Abstract
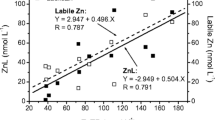
The complexation of Cu and Cd by ligands observed in filtered unfractionated lakewaters is compared to the complexation by humic and fulvic acids. Complexation parameters (conditional stability constants and ligand concentrations) of Suwannee River fulvic acids (FA), purified peat humic acids (HA) and of ligands in lakewater samples have been determined using the same methods (ligand-exchange and CSV (cathodic stripping voltammetry) or ASV (anodic stripping voltammetry)), and the same titration ranges of Cu, Cd and organic carbon concentrations. The performance of the used techniques is first evaluated in FA and HA suspensions, and gives comparable results with the literature values for the same materials, according to published models (5-site model, NICA model) and parameters. Model calculations using the WHAM model for FA and HA (Tipping, 1994) are also presented. The comparison of titrations of FA and HA with Cu and Cd with those of lakewater samples indicates that stronger ligands than FA and HA are present at low concentrations in the lakewaters. Specific strong ligands occur in particular in eutrophic lake waters, whereas in a lake with higher metal concentrations and low biological productivity the ligands more closely match the fulvic acid characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achterberg, E. P., Van den Berg, C. M. G., Boussemart, M., and Davison, W. (1997) Speciation and cycling of trace metals in Esthwaite Water: A productive English lake with seasonal deep-water anoxia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 5233-5253.
Bartschat, B. M., Cabaniss, S. E., and Morel, F. M. M. (1992) Oligoelectrolyte model for cation binding by humic substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 26(2), 284-294.
Benedetti, M. F., Milne, C. J., Kinniburgh, D. G., Van Riemsdijk, W. H., and Koopal, L. K. (1995) Metal ion binding to humic substances: Application of the non-ideal competitive adsorption model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 446-457.
Biber M. V., Gülaçar F. O., and Buffle, J. (1996) Seasonal variations in principal groups of organic matter in a eutrophic lake using pyrolysis/GC/MS. Environ, Sci. Technol. 30, 3501-3507.
Brand, L. E., Sunda, W. G., and Guillard, R. R. L. (1986) Reduction of marine phytoplankton reproduction rates by copper and cadmium. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 96, 225-250.
Breault, R. F., Colman, J. A., Aiken, G. R., and McKnight, D. (1996) Copper speciation and binding by organic matter in copper-contaminated streamwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 3477-3486.
Bruland, K. W. (1992) Complexation of cadmium by natural organic ligands in the central North Pacific. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37, 1008-1017.
Bruland, K. W., Donat, J. R., and Hutchins, D. A. (1991) Interactive influence of bioactive trace metals on biological production in oceanic waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 36, 1555-1577.
Buffle, J. (1988) Complexation Reactions in Aquatic Systems: An Analytical Approach. Ellis Horwood.
Buffle, J., Greter F., and Haerdi, W. (1977) Measurement of complexation properties of humic and fulvic acids in natural waters with lead and copper ion-selective electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 118, 29-44.
Cabaniss, S. E. and Shuman, M. S. (1988) Copper binding by dissolved organic matter: I. Suwanee River fulvic acid equilibria. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 185-193.
Campos, M. L. A. L. and Van den Berg, C. M. G. (1994) Determination of copper complexation in sea water by cathodic stripping voltammetry and ligand competition with salicylaldoxime. Anal. Chim. Acta 284(3), 481-496.
Coale, K. H. and Bruland, K. W. (1990) Spatial and temporal variability in copper complexation in the North Pacific. Deep-Sea Res. 37, 317-336.
Donat, J. R., Kango, R. A., and Gordon, A. S. (1997) Evaluation of immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) for isolation and recovery of strong copper-complexing ligands from marine waters. Mar. Chem. 57, 1-10.
Donat, J. R., Lao, K. A., and Bruland, K. W. (1994) Speciation of dissolved copper and nickel in South San Francisco Bay: A multimethod approach. Anal. Chim. Acta 284, 547-571.
Donat, J. R. and Van den Berg, C. M. G. (1992) A new cathodic stripping voltammetric method for determining organic copper complexation in seawater. Mar. Chem. 38, 69-90.
Gordon, A. S., Dyer, B. J., Kango, R. A., and Donat, J. R. (1996) Copper ligands isolated from estuarine water by immobilized metal affinity chromatography: Temporal variability and partial characterization. Mar. Chem. 53, 163-172.
Hering, J. G. and Morel, F. M. M. (1988) Humic acid complexation of calcium and copper. Environ. Sci. Technol. 22, 1234-1237.
Kinniburgh, D. G., Milne, C. J., Benedetti, M. F., Pinheiro, J. P., Filius, J., Koopal, L. K., and Van Riemsdijk, W. H. (1996) Metal ion binding by humic acid: Application of the NICA-Donnan model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 1687-1698.
Knauer, K., Ahner, B., Xue, H. B., and Sigg, L. (1998) Metal and phytochelatin content in phytoplankton from freshwater lakes with different metal concentrations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 2444-2452.
Leenheer, J. A. (1981) Comprehensive approach to preparative isolation and fraction of dissolved organic carbon from natural water and wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15(5), 578-587.
Leenheer, J. A., McKnight, D.M., Thurman, E. M., and MacCarthy, P. (1989) Structural components and proposed structural models of fulvic acid from the Suwannee River. In R. C. Averett, J. A. Leenheer, D. M. McKnight, and K. A. Thorn (eds.), Humic Substances in the Suwannee River, Georgia: Interactions, Properties, and Proposed Structures, Vol. Open-File Report 87-557. U.S. Geology Survey, pp. 331-360.
Mantoura, R. F. C., Dickson, A., and Riley, J. P. (1978) The complexation of metals with humic materials in natural waters. Estuarine Coastal Mar. Sci. 6, 387-408.
McKnight, D. M., Feder, G. L., Thurman, E. M., Wershaw, R. L., and Westall, J. C. (1983) Complexation of copper by aquatic humic substances from different environments. Sci. Total Environ. 28, 65-76.
McKnight, D. M. and Wershaw, R. L. (1989) Complexation of copper by fulvic acid from the Suwannee River — Effect of counter-ion concentration. In R. C. Averett, J. A. Leenheer, D. M. McKnight, and K. A. Thorn (eds), Humic Substances in the Suwannee River, Georgia: Interactions, Properties, and Proposed Structures, Vol. USGS Open File Report, 87-557, U.S. Geology Survey, pp. 63-69.
Midorikawa, T. and Tanoue, E. (1996) Extraction and characterization of organic ligands from oceanic water columns by immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography. Mar. Chem. 52, 157-171.
Milne, C. J., Kinniburgh, D. G., De Wit, J. C. M., Van Riemsdijk, W. H., and Koopal, L. K. (1995) Analysis of proton binding by a peat humic acid using a simple electrostatic model. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59(6), 1101-1112.
Moffett, J. W. (1995) Temporal and spatial variability of Cu complexation by strong chelators in the Sargasso Sea. Deep-Sea Res. 42, 1273-1295.
Moffett, J.W., Brand, L. E., Croot, P. L., and Barbeau, K. A. (1996) Cu speciation and cyanobacterial distribution in harbors subject to anthropogenic Cu inputs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 42(5), 789-799.
Morel, F. M. M., Hudson, R. J. M., and Price, N. M. (1991) Limitation of productivity by trace metals in the sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 36, 1742-1755.
Muller, F. L. L. (1996) Interactions of copper, lead and cadmium with the dissolved, colloidal and particulate components of estuarine and coastal waters. Mar. Chem. 52, 245-268.
Pinheiro, J. P., Mota, A. M., and Gonçalves, M. L. S. (1994) Complexation study of humic acids with cadmium(II) and lead(II). Anal. Chim. Acta 284, 525-537.
Sunda, W. G. and Guillard R. R. L. (1976) The relationship between cupric ion activity and the toxicity of copper to phytoplankton. J. Mar. Res. 34, 511-529.
Sunda, W. G. and Huntsman, S. A. (1991) The use of chemiluminescence and ligand competition with EDTA to measure copper concentration and speciation in seawater. Mar. Chem. 36, 137-163.
Sunda, W. G. and Huntsman, S. A. (1995) Regulation of copper concentration in the oceanic nutricline by phytoplankton uptake and regeneration cycles. Limnol. Oceanogr. 40, 132-137.
Thurman, E. M. (1985) Organic Geochemistry of Natural Water. Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Tipping, E. (1994) WHAM — A chemical equilibrium model and computer code for waters, sediments, and soils incorporating a discrete site/electrostatic model of ion-binding by humic substances. Comput. Geosci. 20(6), 973-1023.
Tipping, E. and Hurley, M. A. (1992) A unifying model of cation binding by humic substances. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56, 3627-3641.
Turner, D. R., Varney, M. S., Whitfield, M., Mantoura, R. F. C., and Riley, J. P. (1986) Electrochemical studies of copper and lead complexation by fulvic acid. 1. Potentiometric measurements and a critical comparison of metal binding models. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 289-297.
Van den Berg, C. M. G. (1984) Determination of copper in sea water by cathodic stripping voltammetry of complexes with catechol. Anal. Chim. Acta 164, 195-207.
Voelker, B. M. and Sulzberger, B. (1996). Effects of fulvic acid on Fe(II) oxidation by hydrogen peroxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 1106-1114.
Westall, J. C. (1982) FITEQL, A Program for the Determination of Chemical Equilibrium Constants from Experimental Data. Chemistry Department, Oregon State University.
Xue, H. B., Oestreich, A., Kistler, D., and Sigg, L. (1996) Free cupric ion concentrations and Cu complexation in selected Swiss lakes and rivers. Aquat. Sci. 58, 69-87.
Xue, H. B. and Sigg, L. (1993) Free cupric ion concentration and Cu(II) speciation in a eutrophic lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 38, 1200-1213.
Xue, H. B. and Sigg, L. (1998) Cd speciation and complexation by natural organic ligands in freshwater. Anal. Chim. Acta 363(3), 249-259.
Xue, H. B. and Sunda, W. G. (1997) Comparison of [Cu2+] measurements in lake water determined by ligand exchange and cathodic stripping voltammetry and by ion-selective electrode. Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 1902-1909.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, H., Sigg, L. Comparison of the Complexation of Cu and Cd by Humic or Fulvic Acids and by Ligands Observed in Lake Waters. Aquatic Geochemistry 5, 313–335 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009679819002
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009679819002