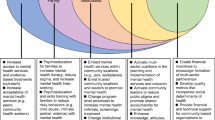
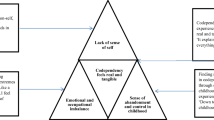
Abstract
The holistic, developmental, systems-oriented perspective, an extension of the work of Heinz Werner and his associates, is characterized including basic assumptions of the approach and explication with respect to such problems as child development (including transition to nursery school; child-centered urban planning; microgenesis and ontogenesis); adult development (including becoming a parent and retiring); social relationships (including residential living of first year undergraduates; abused women; marital interaction); health problems (including protection against sexual transmission of HIV, reading disabilities, weight loss, and alcohol and tobacco use); changes in the physical environment; cross-cultural psychology (including cultural differences in values; values mothers hold for preschoolers; necessities, amenities, and luxuries; sojourner experience and action; cross-cultural differences in compliance with automobile safety belt legislation); psychopathology including neuropathology; organizational psychology; conditions facilitating developmental advance; and some significant open research problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Agli, S., Raeff, C., & Wapner, S. (1992, April). General factors and precipitating events involved in the cessation of alcohol consumption among college women. Presented at the Annual Meeting of the Eastern Psychological Association, Boston, MA.
Ainsworth, M. D., & Wittig B. A. (1969). Attachment and exploratory behavior of one-year-old children in a Strange Situation. In B. M. Goss (Ed.), Determinants of infant behavior: Vol. 4 (pp. 111–136). London: Methuen.
Altman, I., & Rogoff, B. (1987). World views in psychology: Trait, interactional, organismic and transactional perspectives. In D. Stokols & I. Altman (Eds.), Handbook of environmental psychology (pp. 7–40). New York: Wiley.
Barley, S. R., Freeman, J., & Hybels, R. C. (1992). Strategic alliances in commercial biotechnology. In N. Norhia & B. Eccles (Eds.), Networks and organizations (pp. 311–347). Boston: Harvard Business School Press.
Barten, S. S., & Franklin, M. B. (1978). Developmental processes: Heinz Werner's selected writings. New York: International Universities Press.
Bertini, M., Braibante, P., & Wapner, S. (1996). Sleep-wake phenomena from a holistic, developmental, systems-oriented perspective. Manuscript in preparation.
Carini, L. P. (1955). An experimental investigation of perceptual behavior in schizophrenics. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Clark University, Worcester,MA(Microfilm No. 13009).
Chea, W. E., & Wapner, S. (1995). Retrospections of Bahamians concerning the impact of hurricane Andrew. In J. L. Nasar, P. Grannis, & K. Hanyu (Eds.), Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth Annual Conference of the Environmental Design Research Association (pp. 87–92). Oklahoma: EDRA.
Ciottone, R. A., Demick, J., Pacheco, A. P., Quirk, M. E., & Wapner, S. (1980, November). Children's transition from home to nursery school: The integration of two cultures. Presented at The American Association of Psychiatric Services for Children (AAPSC), New Orleans, LA.
Ciottone, R. A., & Quirk, M. (1985). The integration of two worlds: Home and preschool. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the Eastern Psychological Association, Boston, MA.
Clark, E. F. (1995). Women's self-reported experience and action in relations to protection against sexual transmission of HIV: A randomized case comparison study of three interventions. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Clark University, Worcester, MA.
Clark, W. (1998). Planning for parenthood: Multiple worlds of dual career couples. Doctoral dissertation proposal, Clark University, Worcester, MA.
Clark, E. F., Wapner, S., & Quirk, M. (1995, August). Interventions in protecting women against sexual transmission of HIV. Presented at American Psychological Association, New York.
Coltrera, D. (1978). Experiential aspects of the transition to parenthood. Master's thesis proposal, Clark University, Worcester, MA.
Cowan, C. P., & Cowan, P. A. (1992). When partners become parents: The big life change for couples. New York: Basic Books.
Cowan, C. P., & Cowan, P. A. (1995). Interventions to ease the transition to parenthood: Why they are needed and what they can do. Family Relations, 44, 412–423.
Cowan, P. A., & Cowan, C. P. (1988). Changes in marriage during the transition to parenthood: Must we blame the baby? In G. Y. Michaels & W. A. Goldberg (Eds.), The transition to parenthood: Current theory and research (pp. 114–154). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Demick, J., Inoue, W., Wapner, S., Ishii, S., Minami, H., Nishiyama, S., & Yamamoto, T. (1992). Cultural differences in impact of governmental legislation: Automobile safety belt use. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 23 (4), 468–487.
Demick, J., Ishii, S., & Inoue, W. (1997). Body and self experience: Japan versus USA. In S. Wapner, J. Demick, T. Yamamoto, & T. Takahashi (Eds.), Handbook of Japan-US environment behavior research: Towards a transactional approach (pp. 83- 99). New York: Plenum.
Demick, J., & Wapner, S. (1980). Effect of environmental relocation upon members of a psychiatric therapeutic community. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 89, 444–452.
Demick, J., & Wapner, S. (1991). Field dependence-independence in adult development and aging. In S. Wapner & J. Demick (Eds.), Field dependence-independence: Cognitive style across the life span (pp. 245–268). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Des Lauriers, A. (1962). The experience of reality in childhood schizophrenia. New York: International Universities Press.
DiDonato, G. M. (1999). Changes in experience and action during residential hall living of first year undergraduates. Unpublished Honors Thesis, Clark University.
Dyl, J., & Wapner, S. (1996). Age and gender differences in the nature, meaning, and function of cherished possessions for children and adolescents. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 62, 340–377.
Ellefsen, K. F. (1987). Entry into nursery school: Children's transactions as a function of experience and age. Unpublished Master's Thesis, Clark University, Worcester, MA.
Fraenkel. G. S., & Gunn, D. L. (1961). The orientation of animals: Kinesis, taxes and compass reactions. (Reprint of original 1940 edition). New York: Dover.
Franklin, M. B. (1990). Reshaping psychology at Clark: The Werner era. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences, 26, 176–189.
Friedman, H. (1952). Perceptual regression in schizophrenia: An hypothesis suggested by use of the Rorschach test. Journal of Genetic Psychology, 81, 63–98.
Görlitz, D., Harloff, H. J., Mey, G., & Valsiner, J. (1998). Children, cities and psychological theories: Developing relationships. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Hanlon, R. E. (1991). Cognitive microgenesis: A neurophysiological perspective. New York: Springer.
Hanson, K., & Wapner, S. (1994). Transition to retirement: Gender differences. The International Journal of Aging and Human Development, 39 (3), 189–208.
Havighurst, R. (1953). Human Development and Education. New York: Longmans Green.
Hornstein, G. A., & Wapner, S. (1984). The experience of the retiree's social network during the transition to retirement. In C. M. Aanstoos (Ed.), Exploring the lived world readings in phenomenological psychology (pp. 119–136). Carrolton, GA: West Georgia College Press.
Hornstein, G. A., & Wapner, S. (1985). Modes of experiencing and adapting to retirement. International Journal on Aging & Human Development, 21 (4), 291–315.
Ito, T., & Wapner, S. (1999, April). Cultural differences in values: Japanese and American college students. Presented at the Annual Meeting of the Eastern Psychological Association, Providence, RI.
Kaden, S. (1958). A formal comparative analysis of the relationship between the structuring of marital interaction and Rorschach blot stimuli. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Clark University. Worcester, MA. (Microfilm No. AAG5807090)
Kaplan, B. (1959). The study of language in psychiatry. In S. Arieti (Ed.), American handbook of psychiatry, Vol. 3 (pp. 659–668). New York: Basic Books.
Kaplan, B. (1967). Mediations on genesis. Human Development, 10, 65–87.
Kaplan, B. (1983). Genetic dramatism: Old wine in new bottles. In S. Wapner & B. Kaplan (Eds.), Toward a holistic, developmental psychology (pp. 53–74). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Kaplan, B., Pemstein, D., Cohen, S. B., & Wapner, S. (1974). A new methodology for studying the processes underlying the experience of a new environment: Self observation and group debriefing. Working notes.
Kaplan, E. (1980). Changes in cognitive style with aging. In K. Obler, & M. L. Obler (Eds.). Language and communication in the elderly. Lexington, MA: Heath.
Kaplan, E. (1983). Process and achievement revisited. In S. Wapner & B. Kaplan (Eds.) Toward a holistic developmental psychology. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Kitayama, S., & Markus, H. R. (1994). Emotion and culture: Empirical studies of mutual influences. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association Press.
Lemme, B. H. (1999). Development in adulthood. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Machover, K. (1949). Personality projection in the drawing of the human figure, Chicago, IL: Charles C. Thomas.
Marcus, A. A., & Goodman, R. S. (1991). Victims and shareholders: The dillemas of presenting corporate policy during a crisis. Academy of Management Journal, 34, 281–305.
Mayo, M., Meindl, J., & Pastor, J. C. (1994). Diversity as a context for the emergence of charismatic leadership. Unpublished manuscript, State University of New York, Buffalo.
Mayo, M., Pastor, J. C., & Wapner, S. (1995). Linking organizational behavior and environmental psychology. Relations between environmental psychology and allied fields. Environment and Behavior, 27 (1), 73–89.
McAvay, D. G. (1977). An organismic-development analysis of marital interaction. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Clark University, Worcester, MA. (Microfilm No. AAG7803413)
Minami, H. (1985a). Establishment and transformation of personal networks during the first year of college: A developmental analysis. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Clark University, Worcester, MA (Microfilm No. AAG8608772).
Minami, H. (1985b). Development of personal networks during the first year of college. Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the Eastern Psychological Association, Boston, MA.
Nair, P. J. (1961). Distancing: The application of a developmental construct to learning disability. Doctoral dissertation, Clark University, Worcester, MA (Microfilm No. 61/05008).
Neuhaus, E. C. (1988). A developmental approach to children's planning. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Clark University, Worcester, MA (Microfilm No. AAG8825801).
Pacheco, A. M., Lucca, N., & Wapner, S. (1979). Migration as a critical person-in-environment transition: An organismicdevelopmental interpretation. Revista de Ciencias Sociales (Social Sciences Journal), 21, 123–157.
Pacheco, A. M., Lucca, N., & Wapner, S. (1985). The assessment of interpersonal relations among Puerto Rican migrant adolescents. In R. Diaz-Guerrero (Ed.), Cross-cultural and national studies in social psychology (pp. 169–176). North Holland: Elsevier Science.
Pollowy, A. M. (1977). The urban nest. Stroudsberg, PA: Dowden, Hutchinson & Ross.
Quilici-Matteucci, F. (1999). Women's self-reported experience and action in relation to their abusive partner: A holistic, developmental, systems-oriented analysis. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Clark University, Worcester, MA.
Quirk, M., Ciottone, R., Minami, H., Wapner, S., Yamamoto, T., Ishii, S., Lucca-Irizarry, N., & Pacheco, A. (1986). Values mothers hold for handicapped and non-handicapped preschool children in Japan, Puerto Rico, and the United States Mainland. International Journal of Psychology, 21, 463–485.
Raeff, C. (1990). General factors and precipitating events influencing action: Initiation of a weight loss regimen. Unpublished Master's Thesis, Clark University, Worcester, MA.
Reischauer, E. O. (1981). The Japanese. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Rioux, S., & Wapner, S. (1986). Commitment to use of automobile seat belts: An experiential analysis. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 6, 189.
Schouela, D. A., Steinberg, L. M., Leveton, L. B., & Wapner, S. (1980). Development of the cognitive organization of an environment. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science, 12 (1), 1–16.
Shapiro, E. (1973, April). The effect of verbalization of plans on sequence learning by children and adults. Presented at University of New Hampshire Psychology Conference, Durham.
Shapiro, E., Rierdan, J., & Wapner, S. (1972). Effect of articulating plans of how to solve a sequence learning task on the learning of this task by children and adults. Unpublished manuscript, Clark University, Worcester, MA.
Siegel, E. L. (1951). Genetic parallels of perceptual structurization in paranoid schizophrenia. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Clark University, Worcester, MA.
Siegler, R. S., & Crowley, K. (1991). The microgenetic method: Adirect means for studying cognitive development. American Psychologist, 46, 606–620.
Tirelli, L. (1992). General factors involved in smoking cessation: A cross-cultural study. Unpublished manuscript, Clark University, Worcester, MA.
Triandis, H. D. (1995). Individualism & collectivism. Colorado: Westview Press.
Wapner, S. (1968). Age changes in perception of verticality and of the longitudinal body axis under body tilt. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 6, 543–555.
Wapner, S. (1972, August). An organismic-developmental approach to the study of man-environment transactions. Presented as Special Lecture at Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan.
Wapner, S. (1976). Environmental transitions. In C. Winsor (Ed.), Schooling: A social moral force. Lucy Sprague Mitchell Memorial Conference (pp. 16–42). New York: Bank Street College of Education.
Wapner, S. (1977). Environmental transition:Aresearch paradigm deriving from the organismic-developmental systems approach. In L. van Ryzin (Ed.), Wisconsin Conference on Research Methods in Behavior Environment Studies Proceedings (pp. 1–9). Madison: University of Wisconsin.
Wapner, S. (1986). An organismic-developmental systems approach to the analysis of experience and action. Paper presented at the Conference on Holistic Approaches to the Analysis of Experience and Action. University of Catania, Sicily, Italy.
Wapner, S. (1987). A holistic, developmental, systems-oriented environmental psychology: Some beginnings. In D. Stokols & I. Altman (Eds.), Handbook of environmental psychology (pp. 1433–1465). New York: Wiley.
Wapner, S. (1988). Unifying psychology: Strategies from a holistic, developmental, systems perspective. Hiroshima Forum for Psychology, 13, 1–15.
Wapner, S. (1990). Introduction: Symposium on centennial of the founding of the psychology department and laboratory at Clark University. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences, 26 (2), 107–113.
Wapner, S. (1995). Toward integration: Environmental psychology in relation to other subfields of Psychology. Environment and Behavior, 27 (1), 9–32.
Wapner, S. (1998). A holistic, developmental, systems-oriented perspective: Child-environment relations. In D. Görlitz, H. J. Harloff, G. Mey, & J. Valsiner (Eds.), Children, cities, and psychological theories: Developing relationships (pp. 278- 300). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Wapner, S., Ciottone, R., Hornstein, G., McNeil, O., & Pacheco, A. M. (1983). An examination of studies of critical transitions through the life cycle. In S. Wapner & B. Kaplan (Eds.), Toward a holistic developmental psychology (pp. 111–132). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Wapner, S., & Demick, J. (1990). Development of experience and action: Levels of integration in human functioning. In G. Greenberg & E. Tobach (Eds.), Theories of the evolution of knowing. The T.C. Schneirla Conference Series (Vol. 4, pp. 47–68). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Wapner, S., & Demick, J. (1998). Developmental analysis:A holistic, developmental, systems oriented perspective. In R. M. Lerner (Ed.), Theoretical models of human development, Vol. 4. Handbook of child psychology (5th ed., Editor-in-chief: W. Damon). New York: Wiley.
Wapner, S., Demick, J., & Damrad, R. (1988, April). Transition to retirement: Eight years after. Presented at the Annual Meetings of Eastern Psychological Association, Buffalo, NY.
Wapner, S., Demick, J., Inoue, W., Ishii, S., & Yamamoto, T. (1986). Relations between experience and action: Automobile seat belt usage in Japan and the United States. In W. H. Ittelson, M. Asai, & M. Carr (Eds.), Proceedings of the 2nd USA/Japan Seminar on Environment and Behavior (pp. 279- 295). Tucson: Department of Psychology, University of Arizona.
Wapner, S., Demick, J., Yamamoto, T., & Minami, H. (Eds.) (2000). Theoretical perspectives in environment-behavior research: Underlying assumptions, research problems, and methodologies. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers.
Wapner, S., Fujimoto, J., Imamichi, T., Inoue, Y., & Toews, K. (1997). Sojourn in a New Culture: Japanese Students in American Universities and American Students in Japanese Universities. In S. Wapner, J. Demick, T. Yamamoto, & T. Takahashi (Eds.), Handbook of Japan-US environmentbehavior research: Towards a transactional approach. New York: Plenum.
Wapner, S., Kaplan, B., & Ciottone, R. (1981). Self-world relationships in critical environmental transitions: Childhood and beyond. In L. Liben, A. Patterson, & N. Newcombe (Eds.), Spatial representation and behavior across the life span (pp. 251–282). New York: Academic Press.
Wapner, S., Quilici-Matteucci, F., & Cool, K. (1991). Crosscultural comparison of necessities, amenities and luxuries in the physical, interpersonal and sociocultural aspects of the environment. In T. Niit, M. Raudsepp, & K. Liik (Eds.), Environment and social development. Proceedings of the East-West Colloquium in Environmental Psychology (pp. 47–56). Tallinn, Estonia: Tallinn Pedagogical Institute.
Wapner, S., Quilici-Matteucci, F., Yamamoto, T., & Ando, T. (1990). Cross-cultural comparison of the concept of necessity, amenity and luxury. In Y. Yoshitake, R. B. Bechtel, T. Takahashi, & M. Asai (Eds.), Current Issues in Environment Behavior Research. Proceedings of the Third Japan-United States Seminar (held in Kyoto, Japan; pp. 21–32). Tokyo: University of Tokyo.
Wapner, S., & Werner, H. (1957). Perceptual development. Worcester, MA: Clark University Press.
Wapner, S., & Werner, H. (1965). An experimental approach to body perception from the organismic-developmental point of view. In S. Wapner and H. Werner (Eds.), The body percept (pp. 9–25). New York: Random House.
Weinstein, N. D. (1989). Effects of personal experience on selfprotective behavior. Psychological Bulletin, 105, 31–50.
Werner, H. (1937). Process and achievement: A basic problem of education and developmental psychology. Harvard Educational Review, 7, 353–368.
Werner, H. (1940/1957). Comparative psychology of mental development. New York: Harper. (2nd ed., Chicago, Follett, 1948; 3rd ed., New York: International Universities Press).
Werner, H. (1957). The concept of development from a comparative and organismic point of view. In D. B. Harris (Ed.). The concept of development: An issue in the study of human behavior. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Werner, H., & Kaplan, B. (1956). The developmental approach to sognition: Its relevance to the psychological interpretation of anthropological and ethnological data. American Anthropologist, 58, 866–880.
Werner, H. & Kaplan, B. (1963). Symbol formation. New York: Wiley.
Werner, H., & Wapner, S. (1952). Toward a general theory of perception. Psychological Review, 59, 324–338.
Winnicott, D. W. (1958). Through pediatrics to psychoanalysis. New York: Basic Books.
Winnicott, D. W. (1971). Playing and reality. New York: Basic Books.
Witkin, H. A. (1965). Heinz Werner: 1890-1964. Child Development, 30, 307–328.
Witkin, H. A., Lewis, H. B., Hertzman, M., Machover, K., Meisner, P. B., & Wapner, S. (1954). Personality through perception. New York: Harper & Brothers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wapner, S. Person-in-Environment Transitions: Developmental Analysis. Journal of Adult Development 7, 7–22 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009546900630
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009546900630