophys., 1973, vol. 24, pp. 337-355.
Schmidt, O.Yu., Four Lectures on the Earth's Origin, Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1957, 3rd ed.
Schmitt, W., Henning, T., and Mucha, R., Dust Evolution in Protoplanetary Accretion Disks, Astron. Astrophys., 1997, vol. 325, pp. 569-584.
Sinaiskii, E.G., Gidrodinamika fiziko-khimicheskikh protsessov (Hydrodynamics of Physicochemical Processes), Moscow: Nedra, 1997.
Smoluchowski, M., Three Lectures on Diffusion, Brownian Molecular Motion, and Coagulation of Colloid Particles, in Brownian Motion, Moscow: ONTI, 1936; Colloid Coagulation, Moscow: ONTI, 1936.
Spitzer, L., Jr., Physical Processes in Interstellar Medium, New York: Wiley, 1978. Translated under the title Fizicheskie protsessy v mezhzvezdnoi srede, Moscow: Mir, 1981.
Sterzic, M.F. and Morfill, G.E., Evolution of Protoplanetary Disk with Condensation and Coagulation, Icarus, 1994, vol. 111, pp. 536-546.
Tassoul, J.-L., Theory of Rotating Stars, Princeton: Princeton Univ. Press, 1979. Translated under the title Teoriya vrashchayushchikhsya zvezd, Moscow: Mir, 1982.
Vityazev, A.V., Pechernikova, G.V., and Safronov, V.S., Planety zemnoi gruppy. Proiskhozhdenie i rannyaya evolutsiya (Terrestrial Planets: Origin and Early Evolution), Moscow: Nauka, 1990.
Voloshchuk, V.M., Kineticheskaya teoriya koagulyatsii (Kinetic Theory of Coagulation), Moscow: Gidrometeoizdat, 1984.
Zeldovich, Ya.B., On the Friction Fluids between Rotating Cylinders, Proc. R. Soc., 1981, vol. A374, pp. 299-312.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolesnichenko, A.V. Hydrodynamic Aspects of Modeling of the Mass Transfer and Coagulation Processes in Turbulent Accretion Disks. Solar System Research 35, 125–140 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010300723742
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010300723742