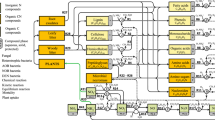
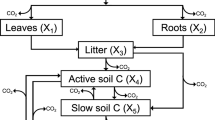
Abstract
Gaseous NO and NO2 (collectively termed NOx) are trace atmospheric constituents with important functions in various atmospheric and ecosystem processes. Because nitrification and denitrification in soil are included among major sources of the gases, simulation models for predicting soil-atmosphere NOx exchange should incorporate the strong dependence of these two microbial processes on soil temperature, soil water content, and substrate N availability. We briefly review current understanding of these controls, then describe how various authors have incorporated that knowledge into model parameterization schemes, and finally present some general thoughts regarding how well those schemes work and what might be missing. Existing coarse-scale models have evolved to the point that they are beginning to explicitly address the influences, interactions, and dynamics of all three microscale controllers in formulations suitable for studies at regional to global and seasonal to interannual scales. Perhaps the greatest limitation of the models, as well as their predictor variables, is that they often fail to account for the large pulse of gaseous N oxide emissions commonly observed following wetting of very dry soil. This failure is exacerbated by mounting evidence that similar pulses may occur following sudden removal of other environmental limitations on microbial growth and metabolism. Such pulses ostensibly make a large contribution to soil- atmosphere NOx exchange, especially in semi- arid, subhumid, and seasonally dry tropical regions of the globe where the exchange has been poorly characterized despite being subject to intense anthropogenic disturbance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson IC and Levine JS (1987) Simultaneous field measurements of biogenic emissions of nitric oxide and nitrous oxide. J Geophys Res 92: 965–976
Anderson IC, Levine JS, Poth MA and Riggan PJ (1988) Enhanced biogenic emissions of nitric oxide and nitrous oxide following surface biomass burning. J Geophys Res 93: 3893–3898
Anthony WH, Hutchinson GL and Doxtader KG (1997) Oxygen concentration controls on soil-atmosphere NO and N2O exchange. Soil Biol Biochem (In review)
Davidson EA (1991) Fluxes and nitrous oxide and nitric oxide from terrestrial ecosystems. In: Rogers JE and Whitman WB (ed) Microbial Production and Consumption of Greenhouse Gases: Methane, Nitrogen Oxides, and Halomethanes, pp 219–235. Washington DC: American Society of Microbiology
Davidson EA (1992) Sources of nitric oxide and nitrous oxide following wetting of dry soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56: 95–102
Davidson EA (1993) Soil water content and the ratio of nitrous oxide to nitric oxide emitted from soil. In: Oremland RS (ed) Biogeochemistry of Global Change: Radiatively Active Trace Gases, pp 369–386. New York: Chapman and Hall
Davidson EA and Kingerlee W (1997) A global inventory of nitric oxide emissions from soils. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems (this issue)
Davidson EA, Matson PA, Vitousek PM, Riley R, Dunkin K, Garcìa-Mèndez G and Maass JM (1993) Processes regulating soil emissions of NO and N2O in a seasonally dry tropical forest. Ecology 74: 130–139
Davidson EA, Vitousek PM, Matson PA, Riley R, Garcìa-Mèndez G and Maass JM (1991) Soil emissions of nitric oxide in a seasonally dry tropical forest of México. J Geophys Res 96: 15, 439–15, 445
Davidson EA, Stark JM and Firestone MK (1990) Microbial consumption and consumption of nitrate in an annual grassland. Ecology 71: 1968–1975
Dignon J, Penner JE, Atherton CS and Walton JJ (1992) Atmospheric reactive nitrogen: A model study of natural and anthropogenic sources and the role of microbial soil emissions. Abstr CHEMRAWN VII World Conf Atmos Chem. Baltimore, Md
Doran JW, Mielke LN and Power JF (1990) Microbial activity as regulated by soil water-filled pore space. Trans 14th Int Congr Soil Sci, pp III-94–III-99
Firestone MK and Davidson EA (1989) Microbiological basis of NO and N2O production and consumption in soil. In: Andreae MO and Schimel DS (ed) Exchange of Trace Gases Between Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Atmosphere, pp 7–21. Chichester: J Wiley and Sons
Firestone MK (1982) Biological denitrification. In: Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen in Agricultural Soils, pp 289–326. Madison, Wisc: American Society of Agronomy
Flessa H, Dörsch P and Beese F (1995) Seasonal variation of N2O and CH4 fluxes in differently managed arable soils in southern Germany. J Geophys Res 100: 23, 115–23, 124
Focht DD and Verstraete W (1977) Biochemical ecology of nitrification and denitrification. Adv Microb Ecol 1: 135–214
Grant RF (1994) Simulation of ecological controls on nitrification. Soil Biol Biochem 26: 305–315
Grant RF (1995) Mathematical modelling of nitrous oxide evolution during nitrification. Soil Biol Biochem 27: 1117–1125
Harris GW, Wienhold FG and Zenker T (1996) Airborne observations of strong biogenic NOx emissions from the Namibian Savanna at the end of the dry season. J Geophys Res 101: 23, 707–23, 711
Holland EA and Lamarque JF (1997) Modeling bio-atmospheric coupling of the nitrogen cycle through NOx emissions and NOy deposition. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems (this issue)
Hooper AB and Terry KR (1979) Hydroxylamine oxidoreductase of Nitrosomonas: Production of nitric oxide from hydroxylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta 571: 12–20
Hutchinson GL (1995) Nitrogen cycle interactions with global change processes. In: Nierenberg WA (ed) Encyclopedia of Environ Biol Vol 2, pp 563–577. San Diego, Calif: Academic Press, Inc
Hutchinson GL and Brams EA (1992) NO vs. N2O emissions from an NH +4 -amended Bermuda grass pasture. J Geophys Res 97: 9889–9896
Hutchinson GL and Davidson EA (1993) Processes for production and consumption of gaseous nitrogen oxides in soil. In: Harper LA, Mosier AR, Duxbury JM and Rolston DE (ed) Agricultural Ecosystem Effects on Trace Gases and Global Climate Change, pp 79–93. Madison, Wisc: American Society of Agronomy
Hutchinson GL, Guenzi WD and Livingston GP (1993) Soil water controls on aerobic soil emission of gaseous N oxides. Soil Biol Biochem 25: 1–9
Jacob DJ and Wofsy SC (1990) Budgets of reactive nitrogen, hydrocarbonds, and ozone over the Amazon rain forest during the wet season. J Geophys Res 95: 16, 737–16, 754
Johansson C, Rodhe H and Sanhueza E (1988) Emission of NO in a tropical savanna and a cloud forest during the dry season. J Geophys Res 93: 7180–7192
Leffelar PA and Wessel WW (1988) Denitrification in a homogeneous closed system: Experiment and simulation. Soil Sci 146: 335–349
Levine JS, Cofer WR III, Sebacher DI, Rhinehart RP, Winstead EL, Sebacher S, Hinkle CR, Schmalzer PA and Koller AM Jr (1990) The effects of fire on biogenic emissions of methane and nitric oxide from wetlands. J Geophys Res 95: 1853–1864
Levine JS, Winstead EL, Parsons DAB, Scholes MC, Scholes RJ, Cofer WR III, Cahoon DR Jr and Sebacher DI (1996) Biogenic soil emissions of nitric oxide (NO) and nitrous oxide (N2O) from savannas in South Africa: the impact of wetting and burning. J Geophys Res 101: 23, 689–23, 697
Linn DM and Doran JW (1984) Effect of water-filled pore space on carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide production in tilled and nontilled soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48: 1267–1272
Lipschultz F, Zafiriou OC, Wofsy SC, McElroy MB, Valois FW and Watson SW (1981) Production of NO and N2O by soil nitrifying bacteria. Nature 294: 641–643
Livingston GP and Hutchinson GL (1995) Enclosure-based measurement of trace gas exchange: Applications and sources of error. In: Matson PA and Harriss RC (ed) Biogenic Trace Gases: Measuring Emissions from Soil and Water, pp 14–51. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Sci, Ltd
McConnaughey PK and Bouldin DR (1985) Transient microsite models of denitrification: I. Model development. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49: 886–891
Meixner FX, Fickinger Th, Marufu L, Serça D, Nathaus FJ, Makina E, Mukurumbira L and Andreae MO (1997) Preliminary results on nitric oxide emission from a southern African savanna ecosystem. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems (this issue)
Müller J (1992) Geographical distribution and seasonal variation of surface emissions and deposition velocities of atmospheric trace gases. J Geophys Res 97: 3787–3804
Parsons DAB, Scholes MC, Scholes RJ and Levine JS (1996) Biogenic NO emissions from savanna soils as a function of fire regime, soil type, soil nitrogen, and water status. J Geophys Res 101: 23, 683–23, 688
Parton WJ, Schimel DS, Cole CV and Ojima DS (1987) Analysis of factors controlling soil organic matter levels in Great Plains grasslands. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51: 1173–1179
Parton WJ, Mosier AR and Schimel DS (1988) Dynamics of C, N, P, and S in grassland soils: A model. Biogeochem 5: 109–131
Poth M and Focht DD (1985) 15N kinetic analysis of N2O production by Nitrosomonas europaea: an examination of nitrifier denitrification. Appl Environ Microbiol 49: 1134–1141
Potter CS, Matson PA, Vitousek PM and Davidson EA (1996) Process modeling of controls on nitrogen trace gas emissions from soils worldwide. J Geophys Res 101: 1361–1377
Potter CS, Randerson JT, Field CB, Matson PA, Vitousek PM, Mooney HA and Klooster SA (1993) Terrestrial ecosystem production: A process model based on global satellite and surface data. Global Biogeochem Cycles 7: 811–841
Reicosky DC and Lindstrom MJ (1993) Fall tillage method: effect on short-term carbon dioxide flux from soil. Agron J 85: 1237–1243
Remde A and Conrad R (1990) Production of nitric oxide in Nitrosomonas europaea by reduction of nitrite. Arch Microbiol 154: 187–191
Remde A, Slemr F and Conrad R (1989) Microbial production and uptake of nitric oxide in soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62: 221–230
Sanhueza E, Hao WM, Scharffe D, Donoso L and Crutzen PJ (1990) N2O and NO emissions from soils of the northern part of the Guayana Shield. J Geophys Res 95: 22, 481–22, 488
Schimel DS and Potter CS (1995) Process modelling and spatial extrapolation. In: Matson PA and Harriss RC (ed) Biogenic Trace Gases: Measuring Emissions from Soil and Water, pp 358–383. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Sci, Ltd
Shepherd M, Barzetti S and Hastie DR (1991) The production of atmospheric NOx and N2O from a fertilized agricultural soil. Atmos Environ 25A: 1961–1969
Skopp J, Jawson MD and Doran JW (1990) Steady-state aerobic microbial activity as a function of soil water content. Soil Sci Soc Am J 54: 1619–1625
Smith MS and Parsons LL (1985) Persistence of denitrifying enzyme activity in dried soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 49: 316–320
Tiedje JM (1988) Ecology of denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium. In: Zehnder AJB (ed) Biology of Anaerobic Microorganisms, pp 179–244. Chichester, UK: J Wiley and Sons
Tortoso AC and Hutchinson GL (1990) Contributions of autotrophic and heterotrophic nitrifiers to soil NO and N2O emissions. Appl Environ Microbiol 56: 1799–1805
Williams EJ and Fehsenfeld FC (1991) Measurement of soil nitrogen oxide emissions at three North American ecosystems. J Geophys Res 96: 1033–1042
Williams EJ, Guenther A and Fehsenfeld FC (1992a) An inventory of nitric oxide emissions from soils in the United States. J Geophys Res 97: 7511–7520
Williams EJ, Hutchinson GL and Fehsenfeld FC (1992b) NOx and N2O emissions from soil. Global Biogeochem Cycles 6: 351–388
Yienger JJ and Levy H (1995) Empirical model of global soilbiogenic NOx emissions. J Geophys Res 100: 11, 447–11, 464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hutchinson, G., Vigil, M., Doran, J. et al. Coarse-scale soil–atmosphere NOx exchange modeling: status and limitations. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 48, 25–35 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009753810675
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009753810675