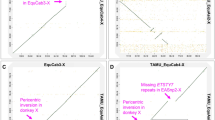
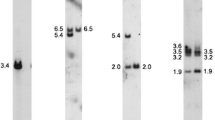
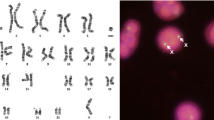
Abstract
The hypothesis that the conservation of sex-chromosome-linked genes among placental mammals could be extended to the horse genome was tested using the UCDavis horse–mouse somatic cell hybrid (SCH) panel. By exploiting the fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) technique to localize an anchor locus, X-inactivation-specific transcript (XIST) on the horse X chromosome, together with the fragmentation and translocation of the X- and Y-chromosome fragments in a somatic cell hybrid panel, we regionally assigned 13 type I and 13 type II (microsatellite) markers to the horse X- and Y-chromosomes. The synteny groups that correspond to horse X- and Y-chromosomes were identified by synteny mapping of sex-specific loci zinc finger protein X-linked (ZFX), zinc finger protein Y-linked (ZFY) and sex-determining region Y (SRY) on the SCH panel. A non-pseudoautosomal gene in the human steroid sulfatase (STS) was identified in both X- and Y-chromosome- containing clones. The regional order of the X-linked type I markers examined in this study, from Xp- to Xq-distal, was [STS- X, the voltage-gated chloride channel 4 (CLCN4)], [ZFX, delta- aminolevulinate synthase 2 (ALAS2)], XIST, coagulation factor IX (F9) and [biglycan (BGN), equine F18, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)] (precise marker order could not be determined for genes within the same brackets). The order of the Y-linked type I markers was STS-Y, SRYand ZFY. These orders are the same arrangements as reported for the human X- and Y-chromosomes, supporting the conservation of genomic organization between the human and the horse sex chromosomes. Regional ordering of X- linked type I and microsatellite markers provides the first integration of type I and type II markers in the horse X chromosome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasen E, Medrano JF (1990) Amplification of the ZFX and ZFY genes for sex identification in humans, cattle, sheep and goat. Bio/Tech 8: 1279–1281.
Regional assignment of equine chromosome X-and Y-specific markers 53 Archer RK (1961) True haemophilia (haemophilia A) in a Thoroughbred. Vet Rec 73: 338–340.
Bailey E, Graves KT, Cothran EG, Reid R, Lear TL, Ennis RB (1995) Synteny-mapping horse microsatellite markers using a heterohybridoma panel. Anim Genet 26: 177–180.
Bickel LA, Shiue Y-L, Pidgeon D et al. (1998) The use of RAPD and microsatellite markers to generate a preliminary synteny map for the horse. Proceedings of the 6th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production, Armidale, Australia, 24: 424–427.
Bowling AT, Millon LV, Dileanis S (1997) Physical mapping of genetic markers to chromosome 30 using a trisomic horse and evidence for a maternal origin of the extra chromosome. Chromosome Res 5: 429–431.
Bruno WJ, Knill E, Balding DJ et al. (1995) Efficient pooling designs for library screening. Genomics 26: 21–30.
Caetano AR, Pomp D, Murray JD, Bowling AT (1999a) Comparative mapping of 18 equine type I genes assigned by somatic cell hybrid analysis. Mamm Genome 10: 271–276.
Caetano AR, Lyons LA et al. (1999b) A comparative gene map of the horse (Equus caballus). Genome Res (in press).
Chang C, Yoshida A (1994) Cloning and characterization of the gene encoding mouse mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase. Gene 148: 331–336.
Chevalet C, Corpet F (1986) Statistical decision rules concerning synteny or independence between markers. Cytogenet Cell Genet 43: 132–139.
Comparative Genome Organization (1996) First international workshop. Mamm Genome 7: 717–734.
Coogle L, Bailey E, Reid R, Russ M (1996a) Equine dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at loci LEX002,-003,-004,-005,-007,-008,-009,-010,-011,-013 and-014. Anim Genet 27: 126–127.
Coogle L, Reid R, Bailey E (1996b) Equine dinucleotide repeat loci from LEX015 to LEX024. Anim Genet 27: 217–218.
Coogle L, Reid R, Bailey E (1996c) Equine dinucleotide repeat loci from LEX025 to LEX033. Anim Genet 27: 289–290.
Eggleston-Scott ML, DelValle A, Bautista MM, Dileanis S, Wictum E, Bowing AT (1997) Nine equine dinucleotide repeats at microsatellite loci UCDEQ136, UCDEQ405, UCDEQ412, UCDEQ425, UCDEQ437, UCDEQ467, UCDEQ487, UCDEQ502 and UCDEQ505. Anim Genet 28: 370–371.
George LA, Miller LM, Valberg SJ, Mickelson JR (1998) Fourteen new polymorphic equine microsatellites. Anim Genet 29, 469–470.
Godard S, Vaiman D, Oustry A et al. (1997) Characterization, genetic and physical mapping analysis of 36 horse plasmid and cosmid-derived microsatellites. Mamm Genome 8: 745–750.
Godard S, Schibler L, Oustry A, Cribiu EP, Guérin G (1998) Construction of a horse BAC library and cytogenetical assignment of 20 Type I and microsatellite markers. Mamm Genome 9: 633–637.
Griffiths R, Tiwari B (1993) Primers for the differential amplification of the sex-determining region Y gene in a range of mammal species. Mol Ecol 2: 405–406.
Guérin G, Bailey E, Bernoco D et al. (1999) Report of the International Equine Gene Mapping Workshop: Male linkage map. Anim Genet (in press).
Hsu LC, Bendel RE, Yoshida A (1988) Genomic structure of the human mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase gene. Genomics 2: 57–65.
Johansson J, von Bahr-Lindstrom H, Jeck R, Woenckhaus C, Jornvall H (1988) Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase from horse liver. Correlations of the same species variants for both the cytosolic and the mitochondrial forms of an enzyme. Eur J Biochem 172: 527–534.
Lear TL, Adams MH, Sullivan ND, McDowell KJ, Bailey E (1998a) Assignment of the horse progesterone receptor (PGR) and estrogen receptor (ESR1) genes to horse chromosomes 7 and 31, respectively, by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 82: 110–111.
Lear TL, Coogle LD, Bailey E (1998b) Assignment of the horse mitochondrial glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase 2 (GOT2) and v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KIT) to horse chromosome 3 by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 82: 112–113.
Lear TL, Breen M, Ponce de Leon FA et al. (1998c) Cloning and chromosomal localization of MX1 and ETS2 to chromosome 26 of the horse (Equus caballus). Chromosome Res 6: 333–335.
Lincoln SE, Daly MJ, Lander ES (1991) Primer: a computer program for automatically selecting PCR primers. v. 0.5, May 1991.
Lindgren G, Sandberg K, Persson H et al. (1998) A primary male autosomal linkage map of the horse genome. Genome Res 8: 951–966.
Lyons LA, Laughlin H, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Womack JE, O'Brien SJ (1997) Comparative anchor tagged sequences (CATS) for integrative mapping of mammalian genomes. Nat Genet 15: 47–56.
Meyer AH, Valberg SJ, Hillers KR, Schweitzer JK, Mickelson JR (1997) Sixteen new polymorphic equine microsatellites. Anim Genet 28: 69–70.
O'Brien SJ, Womack JE, Lyons LA, Moore KJ, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG (1993) Anchored reference loci for comparative genome mapping in mammals. Natl Genet 3: 103–112.
Ohno S (1967) Conservation of the original X and homology of the X-linked genes in placental mammals. In: Sex Chromosomes and Sex-linked Genes. New York: Spring-Verlag, pp 46–72.
Palmer S, Perry J, Ashworth A (1995) A contravention of Ohno's law in mice. Natl Genet 10: 472–476.
Raudsepp T, Fronicke L, Scherthan H, Gustavsson I, Chowdhary BP (1996) Zoo-FISH delineates conserved chromosomal segments in horse and man. Chromosome Res 4: 218–225.
Rugarli EI, Adler DA, Borsani G et al. (1995) Different chromosomal localization of the Clcn4 gene in Mus spretus and C57BL/ 6J mice. Natl Genet 10: 466–471.
Salido EC, Li XM, Yen PH, Martin N, Mohandas TK, Shapiro LJ (1996) Cloning and expression of the mouse pseudoautosomal steroid sulfatase gene (Sts). Natl Genet 13: 83–86.
Senese C, Penedo MCT, Shiue Y-L, Bowling AT, Millon LV (1999) A HaeIII PCR-RFLP in the ZFY/ZFX gene of horses. Anim Genet (in press).
Shiue Y-L, Bickel LA, Caetano AR et al. (1999) A synteny map of the horse genome comprised of 240 microsatellite and RAPD markers. Anim Genet 29: 1–9.
Shizuya H, Birren B, Kim UJ et al. (1992) Cloning and stable maintenance of 300-kilobase-pair fragments of human DNA in Escherichia coli using an F-factor-based vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 8794–8797.
Toder R, Gläser B, Schiebel K et al. (1997) Genes located in and near the human pseudoautosomal region are located in the X-Y pairing region in dog and sheep. Chromosome Res 5: 301–306.
Tozaki T, Hirota K, Mashima S, Tomita M, Mukoyama H (1998) Cloning and characterization of the equine F18 gene, which has a novel exon. Anim Genet 29: 381–384.
Trask BJ (1991) DNA sequence localization in metaphase and interphase cells by fluorescence in situ hybridization. In: Hamkalo BA, ed. Methods in Cell Biology. San Diego: Academic Press, Vol. 35, pp 3–35.
Trujillo JM, Walden B, O'Neil P, Anstall HB (1965) Sex-linkage of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the horse and donkey. Science 148: 1603–1604.
Van Haeringen WA, Van de Goor LH, Van der Hout N, Lenstra JA (1998) Characterization of 24 equine microsatellite loci. Anim Genet 29: 153–156.
Van Slegtenhorst MA, Bassi MT, Borsani G et al. (1994) A gene from the Xp22.3 region shares homology with voltage-gated chloride channels Hum Mol Genet 3: 547–552
Vogt PH, Affara N, Davey P et al. (1997) Report of the third international workshop on Y chromosome mapping 1997. Cytogenet Cell Genet 79: 1–20.
Yen PH, Marsh B, Allen E et al. (1988) The human X-linked steroid sulfatase gene and a Y-encoded pseudogene: evidence for an inversion of the Y chromosome during primate evolution. Cell 55: 1123–1136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiue, YL., Millon, L.V., Skow, L.C. et al. Synteny and Regional Marker Order Sssignment of 26 type I and Microsatellite Markers to the Horse X- and Y-Chromosomes. Chromosome Res 8, 45–55 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009275102977
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009275102977