Abstract
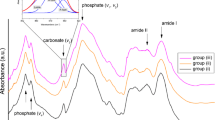
Selenium, being an essential mineral in the mammalian diet, is important in providing protection against oxidative damage. Numerous in vitro studies of selenium compounds reveal a very high correlation between catalytic activity of selenium compounds and toxicity. The present study was designed to investigate the effects of dietary selenium on the biomechanical properties of bone. New born rats of both sexes were fed with either a control, or a selenium- and vitamin E-deficient, or a selenium-excess and vitamin E-adequate diet. We obtained the stiffness (modulus of elasticity) of bones (femur and tibia) by tensile test for all groups considered. Both the deficient and the excess groups have decreased biomechanical strength with respect to the control group. To support our biomechanical results for both experimental groups, X-ray diffraction analysis and FTIR spectroscopic study were performed on the femurs and tibiae. The X-ray diffraction analysis showed that the intensities of the peak observed at around 2θ°=31.820, in the control femur and tibia are stronger than the intensities of the corresponding peak of two experimental groups. In FTIR spectroscopy, the disappearance and/or reduction of the intensities of some carbonate bands in the two experimental groups indicate that there is a decrease in crystallinity and mineral contents which, together with X-ray diffraction analysis, correlate very well with the biomechanical data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anundi I, Hogberg J, Stahl A. 1982Involvement of glutathione reductase in selenite metabolism and toxicity, studied in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 50, 113–123
Betts F, Blumental NC, Posner AS. 1981Bone mineralization, J Crystal Growth 53, 63–73
Boskey AL. 1990Bone mineral and matrix. Are they altered in osteoporosis? The Orthop Clin North Am 21(1), 19–29
Chen X, Yang G, Chen J, Chen X, Wen Z, Ge K. 1980Studies on the relationships of selenium and Keshan disease. Biol Trace Element Res 2, 91–107
Cummins LM, Martin JL. 1967Are selenocystine and selenomethionine synthesized in vivo from sodium selenite in mammals. Biochemistry 6, 3163–6168
Dalay N, Turan B, Koc E, Afrasyap L, Delilbasi E. 1993The effects of in vivo selenium supplementation on the amplitude of the spontaneous contractions and the responses to acetylcholine in isolated rabbit ileum. Neurobiology 1(1), 83–90
Dickson RC, Tappel AL. 1969Reduction of selenocystine by cysteine or glutathione. Arch Biochem Biophysics 130, 547–550
Ginsberg JS, Kowalchuk G, Hirsch J, Edwards PB, Burrows R, Coates G, Webber C. 1990Heparin effect on bone density. Thrombosis Haemostasis 64(2), 286–289
Glimcher MJ. 1976In Greepp RO, Astwood EBB, eds.: Handbook of Physiology: Endocrinology, Vol. 7, Eds. Washington, DC: Am. Physiological Soc.
Glimcher MJ, Bonar LC, Grynpas MD, Landis WJ, Roufosse AH. 1981Recent studies of bone mineral: is the amorphous calcium phosphate theory. J Crystal Growth 53, 100–119
Hakkarainen J, Lindberg P, Bengtsson G, Jonsson L, Lannek N. 1978Requirement for selenium (as selenite) and vitamin E (as a-tocopherol) in weaned pigs. III. The effect on the development of the VESD syndrome of varying selenium levels in a low-tocopherol diet. J Anal Sci 46, 1001–1008
Lin-Shiau SY, Liu SH, Fu WM. 1989Studies on the contracture of the mouse diaphragm induced by sodium selenite. Eur J Pharmacol 167, 137–146
Matzsch T, Bergqvist D, Hedner U, Nilsson B, Østergaard P. 1990Effects of low molecular weight heparin and unfragmented heparin on induction of osteoporosis in rats. Thrombosis Haemostasis 63(3), 505–509
Olson JA, Kobayashi S. 1992Antioxidants in health and disease: overview. Poc Soc Exp Biol Med 200, 245–247
Olson OE, Novacek EJ, Whitehead EI, Palmer IS. 1970Investigation on selenium im wheat. Phytochemistry 9, 1181–1188
Rey C, Beshah K, Griffin R, Glimcher MJ. 1991a Structural studies of the mineral phase of calcifying cartilage. J Bone Mineral Res 6, 515–525
Rey C, Renugopalakrishnan V, Collins B, Glimcher MJ 1991b Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Study of the Carbonate Ions in Bone Mineral During Aging. Calcif Tissue Int 49, 251–258
Sasaki S, Iwata H, Ishigura N, Habuchi O, Miura T. 1994Lowselenium diet, bone and articular cartilage in rats. Nutrition 10(6), 538–543
Schwarz K, Foltz CM. 1957Selenium as an integral part of factor 3 against necrotic dietary liver generation. J Am Chem Soc 79, 3292–3293
Scott ML, Olson G, Krook L, Brown WR. 1967Seleniumresponsive myopathies of myocardium and of smooth muscle in the young poult. J Nutr 91, 573–583
Severcan F, Kazanci N, Baykal U, Süzer S. 1995IR and Turbidity studies of vitamin E-cholesterol-phospholipid membrane interactions. Bioscience Reports 15(4), 221–229
Smyth JBA, Wang JH, Barlow RM, Humphreys DJ, Robins M, Stodulski JBJ. 1990Experimental acute selenium intoxication in lambs. J Comp Path 102, 197–209
Sokoloff L. 1985Endemic forms of osteoarthritis. Clin Rheum Dis 11, 187–212
Spallholz, JE. 1994On the nature of selenium toxicity and carcinostatic activity. Free Rad Biol Med 17(1), 45–64
Turan B, Desilets M, Açan LN, Hotomaroglu Ö, Vannier C, Vassort G. 1996Oxidative effects of selenite on rat ventricular contractility and Ca movements. Cardiovasc Res 32, 351–361
Turan B, Hotomaroglu O, Kilic M, Demirel-Yilmaz E. 1999Cardiac dysfunction induced by low and high diet antioxidant levels comparing selenium and vitamin E in rats. Regulatory Tox Pharmacol 29, 132–150
Turan B, Zaloglu N, Koc E, Saran Y, Akkas N. 1997a Dietary selenium and vitamin E induced alterations in some rabbit tissues. Biol Trace Elem Res 58(3–4), 237–253
Turan B, Koc E, Zaloglu N. 1997b Deficiency and toxicity of selenium alter the acetycholine stimulated contraction of isolated rabbit ileum. Trace Elem Electrolytes 14(1), 13–18
Turan B, Balcik C, Akkas N. 1997c Effect of dietary selenium and vitamin E on the biomechanical properties of rabbit bones. Clinical Rheumatol 16(5), 441–449
Turner CH, Burr DB. 1993Basic biomechanical measurements of bone. A Tutorial Bone 14, 595–608
Venugopal B, Luckey TD. 1974Toxicology of non-radioactive heavy metals and their salts. Environ Qual Saf Suppl 2, 4–73
Yang C, Wolf E, Roser K, Delling G, Muller PK. 1993a Selenium deficiency and fulvic acid supplementation induces fibrosis of cartilage and disturbs subchondral ossification in knee joints of mice: an animal model study of Kashin-Beck disease. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 423(6), 483–491
Yang C, Niu C, Bodo M, Gabriel E, Notbohm H, Wolf E, Muller PK. 1993b Fulvic acid supplementation and selenium deficiency distrub the structural integrity of mouse skeletal tissue. J Biochem 289, 829–835
Young JD, Crowley C, Tucker EM. 1981Haemolysis of normal and glutathione-deficient erythrocytes by selenite and tellurite. Biochem Pharmacol 30, 2527–2530
Ytrehus K, Ringstad J, Myklebust R, Norheim G, Mjos OD. 1988 The selenium-deficient rat heart with special reference to tolerance against enzymatically generated oxygen radicals. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 48, 289–295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turan, B., Bayari, S., Balcik, C. et al. A biomechanical and spectroscopic study of bone from rats with selenium deficiency and toxicity. Biometals 13, 113–121 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009206206324
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009206206324