Abstract
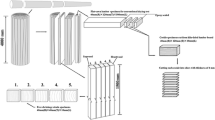
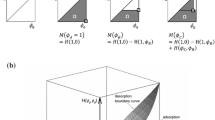
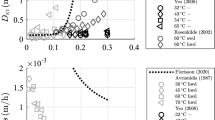
The mechano-sorptive effect (MSE) can be classified as a veryinteresting, but not yet completely explained phenomenon of woodbehaviour. We therefore decided to try to discover its most relevantmechanisms, by conducting two independent series of measurements:accurate measurements of bending deflections on small, clear specimensof spruce wood in changeable climate conditions; and average moisturecontent (MC) in three parts of the cross-section of unloaded dummysamples. The paper emphasises on the sorptive part of MSE. A computersimulation of the wetting experiment is done to determine the space andtime-dependent MC field in the cross-section of the sample. Using aso-called inverse problem identification method, where the equivalenceof the computed and measured responses of the numerical model and realsample is imposed, we identified unknown material properties. Thesolution of the inverse problem enabled us simultaneously to estimatethe moisture diffusion coefficients and to determine the MC field. Twokinds of boundary conditions were used in simulations. To estimate themagnitude of sorption stresses a numerical analysis using Finite ElementMethod (FEM) was done. The sorptive stresses resulting from thenonhomogeneous MC distribution in the sample were obtained. The decisivefactor is the gradient of moisture content and resulting sorptivestresses must be taken into account because their magnitude is of thesame order as the load induced bending stresses. Our experiments and thecalculations following enabled us to conclude that the reason for MSbehaviour could be the simultaneous action of permanent load stressesand the transient triaxial sorptive stress state.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABAQU®, Version 5.8, Hibbit, Karlsson &;; Sorensen, Pawtucket, RI, 1998.
Arora, J.S., Introduction to Optimum Design, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1989.
Beck, J.V. and Arnold, K.J., Parameter Estimation in Engineering and Science, Wiley and Sons, New York, 1977.
Bodig, J. and Jayne, A., Mechanics of Wood and Wood Composites, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1982.
Claeson, J., 'Mathematical modelling of moisture transport', in International Conference on Wood-Water Relations, P. Hoffmeyer (ed.), COST Action E8, Copenhagen, 1997, 61-88.
Cunningham, M.J., 'A model to explain anomalous moisture sorption in wood under step function driving forces', Wood and Fibre Sci. 27(3), 1995, 265-277.
Grosssman, P.A., 'Requirements for a model that exhibits mechano-sorptive behaviour', Wood Sci. Technol. 10, 1976, 163-168.
Hoffmeyer, P. and Davidson, P., 'Mechano-sorptive creep mechanism of wood in compression and bending', Wood Sci. Technol. 23, 1989, 215-227.
Houška, M. and Bu?ar, B., 'Mechano-sorptive behaviour of the different categories of sprucewood', in Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Mechanics of Time Dependent Materials, Ljubljana, I. Emri and W.G. Knauss (eds.), Society for Experimental Mechanics, Bethel, 1995, 173-178.
Hunt, D.G., 'Longitudinal shrinkage-moisture relations in softwood', J. Mater. Sci. 25, 1990, 3671-3676.
Hunt, D.G. and Shelton, C.F., 'Longitudinal moisture-shrinkage coefficients of softwood at the mechano-sorptive creep limit', Wood Sci. Technol. 22, 1988, 199-210.
Kelley, S. and Rials, T., 'Relaxation behaviour of the amorphous components of wood', J. Mater. Sci. 22, 1987, 617-624.
Martenson, A., 'Mechano-sorptive effects in wooden material', Wood Sci. Technol. 28, 1994, 437-449.
Mohager, S. and Toratti, T., 'Long term bending creep of wood in cyclic relative humidity', Wood Sci. Technol. 27, 1993, 49-59.
Schniewind, A.P., Wood &;; Wood Based Materials, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1989.
Söderström, O. and Salin, J., 'On determination of surface emission factors in wood drying', Holzforschung 47, 1993, 391-397.
Stamm, A.J., Wood and Cellulose Science, Ronald, New York, 1964, 549.
Toratti, T., 'Creep of timber beams in a variable environment', Helsinki University of Technology, Report 31, 1992.
Wålinder, M. and Söderström, O., 'Transverse moisture diffusion and surface resistance in pine within the lower hygroscopic range', in International Conference on Wood-Water Relations, P. Hoffmeyer (ed.), COST Action E8, Copenhagen, 1997, 133-142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Houška, M., Koc, P. Sorptive Stress Estimation: An Important Key to the Mechano-Sorptive Effect in Wood. Mechanics of Time-Dependent Materials 4, 81–98 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009897822196
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009897822196