Abstract
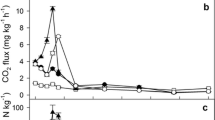
The behavior of nitrous oxide (N2O) in fertilized soil was studied in terms of soil fluxes, the production rates at various depths and the turnover in soil. The diffusive losses of N2O to the atmosphere calculated from soil N2O profile compared favorably with the flux directly determined with a closed chamber technique. The estimate of N2O production rates at several depths demonstrated that the sites of N2O production was only near the soil surface. The calculated residence time of N2O in the entire soil column studied was only 1.4 hour during active emission period and less than 1 day even in the later period having trace N2O emission. The prolonged N2O emission observed after the active phase was due likely to a lasting N2O production rather than a supply from the soil N2O reservoir. The results suggested that most N2O in soil was emitted quite promptly to the atmosphere after its production. A minor role of soil as an N2O reservoir is emphasized from the viewpoint of the origin of groundwater N2O.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burford J R & Stefanson R C (1973) Measurement of gaseous losses of nitrogen from soils. Soil Biol Biochem 5: 133–141
Cicerone R J (1987) Change in stratospheric ozone. Science 237: 35–42
Conrad R, Seiler W & Bunse G (1983) Factors influencing the loss of fertilizer nitrogen into the atmosphere as N2O. J Geophys Res 88(C11): 6709–6718
de Jong E & Schappert H J V (1972) Calculation of soil respiration and activity from CO2 profiles in the soil Soil Science 113: 328–333
Dowdell R J, Burford J R & Crees R (1979) Losses of nitrous oxide dissolved in drainage water from agricultural land. Nature 278: 342–343
Kotake M & Kasuya M (1994) N2O in groundwater of agricultural area in Aichi Prefecture. 1994 Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society of Limnology p 56 Proceeding (in Japanese)
Hillel D (1982) Introduction to Soil Physics. New York: Academic Press
Minami K & Ohsawa A (1990) Emission of nitrous oxide dissolved in drainage water from agricultural land. In Bouwman A F (ed) Soils and the Greenhouse Effect, pp 503–509. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Osozawa S (1987) Measurement of soil-gas diffusion coefficient for soil diagnosis. Soil Physical Conditions and Plant Growth, Japan 55: 53–60 (in Japanese)
Rolston D E, Fried M & Golkhamer D A (1976) Denitrification measured directly from nitrogen and nitrous oxide gas fluxes. Soil Sci Soc Am J 40: 259–266
Ronen D, Magaritz M & Almon E (1988) Contaminated aquifers are a forgotten component of the global N2O budget. Nature 335: 57–59
Ueda S, Yoshinari T, Wada E & Ogura N (1991) Nitrogen stable isotope ratio of N2O in groundwater: a possible tool to determine the source mechanisms. J Chem Soc Jpn 5: 448–453 (in Japanese)
Ueda S, Ogura N & Wada E (1991) Nitrogen stable isotope ratio of groundwater N2O. Geophys Res Lett 18: 1449–1452
Yung Y L, Wang W C & Lacis A A (1976) Greenhouse effect due to atmospheric nitrous oxide. Geophys Res Lett 3: 619–621
Watson R T, Rodhe H, Oeschger H & Siegenthaler U (1990) Greenhouse gases and aerosols. In: Houghton J T, Jenkins G J & Ephraums J J (eds) Climate Change, The IPCC Scientific Assessment, pp 1–40. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoh, M., Toda, H., Kanda, Ki. et al. Diffusion analysis of N2O cycling in a fertilized soil. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 49, 29–33 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009757829417
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009757829417