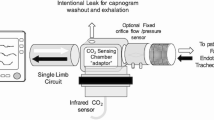
Abstract
Objective.The performance of a point-of-care, noninvasive end tidalbreath carbon monoxide analyzer (CO-Stat™ End Tidal BreathAnalyzer, Natus Medical Inc.) that also reports end tidal carbon dioxide(ETCO2) and respiratory rate (RR), was compared to established,marketed (predicate) devices in children (n = 39) and adults(n = 48) who are normal or at-risk of elevated CO excretion.Methods.Concentrations of end tidal breath CO (ETCO), room air CO,ETCO corrected for inhaled CO (ETCOc), ETCO2, and RR were measuredwith the CO-Stat™ analyzer and the data compared to thoseobtained from the same subjects using the Vitalograph BreathCO monitor(Vitalograph, Inc.) for ETCOc and the Pryon CO2 monitor (SC210 andSC300, Pryon Corp) for ETCO2 and RR. Adults and children werestudied at three medical centers. The data were analyzed by paired t-tests andlinear regression. Bias and imprecision between the CO-Stat analyzer and thepredicate devices was calculated by the method of Bland and Altman.Results.Paired t-tests, performed on the three parametersmeasured with the CO-Stat analyzer and predicate devices showed that only theETCOc values in the adults and the ETCO2 values in the childrenwere significantly different (lower, p ≤ 0.0001, and higher, p≤ 0.0001, respectively). The mean bias and imprecision of the CO-Statanalyzer for adult ETCOc and children ETCO2measurements were−0.9 ± 1.2 ppm and 0.4 ± 0.6%, respectively. Linearregression analysis for the ETCOc results in children and adults had a highdegree of correlation (r= 0.91 and 0.98, respectively).Conclusions.We conclude that in a clinical environment the NatusCO-Stat™ End Tidal Breath Analyzer performs at least as wellas predicate devices for the measurements of ETCOc, ETCO2, and RR.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Smith DW, Hopper AO, Shahin SM, Cohen RS, Ostrander CR, Ariagno RL, Stevenson DK. Neonatal bilirubin production estimated from “end-tidal” carbon monoxide concentration. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1984; 3: 77–80
EPA 600/8–90/045F. Population exposure to carbon monoxide. In: Air quality criteria for carbon monoxide. Research Triangle Park: Environmental Criteria and Assessment O¤ce, O¤ce of Health and Environmental Assessment, O¤ce of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 1991: 8.1–8.115
Wallace L, Thomas J, Mage D, Ott W. Comparison of breath CO, CO exposure, and Coburn model predic-tions in the U.S. EPA,Washington-Denver (CO) Study. Atmos Environ 1988; 22: 2183–2193
Vreman HJ, Mahoney JJ, Stevenson DK. Carbon mon-oxide and carboxyhemoglobin. Adv Pediatr 1995; 42: 303–325
Strocchi A, Schwartz S, Ellefson M, Engel RR, Medina A, Levitt MD. A simple carbon monoxide breath test to estimate erythrocyte turnover. J Lab Clin Med 1992; 120: 392–399
Smith DW, Inguillo D, Martin D, Vreman HJ, Cohen RS, Stevenson DK. Use of noninvasive tests to predict signi¢cant jaundice in full-term infants: Preliminary studies. Pediatrics 1985; 75: 278–280
Yao TC, Stevenson DK. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Clin Perinatol 1995; 22: 741–758
Vreman HJ, Stevenson DK, Oh W, Fanaro¡ AA, Wright LL, Lemons JA, Wright E, Shankaran S, Tyson JE, Korones SB, Bauer CR, Stoll BJ, Papile LA, Donovan EF, Ehrenkranz RA. Semiportable electrochemical in-strument for determining carbon monoxide in breath. Clin Chem 1994; 40: 1927–1933
Stevenson DK, Vreman HJ, Oh W, Fanaro¡ AA, Wright LL, Lemons JA, Verter J, Shankaran S, Tyson JE, Korones SB, Bauer CR, Stoll BJ, Papile LA, Donovan EF, Okah F, Ehrenkranz RA. Bilirubin production in healthy term infants as measured by carbon monoxide in breath. Clin Chem 1994; 40: 1934–1939
Balaraman V, Pelke S, DiMauro S, Cheung S, Stevenson DK, Easa D. End-tidal carbon monoxide in newborn infants: Observations during the 1st week of life. Biol Neonate 1995; 67: 182–185
Vreman HJ, Baxter LM, Stone RT, Stevenson DK. Evaluation of a fully automated end-tidal carbon monoxide instrument for breath analysis. Clin Chem 1996; 42: 50–56
Vreman HJ, Kwong LK, Stevenson DK. Carbon monoxide in blood: An improved microliter blood-sample collection system, with rapid analysis by gas chromatography. Clin Chem 1984; 30: 1382–1386
Matthay MA. Fibrosing alveolitis in the adult respiratory distress syndrome (editorial, comment). Ann Intern Med 1995; 122: 65–66
Stone RT. In vivomeasurement of end-tidal carbon mon-oxide concentration apparatus and methods, Pat. No. 5,293,875, in U.S. Patent O¤ce, USA: Natus Medical Inc., 1994
Sheehan NJ, Rouw SR, Stone RT. Filter unit for end tidal carbon monoxide monitor, Pat. No. 5,357,971, in U.S. Patent O¤ce, USA: NatusMedical Inc., 1994
Jarvis MJ, Belcher M, Vesey C, Hutchison DC. Low cost carbon monoxide monitors in smoking assessment. Thorax 1986; 41: 886–887
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measure-ment. Lancet 1986; 1: 307–310
Vreman HJ, Mahoney JJ, Stevenson DK. Electrochemical measurement of carbon monoxide in breath: Interference by hydrogen. Atmos Environ 1993; 27A: 2193–2198
Fitzgerald MP, Haldane JS. The normal alveolar carbonic acid pressure in man. J Physiol (London) 1905; 32: 486–494
Des Jardins T, Tietsort JA. Assessment skills core to practitioner success. In: Burton GG, Hodgkin JE, Ward JJ, eds. Respiratory care: A guide to clinical practice. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1997: 161
Long-Goding JL. Respiratory care for the infant and child. In: Burton GG, Hodgkin JE, Ward JJ, eds. Respiratory care: A guide to clinical practice. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1997: 965
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vreman, H.J., Wong, R.J., Harmatz, P. et al. Validation of the Natus CO-Stat™ End Tidal BreathAnalyzer in Children and Adults. J Clin Monit Comput 15, 421–427 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009982011226
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009982011226