Abstract
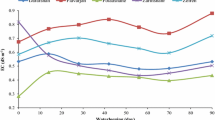
Nitrification rates (n) in the floodwater of an alkaline clay were measured in the absence or presence of rice plants by inhibition of ammonium oxidation and 15N-dilution techniques. Floodwater nitrate concentrations in control treatments showed a marked diurnal variation, and were higher than in the inhibitor treatments after the first day. Ammonium concentrations in floodwater declined exponentially in all treatments, being markedly affected by diffusion and NH3 volatilization but little affected by nitrification and plant uptake. Nitrification rates in floodwater estimated by 15N-dilution were generally higher than the rates estimated by the inhibitor method. Estimates of n were generally higher during daylight hours than at night, and did not differ significantly between planted and unplanted pots. Microbial immobilisation of labelled ammonium and gross N immobilisation were not affected by addition of the nitrification inhibitor 2-ethynylpyridine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barraclough D, Geens EL, Davies GP & Maggs JM (1985) Fate of fertilizer nitrogen III The use of single and double labelled 15N ammonium nitrate to study nitrogen uptake by ryegrass. J Soil Sci 36: 593–603
Bremner JM & Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen-organic forms. In: Page AL, Miller RH & Keeney DR (eds) Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, pp 595–624. Am Soc Agron, Madison, WI
Chen D, Chalk PM & Freney JR (1990) Release of dinitrogen from nitrite and sulphamic acid for isotope ratio analysis of soil extracts containing nitrogen-15 labelled nitrite and nitrate. Analyst 115: 365–370
Chen D, Chalk PM & Freney JR (1998) Nitrogen transformations in a flooded soil in the presence and absence of rice plants: 2. Denitrification. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems (in press)
Chen D, Chalk PM, Freney JR, Smith CJ & Luo QX (1995) Estimation of nitrification rates in flooded soils. Microb Ecol 30: 269–284
Crawford DM & Chalk PM (1992) Mineralization and immobilization of soil and fertilizer nitrogen with nitrification inhibitors and solvents. Soil Biol Biochem 24: 559–568
Crawford DM & Chalk PM (1993) Sources of N uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivumL.) and N transformations in soil treated with a nitrification inhibitor (nitrapyrin). Plant Soil 149: 59–72
Davidson EA, Hart SC, Shanks CA & Firestone MK (1991) Measuring gross nitrogen mineralization, immobilization and nitrification by 15N isotopic pool dilution in intact soil cores. J Soil Sci 42: 335–349
DeLaune RD & Smith CJ (1987) Simultaneous determination of nitrification and nitrate reduction in sediment-water columns by nitrate-15 dilution. J Environ Qual 16: 227–230
Fillery IRP & Vlek PLG(1982) The significance of denitrification of applied nitrogen in fallow and cropped rice soils under different flooding regimes: I Greenhouse experiments. Plant Soil 65: 153- 169
Freney JR, Keerthisinghe DG, Phongpan S, Chaiwanakupt P & Harrington KJ (1995) Effect of urease, nitrification and algal inhibitors on ammonia loss and grain yield of flooded rice in Thailand. Fert Res 40: 225–233
Freney JR, Simpson JR & Denmead OT (1983) Volatilization of ammonia. In: Freney JR & Simpson JR (eds) Gaseous Loss of Nitrogen from Plant-Soil Systems, pp 1–32. Martinus Nijhoff/Dr W Junk Publishers, The Hague
Freney JR, Trevitt ACF, DeDatta SK, Obcemea WN & Real JG (1990) The interdependence of ammonia volatilization and denitrification as nitrogen loss processes in flooded rice fields in the Philippines. Biol Fertil Soils 9: 31–36
Galbally IE, Freney JR, Muirhead WA, Simpson JR, Trevitt ACF & Chalk PM (1987) Emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) from a flooded soil fertilized with urea: Relation to other nitrogen loss processes. J Atmos Chem 5: 343–365
Gowda TKS, Rao VR & Sethunathan N (1977) Heterotrophic nitrification in the simulated oxidized zone of a flooded soil amended with benomyl. Soil Sci 123: 171–175
Hall GH (1984) Measurement of nitrification rates in lake sediments: comparison of the nitrification inhibitors nitrapyrin and allythiourea. Microb Ecol 10: 25–36
Hasebe A, Ito J, Iimura K & Sekiya S (1990) Dynamic aspects of nitrification and subsequent denitrification in lowland rice fields. Trans 14th Int Congr Soil Sci 4: 332–336
Hasebe A, Koike I, Ohmori M & Hattori A (1987) Variations in the process of nitrification and nitrate reduction in submerged paddy soils as measured by 15N isotope dilution technique. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 33: 201–211
Henriksen K (1980) Measurement of in situ rates of nitrification in sediment. Microb Ecol 6: 329–337
Henriksen K & Kemp WM (1988) Nitrification in estuarine and coastal marine sediments. In: Blackburn TH & Sorensen J (eds) Nitrogen Cycling in Coastal Marine Environments, pp 207–248. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York
Huang Z-W & Broadbent FE (1988) The efficiency of potassium nitrate and urea fertilisers on rice in flooded soil. Soil Sci 146: 461–465
Keeney DR & Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen-inorganic forms. In: Page AL, Miller RH & Keeney DR (eds) Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, pp 643–698. Am Soc Agron, Madison, WI
Koike I & Hattori A(1978) Simultaneous determinations of nitrification and nitrate reduction in coastal sediments by a 15N dilution technique. Appl Environ Microbiol 35: 853–857
Lindau CW, DeLaune RD, Williams ML & Patrick WH Jr (1988) Application of N-15 dilution for simultaneous estimation of nitrification and nitrate reduction on soil-water columns. Plant Soil 111: 151–154
Mohanty SK & Mosier AR (1990) Nitrification-denitrification in flooded rice soils. Trans 14th Int Congr Soil Sci 10: 326–331
Patrick WH Jr & Reddy KR (1976) Nitrification-denitrification reactions in flooded soils and water bottoms: Dependence on oxygen supply and ammonium diffusion. J Environ Qual 5: 469–472
Rao PSC, Jessup RE & Reddy KR (1984) Simulation of nitrogen dynamics in flooded soils. Soil Sci 138: 54–62
Reddy KR & Patrick WH Jr (1986) Fate of fertilizer nitrogen in the rice root zone. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50: 649–651
Rochester IJ, Constable GA & MacLeod DA (1992) Preferential nitrate immobilisation in alkaline soils. Aust J Soil Res 30: 737–749
Samson MI, Buresh RJ & De Datta SK (1990) Evolution and soil entrapment of nitrogen gases formed by denitrification in flooded soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 36: 299–307
Schmidt EL (1982) Nitrification in soil. In: Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen inAgricultural Soils. pp 253–289. AmSocAgron, Madison, WI
Shen SM, Pruden G & Jenkinson DS (1984) Mineralization and immobilization of nitrogen in fumigated soil and the measurement of microbial biomass nitrogen. Soil Biol Biochem 16: 437–444
Simpson JR, Freney JR, Muirhead WA & Leuning R (1985) Effects of phenylphosphorodiamidate and dicyandiamide on nitrogen loss from flooded rice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49: 1426–1431
SSMS (1983) Keys to Soil Taxonomy. Soil Management Support Services, United States Department of Agriculture, United States Government Printing Office, Washington, Technical Monograph No 6
Terry RE & Duxbury JM (1985) Acetylene decomposition in soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49: 90–94
Vlek PLG & Craswell ET (1979) Effect of nitrogen source and management on ammonia volatilization losses from flooded rice-soil systems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43: 352–358
Watanabe I, Padre BC Jr & Santiago ST (1981) Quantitative study on nitrification in flooded rice soil. Soil Sci Plant Nutr27: 373–382
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Chalk, P., Freney, J. et al. Nitrogen transformations in a flooded soil in the presence and absence of rice plants: 1. Nitrification. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 51, 259–267 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009736729518
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009736729518