Abstract
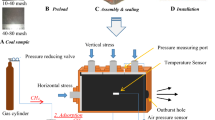
This paper examines the influence of sorbed gas type and pressure on the strength of coal. Particular attention is focused on the influence of gas type and pressures on drillability characteristics of coal and particle size distribution of drill cuttings. Drillability of coal has a strong bearing on the strength properties of coal. Based on fracture mechanics and mechanical rock cutting, weaker rocks are easier to drill and the drill cuttings produced are generally coarse in size. Accordingly a specially designed precision drill was used to drill coal samples under both normal atmospheric and confined gas pressure conditions. Indications of changes to coal strength as a result of increased sorbed gas pressure were examined by analysing the particle size distribution of the drill flushing. A laser controlled Malvern Mastersizer S particle size analyser with measuring range between 0.05 μm and 900 μm was used to study the particle size distribution. This paper demonstrates that there is a definite variation in the range of particle size distribution with particles obtained from drilling coal samples not subjected to gas pressures in comparison with those obtained from samples drilled under confined gas pressure. Gas types also have an influence. Higher proportions of coarse particles were produced when the confined gas was changed from CH4 to CO2. A change in the rate of drilling under varying confining pressure and gas type was also evident. The rate of drilling in air (at normal atmospheric conditions) was slower than at higher confining pressures. The highest drill rates were obtained with CO2 confinement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ates, Y. (1987) The effect of sorption on strength of coal and its influence on coal outbursts. M.Sc. thesis. The University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada. 196 pp.
Ates, Y. and Barron, K. (1988) The effect of gas sorption on the strength of coal, Mining Science and Technology, 6, 291-300.
Czaplin'ski, A. and Holda, S. (1982) Changes in mechanical properties of coal due to sorption of carbon dioxide vapour. Fuel, 61, 1281-1282.
Czaplin'ski, A. and Holda, S. (1985) Changes in compressive strength of sandstones from the Nowa Ruda Mine under the influence of the action of liquids and gases. Archiwum Gornictwa, Tom. 30, 391-399.
Fish, B.R. and Baker, J.S. (1956) Studies in rotary drilling, National Coal Board, MRDE Report 209.
Goodrich, R.H. (1956) High pressure rotary drilling machines. Proceedings of the Second Annual Symposium on Mineral Resources. Missouri University, paper 25, pp. 212-221.
Gregg, S.J. and Sing, K.S.W. (1967) Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity. Academic Press, London.
Gustkiewicz, J. (1985) Deformation and failure of the Nowa Ruda sandstone in a three-axial state of stress with gas under pressure in pore. Archiwum Gornictwa, Tom. 30, 401-424.
Hargraves, A.J. and Upfold, R.W. (1985) Aspects of laboratory simulations of instantaneous outbursts. Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Safety in Mines Research, Sydney, 21–25 Oct., pp. 129-146.
Hiramatsu, Y., Saito, T. and Oda, N. (1983) Studies on mechanism of gas and coal burst in Japanese coal mine. International Congress on Rock Mechanics, Melbourne, pp. 7-10.
Holda, S. (1986) Investigation of adsorption, dilatometry and strength of low rank coal. Archiwum Gornictwa, Tom. 31, 599-608.
Jackson, L.J. (1984) Outbursts in coal mines. IEA Coal Research London Report, No. ICTIS/TR25.
Lama, R.D. (1995) (ed.) Management and control of high gas emissions and outbursts in underground coal mining. Proceedings of Symposium-cum-Workshop, March 20–24, Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 620 pp.
Lama, R.D. and Bartosiewicz, H. (1982) Determination of gas content of coal seams. Proceedings of the Symposium on Seam Gas Drainage with particular reference to the Working Seam. The Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, Illawarra Branch, Wollongong, May, pp. 36-52.
Lama, R.D. and Bodziony, J. (1996) Outbursts of gas, coal and rock in underground. Published by R.D. Lama and Associates, Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 499 pp.
Lama, R.D. and Bodziony, J. (1998) Management of outburst in underground coal mines, Int. Jr. of Coal Geology, 35, 83-115.
Tankard, J.H.G. (1958) The effect of sorbed carbon dioxide upon the strength of coals. Master thesis, Department of Mining Engineering, The University of Sydney.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aziz, N., Ming-Li, W. The effect of sorbed gas on the strength of coal – an experimental study. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 17, 387–402 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008995001637
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008995001637