Abstract
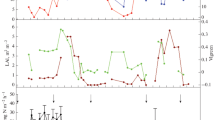
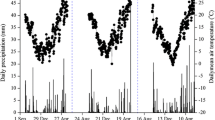
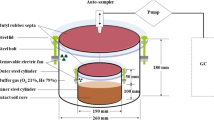
In this paper, we presented the preliminary results of N2O fluxes from Chinese upland and rice paddy fields. The mean N2O flux from upland fields of North China is 30.6 µg N2O-N m-2 h-1; the average N2O flux from Chinese rice paddy field is 39.5 µg N2O-N m-2 h-1. The effects of cropping system, water management and application of N fertilizer and organic manure on N2O emission from rice paddy field have also been presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crutzen P J (1970) The influence of nitrogen oxides on the atmospheric ozone content. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 96: 320–325
Freney J R, Denemead O T, Watanabe I and Craswell E T (1981) Ammonia and nitrous oxide losses following applications of ammonium salfate to flooded rice. Aust J Agric Res 32: 37–45
Lijinsky W (1977) How nitrosamines cause cancer. New Scientist 27: 216–217
Prinn R, Cunnold D, Rasmussen R, Simmonds P, Alyea F, Crawford A, Fraser P, and Rosen R. (1990) Atomspheric emissions and trends of nitrous oxide deduced from 10 years of ALE-GAGE data. J Geophys Res 95: 18369–18385
Rasmussen R A, and Khalil M A K (1986) Atmospheric trace gases: Trends and distributions over the last decade. Science 232: 1623–1624
Su W H, Song W Z, Zhang H, Cao M Q, Lu H R and Zhou Q (1992) Environmental Chemistry (in Chinese) 11: 26–31
Wang S B (1994) Determination of N2O concentration in atmosphere and measurement of its emission fluxes from soils in China. Science in China (Series B, in Chinese) 24: 1275–1280
Wang S B, Song W Z and Su W H (1994) Nitrous oxide emissions from fields of winter wheat. Agricultural Environmental Protection (in Chinese) 13: 210–212
Watson R T, Meirafilho L G, Sanhueza E and Janetos A (1992) Greenhouse gases: Sources and sinks. In: Houghton J T, Callander B A and Varney S K (eds.). Climate Change 1992, The supplementary reports to the IPCC Scientific assessment, pp 25–46. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England
Weiss R F (1981) The temporal and spacial distribution of tropospheric nitrous oxide. J Geophys Res 86: 7185–7195
Yagi K, and Minami K (1990) Effect of organic matter application on methane emission from some Japanese paddy soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 36: 599–610
Zeng J H, Wang Z P, Zhang Y I, Song W Z, Wang S B and Su W H (1995) Estimation of N2O emission fluxes and emission quantities from the soils during the rotation of wheat-maize. Environmental Science (in Chinese) 16: 32–67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, G.X., Zhu, Z.L. Preliminary studies on N2O emission fluxes from upland soils and paddy soils in China. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 49, 17–22 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009775413487
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009775413487