Abstract
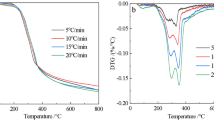
Pyrolysis of extracted oil palm fibers under isothermal and non-isothermal conditions was carried out in a thermogravimetric analyzer. Isothermal curves showed that increasing pyrolysis temperature resulted in a faster pyrolysis and a higher conversion of oil palm fibers into gaseous products. Raw material sizes (below 1.0 mm) had insignificant effects on the isothermal pyrolysis, but the fibers with a size fraction of 1.0 to 2.0 mm resulted in a lesser conversion. Two-step reactions were found in the non-isothermal pyrolysis as evidenced by the presence of two peaks in the derivative thermogravimetry curves. Raw material sizes had no obvious effects on the temperature at which the maximum rate of pyrolysis occurred, but affected the rate of sample mass loss. For the low and high temperature regimes, a three-dimensional diffusion mechanism and a first-order of reaction mechanism respectively were used to describe the non-isothermal pyrolysis kinetics of extracted oil palm fibers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. G. Yeoh, A. Z. Idrus and K. S. Ong, ASEAN J. Sci. Technol. Develop., 5 (1988) 1.
A. V. Bridgewater and J. L. Kuester, (Eds), 'Research in Thermochemical Biomass Conversion', Elsevier Applied Science, London 1988.
G. Grassi, G. Gosse and G. dos Santos, (Eds), 'Biomass for Energy and Industry', Elsevier Applied Science, London 1990.
B. Wunderlich, Thermal Analysis, Academic Press, New York 1990.
C. A. Koufopanos, G. Maschio and A. Lucchesi, The Canadian J. Chem. Eng., 67 (1989) 75.
V. Cozzani, L. Petarca and L. Tognotti, Fuel, 74 (1995) 903.
M. J. Antal Jr. and G. Várhegyi, Ind. and Eng. Chem. Res., 34 (1995) 703.
D. Dollimore, W. E. Brown and A. K. Galway, 'Comprehensive Chemical Kinetics', Vol. 22, Bamford, C. H. and Tipper, C. F. (Eds), Elsevier, Amsterdam 1980.
M. Reading, D. Dollimore and R. Whitehead, J. Thermal Anal., 37 (1991) 2165.
A. Ersoy-Mericboyu, S. Kucukbayrak and B. Durus, J. Thermal Anal., 39 (1993) 707.
S. S. Sofer and O. R. Zaborsky, (Eds), 'Biomass Conversion Processes for Energy and Fuels', Plenum Press, New York and London 1981.
T. B. Reed, (Eds), 'Biomass Gasification: Principles and Technology', Noyes Data Corporation, New Jersey 1981.
P. T. Williams and S. Besler, Fuel, 72 (1993) 151.
D. L. Pyle and C. A. Zaror, Chem. Eng. Sci., 39 (1984) 147.
A. H. Shamsuddin and P. T. Williams, J. of the Inst. of Energy, 65 (1992) 31.
P. Raman, W. P. Walawender, L. T. Fan and J. A. Howell, Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Res. Dev., 20 (1981) 630.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Lua, A.C. Kinetic Study on Pyrolysis of Extracted Oil Palm Fiber. Isothermal and non-isothermal conditions. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 59, 763–774 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010149619877
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010149619877