Abstract
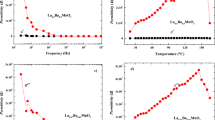
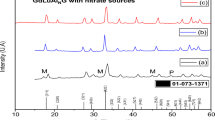
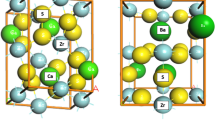
The interaction of perovskite-like solid solutions Sr6 – 2x Ta2 + 2x O11 + 3x (x= 0–0.28) with water is studied, along with dependences of the solutions' conductivity on their composition and the atmosphere's temperature and humidity. The Sr6 – 2x Ta2 + 2x O11 + 3x phases with high concentrations of structural oxygen vacancies are high-temperature mixed oxygen–hydrogen ionic conductors whose conduction is sensitive to the presence of water vapor up to 900°C. According to a thermogravimetric study, the amount of water incorporated into the complex-oxide matrix is proportional to the concentration of structural oxygen vacancies. The process of water incorporation is considered in terms of crystalline and chemical properties of the structure. The oxygen-deficient perovskites containing coordination-unsaturated metalatoms can reconstruct their coordination polyhedron by adding water molecules, with subsequent partial dissociation of water to hydroxyl groups. The proposed mechanism explains different states of water in the oxide and a two-stage nature of its removal: water molecules coordinating the metal atom and those surrounding OH–leave the core in the first and second stages, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Pal'guev, S.F., Vysokotemperaturnye protonnye tverdye elektrolity (High-Temperature Solid State Protonic Electrolytes), Yekaterinburg: Ural. Otd. Ross. Akad. Nauk, 1998.
Du, Y. and Nowick, A.S., Solid State Ionics, 1996, vol. 91, p. 85.
Toyda, K., Ferroelectrics, 1984, vol. 51, p. 239.
Animitsa, I.E. and Neiman, A.Ya., Abstracts of Papers, III Vses. simpoz. “Tverdye elektrolity i ikh analiticheskoe primenenie” (III All-Union Symp. “Solid Electrolytes and Their Analytical Application”), Minsk: Belarus. Gos. Univ., 1990, p. 37.
Animitsa, I.E., Cand. Sci. (Chem.) Dissertation, Sverdlovsk, 1991.
Neiman, A., Animitsa, I., Glockner, R., and Norby, T., Proc. 11th Int. Conf. on Solid State Ionics, Honolulu, 1997, p. 96.
Glockner, R., Neiman, A., Norby, T., and Larring, Y., Proc. 9th Int. Conf. on Solid State Protonic Conductors, Bled (Slovenia), 1998, p. 13.
Glockner, R., Neiman, A., Larring, Y., and Norby, T., Solid State Ionics, 1999, vol. 125, p. 369.
Galasso, F. and Darby, W., J. Phys. Chem., 1962, vol. 66, p. 131.
Galasso, F. and Pyle, J., J. Phys. Chem., 1963, vol. 67, p. 1561.
Browall, K.W., Muller, O., and Doremus, R.H., Mater. Res. Bull., 1976, vol. 11, p. 1475.
Leshchenko, P.P., Lykova, L.N., Kovba, L.M., and Ippolitova, E.A., Zh. Neorg. Khim., 1982, vol. 27, p. 1285.
Spitsyn, V.I., Ippolitova, E.A., Kovba, L.M., et al., Zh. Neorg. Khim., 1982, vol. 27, p. 827.
Neiman, A.Ya., Podkorytov, A.L., and Zhukovskii, V.M., Phys. Status Solidi A, 1987, vol. 101, p. 371.
Lecomte, J., Loup, J.P., Bosser, G., et al., Phys. Status Solidi A, 1981, vol. 65, p. 743.
Lecomte, J., Loup, J.P., Bosser, G., et al., Phys. Status Solidi A, 1981, vol. 66, p. 551.
Lecomte, J., Loup, J.P., Bosser, G., et al., Phys. Status Solidi A, 1982, vol. 69, p. 359.
Norby, T. and Larring, Y., Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 1997, vol. 2, p. 593.
Norby, T., Korean J. Ceram., 1998, vol. 4, p. 128.
Non-stoichiometric Compounds, Mandelcorn, L., Ed., New York: Academic, 1964.
Hagenmuller, P., Pouchard, M., and Grenier, J.C., J. Mater. Educ., 1990, vol. 12, p. 297.
Rao, C.N.R. and Gopalakrishnan, J., New Direction in Solid State Chemistry, Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1997.
Ziolkowski, J. and Dziembai, L., J. Solid State Chem., 1985, vol. 57, p. 291.
Neiman, A.Ya., Animitsa, I.E., and Gorodetskaya, I.E., Zh. Fiz. Khim., 1996, vol. 70, p. 242.
Starikova, Z.A., Yanovskii, A.I., Cheburekov, D.E., et al., Zh. Neorg. Khim., 1998, vol. 43, p. 1308.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Animitsa, I.E., Neiman, A.Y., Sharafutdinov, A.R. et al. Strontium Tantalates with a Perovskite Structure: Their Conductivity and High-Temperature Interaction with Water. Russian Journal of Electrochemistry 37, 266–272 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009025313816
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009025313816