Abstract
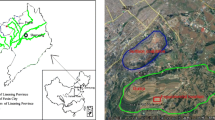
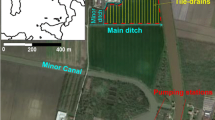
An experimental soil cover was constructed near London, Ontario and monitored for more than a year for percolation and water content data. The cover was a multi-layer system consisting of compacted till barrier soil placed between gravel layers, and a final topsoil cap in one half and a coarse stone cap in the other half. The lower gravel layer was intended to provide a capillary break that would minimize gravity driven drainage in the till, while the capillary barrier created at the upper gravel-till interface would reduce evaporative losses in the till during dry periods. The results showed that while the compacted till maintained a relatively high degree of saturation and low hydraulic conductivity under the coarse stone, it desiccated under the topsoil and resulted in high water percolation rates. The textural or grain size contrast between the relatively fine topsoil and the underlying gravel layer created a capillary break which, together with the relatively low hydraulic conductivity of the topsoil, prevented infiltrating waters from recharging the underlying till. Thus the till was not able to rebound to its pre-desiccation water content. The saturated hydraulic conductivity of the till under the topsoil was about 1 × 10−8 m/s after one year, compared to 2.0 × 10−10 m/s at construction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson, C.H., Abichou, T.H., Olsen, M.A. and Bosscher, P.J. (1995) Winter effects on the hydraulic conductivity of compacted clay. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 121(1): 69-79.
Boynton, S.S. and Daniel, D.E. (1985) Hydraulic conductivity tests on compacted clay. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 111(4): 465-478.
Choo, L. (1996) Evaluation of water flow in unsaturated soils for multi-layer soil covers. Master of Engineering Science Thesis. Department of Civil Engineering, University of Western Ontario.
Daniel, D.E. (1989) In situ hydraulic conductivity tests for compacted clay. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 115(9): 1205-1226.
Daniel, D.E. and Wu, Y. (1993) Compacted clay liners and covers for arid sites. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 119(2): 223-237.
Fernuik, N. and Haug, M.D. (1990) Evaluation of in situ permeability testing methods. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 116(2): 297-311.
Hayhoe, H.N. and Balchin, D. (1988) Time-Domain reflectrometry and electrical conductance measurements during seasonal soil frost. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 15: 195-200.
Hook, W.R. and Livingston, N.J. (1996) Errors in converting Time-Domain reflectometry measurements of propagation velocity to estimates of soil water content. Soil Science, 60(1): 35-41.
MacKay, M. (1997) Evaluation of oxygen diffusion in unsaturated soils. Master of Engineering Science Thesis. The University of Western Ontario. London, Canada.
Rasmusson, A. and Eriksson, J.C. (1986) Capillary barriers in covers for mine tailings dumps. Report 3307, National Swedish Environmental Protection Board, Sweden.
Woyshner, M.R. and Yanful, E.K. (1995) Modelling and field measurements of water percolation through an experimental soil cover on mine tailings. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 32: 601-609.
Yanful, E.K., Haug, M.D. and Wong, L.C. (1990) The impact of synthetic leachate on the hydraulic conductivity of a smectitic till underlying a landfill site near Saskatoon, Saskatechewan, Canada. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 27(4): 507-519.
Yanful, E. (1993) Oxygen diffusion through soil covers on sulphidic mine tailings. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 119(8): 1207-1228.
Yanful, E.K. and Aubé, B. (1993) Modelling moisture-retaining soil covers. Joint CSCE-ASCE National Conference on Environmental Engineering. July 12–14, 1993, Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
Yanful, E.K., Bell, A.V. and Woyshner, M. (1993a) Design of a composite soil cover for an experimental waste rock pile near Newcastle, New Brunswick, Canada. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 30(4): 578-587.
Yanful, E.K., Riley, M.D., Woyshner, M.R. and Duncan, J. (1993b) Construction and monitoring of a composite soil cover on an experimental waste rock pile near Newcastle, New Brunswick, Canada. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 30(4): 588-599.
Yanful, E.K., Simms, P.H. and Payant, S. (1998) Soil covers for controlling acid drainage: a laboratory evaluation of the physics and geochemistry. Water, Air and Soil Pollution (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanful, E., Simms, P., Rowe, R. et al. Monitoring an Experimental Soil Waste Near London, Ontario, Canada. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 17, 65–84 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008986103460
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008986103460