Abstract
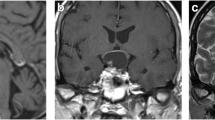
During the past 11 years 69 patients underwent transsphenoidal surgery for symptomatic intra- and suprasellar non-neoplastic cysts in our department. Eighteen of them harbored intra- and suprasellar colloid cysts. The most frequent presenting symptoms were oligomenorrhea, galactorrhea, and headaches. One patient presented with polydipsia. One male patient complained about mild hypogonadism and oligospermia. Two male patients presented with symptoms of panhypopituitarism. Endocrine assessment revealed hyperprolactinaemia in 72% of the female patients. Hypogonadism was found in 72%. Panhypopituitarism was found in two cases. During transsphenoidal surgery, a circumscribed collection of colloid material was removed in each case. Additional tumorous tissue was encountered in three cases that harbored a concomitant pituitary adenoma. Biopsies confirmed the surrounding tissue to be normal pituitary tissue. Postoperatively, regular menstrual cycles were found in 82% of the female patients with oligomenorrhea and headaches improved in 80%. Serum prolactin levels were restored in 92%, galactorrhea ceased in 89%. Only in one case deterioration of pituitary function occurred (diabetes insipidus). Symptomatic SIADH occurred in another one. There were no other postoperative complications. We conclude, that transsphenoidal surgery is a safe therapy for treating symptomatic intra- and suprasellar colloid cysts. Surgery is mainly indicated for female patients in childbearing age to restore fertility and to prevent further deterioration of pituitary function. The differential diagnosis is often unclear preoperatively, but a non-enhancing mass on MRI between anterior and posterior lobe may suggest the presence of an intra- and suprasellar colloid cyst.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskin DS, Wilson CB. Transsphenoidal treatment of nonneoplastic intrasellar cysts. A report of 38 cases. J Neurosurg 1984;60:8–13.
Shanklin WM. On the presence of cysts in the human pituitary. Anat Rec 1949;104:379–407.
Teramoto A, Hirakawa K, Sanno N, et al. Incidental pituitary lesions in 1,000 unselected autopsy specimens. Radiology 1994;193:161–164. Intra-and Suprasellar Colloid Cysts 125
Fahlbusch R. Surgical treatment of pituitary adenomas. In: Beardwell C, Robertson GL, eds. Clinical Endocrinology I, The Pituitary. London, Boston: Butterworths, 1981;76–105.
Harrison MJ, Morgello S, Post KD. Epithelial cystic lesions of the sellar and parasellar region: A continuum of ectodermal derivatives? J Neurosurg 1994;80:1018–1025.
Horvarth E, Kovacs K, Penz G, et al. Origin, possible function and fate of "follicular cells" in the anterior lobe of the human pituitary. An electron microscopy study. Am J Pathol 1974;77:199–212.
Hua F, Asato R, Miki Y, et al. Differentiation of suprasellar nonneoplastic cysts from cystic neoplasms by Gd-DTPA MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1992;16:744–749.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nomikos, P., Buchfelder, M. & Fahlbusch, R. Intra- and Suprasellar Colloid Cysts. Pituitary 2, 123–125 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009983414014
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009983414014