Abstract
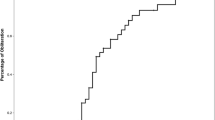
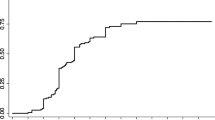
Between 1992 and 1996 γ-knife radiosurgery was performed on 192 patients with the diagnosis of brain intracerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVM) at Na Homolce Hospital, Prague. The largest diameter of the nidus ranged between 0.6–5.4 cm, median 2.2 cm. The nidus volume ranged 0.15–28.6 cm2, median 3.9 cm2. Thus far, the angiographic evaluation after radiosurgery was performed in 162 patients. The treatment result reference was defined as follows: the interval with a lower limit represented by the percentage of the complete obliteration in the whole group of patients and the upper limit represented by the percentage of the obliteration only in the group of patients with control angiography. The total obliteration of the AVM 1 year after radiosurgery was reached in 18–32% patients, after 2 years in 59–72%, after 3 years in 69–81%, and 4 years after radiosurgery in 71–93% patients. The morbidity of radiosurgery was 6% and, in a majority of the cases, was caused by the postirradiation edema and resolved after corticotherapy. The improvement of secondary epilepsy was observed in 35% of the patients and the improvement of the neurological status in 50%. The mortality of radiosurgical procedure itself was zero. The risk of mortality of the patients with AVM treated with the γ-knife was related to the latent period from treatment until complete obliteration. This period took between 1–3 years when the natural risk of the repeated hemorrhage was the same as that in the nontreated patient. The rebleeding occurred in eight patients; three of them died and five patients were without neurological sequela. If the obliteration did not occur up to 3 years after the γ-knife radiosurgery, reirradiation was indicated. AVM of Spetzler grade I–III proved to have a high rate of obliteration after γ-knife radiosurgery, while only one-third of patients with Spetzler grade IV obliterated after the first radiosurgery. Radiosurgery was not indicated for AVMs Spetzler grade V. AVMs with an average diameter up to 3 cm were good indications for primary radiosurgery as a noninvasive treatment. In AVMs with the average diameter larger than 3 cm, radiosurgery, microsurgery, and embolization are the methods of choice and the radical treatment may require an adequate combination of these methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Brown RD, Wiebers DO, Forbes G, O'Fallon WM, Piepgras DO, Marsh WR, Maciunas RJ: The natural history of unruptured intracranial arteriovenous malformations, J Neurosurg 68:352–357, 1988
Brown RD, Wiebers DO, Torner JC, O'Fallon WM: Frequency of intracranial hemorrhage as a presenting symptom and subtype analysis: a population-based study of intracranial vascular malformations in Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Neurosurg 85:29–32, 1996
Ondra SL, Troupp H, George ED, Schwab K: The natural history of symptomatic arteriovenous malformations of the brain: a 24-year follow-up assessment, J Neurosurg 73:387–391, 1990
Colombo F, Pozza F, Chierego G, Casentini L, De Luca G, Francescon P: Linear accelerator radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: an update. Neurosurgery 34:14–21, 1994
Flickinger JC, Pollock BE, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD: A doseresponse analysis of rateriovenous malformation obliteration after radiosurgery. Interm. J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 36:873–879, 1996
Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, et al.: Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Neurosurg 75:512–524, 1991
Steiner L, Lindquist C, Adler JR, Torner JC, Alves W, Steiner M: Clinical outcome of radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 77:1–8, 1992
Vladyka V, Liščák R, Šimonová G, Šubrt O, Novotny´ J: Léčení Nemocných s AVM gama nožem v Nemocnici Na Homolce v prvních 3 letech. Čes a Slov Neurol Neurochir 60/93:253–260, 1997
Benati A: Interventional neuroradiology for the treatment of inaccesible arterio-venous malformations. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 118:76–79, 1992
Frizzel RT, Wink S, Fisher WS: Cure, morbidity, and mortality associated with embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations: a review of 1246 patients in 32 series over a 35-year period. Neurosurgery 37:1031–1040, 1995
Gobin YP, Laurent A, Marienne L et al.: Treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations by embolization and radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 85:19–28, 1996
Krajina A, Náhlovsky´ J, Malec R, et al.: Postavení embolizace při lečbě mozkových arteriovenózních malformací. Čes a Slov Neurol Neurochir 60/93:185–191, 1997.
Vinuela F, Dion JE, Fox AJ: Interventional neuroradiologocy for intracranial arteriovenous malformations. In: Barrow DL (ed.), Intracranial Vascular Malformation. AANS, Illinois 1990, pp. 169–178
Friedman WA, Blatt DL, Bova FJ, Buatti JM, Mendenhall WM, Kubilis PS: The risk of hemorrhage after radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 84:912–919, 1996
Pollock BE, Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Maitz A, Flickinger JC: Patient outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery for ‘operable’ arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 35:1–8, 1994
Pollock BE, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD, Bisosonette DJ, Kondziolka D: Hemorrhage risk after stereotactic radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 38:652–661, 1996
Karlsson B, Lindquist C, Steiner L: Effect of gamma knife surgery on the risk of rupture prior to AVM obliteration. Minimum Invasive Neurosurg 39:21–27, 1996
Beneš V ml, Mohapl M: Chirurgie arteriovenozních malformací. Č es a Slov Neurol Neurochir 61/94:206–214, 1998
Pikus HJ, Beach ML, Harbaugh RE: Microsurgical treatment of arteriovenous malformations: analysis and comparison with stereotactic radiosurgery: J Neurosurg 88:641–646, 1998
Schaller C, Schramm J: Microsurgical results for small arteriovenous malformations accessible for radiosurgical or embolization treatment. Neurosurgery 40:664–674, 1997
Morgan MK, Johnston IH, Hallinan JM, Neville CW: Complications of surgery for arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Neurosurg 78:176–182, 1993
Spetzler RF, Martin NA: A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 65:476–483, 1986
Steiner L, Lindquist C, Cail W, Karlsson B, Steiner M: Microsurgery and radiosurgery in brain arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 79:647–652, 1993
Heffez DS, Osterdock RJ, Alderete L, Grutsch J: The effect of incomplete patient follow-up on the reported results of AVM radiosurgery. Surg Neurol 49:373–384, 1998
Morgan MK, Sekhon LHS, Finfer S, Grinnell V. Delayed neurological deterioration following resection of arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Neurosurg 90:695–701, 1999
Karlsson B, Lindquist C, Steiner L: Prediction of obliteration after gamma knife surgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 40:425–431, 1997
Firlik AD, Levy EI, Kondziolka D, Yonas H: Staged volume radiosurgery followed by microsurgical resection: a novel treatment for giant cerebral arteriovenous malformations: technical case report. Neurosurgery 43:1223–1228, 1998
Steinberg GK, Chang SD, Levy RP, Marks MP, Frankel K, Marcellus M: Surgical resection of large incompletely treated intracranial arteriovenous malformations following stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 84:920–928, 1996
Heros RC, Korosue K, Diebold PM: Surgical excision of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: late results. Neurosurgery 26:570–578, 1990
Korosue K, Heros RC: Complications of complete surgical resection of AVMs of the brain. In: Barrow DL(ed.), Intracranial Vascular Malformation. AANS, Illinois 1990, pp. 157–168
Miyasaka Y, Yada K, Ohwada T, et al.: Retrograde thrombosis of feeding arteries after removal of arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 72:540–545, 1990
Spetzler RF, Wilson CB, Weinstein P, Mehdorn M, Townsend J, Telles D: Normal perfusion pressure pressure breakthrough theory. Clin Neurosurg 25:651–672, 1978
Hudgins WR: Decision analysis of the treatment of AVMs with radiosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 61(suppl 1):11–19, 1993
Deruty R, Pelissou-Guyotat I, Amat D, et al.: Complications after multidisciplinary treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 138:119–131, 1996
Dawson RC, Tarr RW, Hecht ST, Jungreis CA, Lunsford LD, Coffey R, Horton JA: Treatment of arteriovenous malformations of the brain with combined embolization and stereotactic radiosurgery: results after 1 and 2 years. AJNR 11:857–864, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liščák, R., Vladyka, V., Šimonová, G. et al. Results of γ-Knife Radiosurgery of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Journal of Radiosurgery 3, 55–65 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009529332761
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009529332761