Abstract
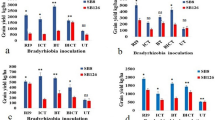
Two field experiments were established to assess the competitiveness of foreign bradyrhizobia in infecting the promiscuous soybean cultivar TGX 536-02D. Seeds were inoculated with antibiotic mutants of the bradyrhizobia strains before planting after land preparation. Soybean plants were harvested at pre-determined days after planting for estimating nodule number, nodule dry weight, nodule occupancy, shoot dry weight and seed yield. Results show that nodule number and dry weight significantly increased and showed great variability at 84 days after planting (DAP), probably due to differences in the ability of inoculant bradyrhizobia to form nodules with the soybean cultivar TGX 536-02D. Increased shoot dry weight, %N, total N and seed yield were a result of increased nodulation by the effective and competitive inoculant Bradyrhizobium strains. Strain USDA 110 occupied the highest percentage of nodule sites because it was more competitive than the other Bradyrhizobium strains. These results show that there was high potential for increasing growth and seed yield of the promiscuous soybean cultivar TGX 536-02D by inoculation with foreign Bradyrhizobium strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, A.H. & McLaughlin, W. 1985 Ecology and genetics of tropical Rhizobium species. Biotechnology Advances 3, 155-170.
Arthur F.W. & Johnson D.A. 1996 Influence of draught on competition between selected Rhizobium melliloti strains and naturalised soil rhizobia in alfafa. Plant and Soil 184, 231-241.
Bremner, J.M. 1965 Total N. In Methods of Soil Analysis, ed. Black. C.A. Agronomy vol, 9, 1149-1179. Madison, Wisconsin, USA: American Society of Agronomy Inco.
Brockwell, J. 1980 Experiments with crop and pasture legumes-Principles and practice. In Methods of Evaluating Biological Nitrogen Fixation, ed. Bergersen F.J. pp. 417-486 New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-127759-2.
Brockwell, J., Diatlof, A., Grassia, A. & Robinson, A.C. 1975 Use of wild soybean (Glycine ussuriensis Ragel and Mack) as a test plant in dilution nodulation frequency tests for counting Rhizobium japonicum. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 7, 305-311.
Brown, R.D. & Ahmed, M.H. 1996 Comprehensive interaction among strains of Rhizobium leguminosarum by phaseoli in the nodulation of kidney beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Biology, Fertilizers and Soils 21, 7-9.
Chowdhury, M.S. 1975 Response of soybean to Rhizobium inoculation at Morogoro Tanzania. In Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Farming Systems of the Tropics, eds. Ayanaba, A. & Dart, P.J. pp. 245-253. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 0 471 935603.
Kvien, C.S., Ham, G.E. & Lambert, J.W. 1981 Recovery of introduced Rhizobium japonicum strains by soybean genotypes. Agronomy Journal 73, 900-905.
Miles, A.A. & Misra, S. 1938 The examination of the bacteriocidal power of blood. Journal of Hygiene 38, 732-749.
Okereke, G.U. & Onochie, C.C. 1996 Screening of native and foreign Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains for nitrogen fixation in soybean. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 12, 639-641.
Okereke, G.U. & Eaglesham, A.R.J. 1993 Nodulation and nitrogen fixation by 79 promiscuous soybean genotypes in soil in eastern Nigeria. Agronomy Afrique V(2), 113-122.
Olufajo, O.O. & Adu, J.K. 1993 Nodulation of soybean grown under field conditions and inoculated with Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains. In Biological Nitrogen Fixation and Sustainability of Tropical Agriculture, eds. Mulongoy, K., Gueye, M. & Spencer, D.S.C. pp. 147-154. New York: John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 0 471 935603.
Pasaribu, D., Sunarlim, N., Sumamo, S.U., Saraswathi, R., Parto, H.S. & Karama, S. 1989 Penelitian inockulasi Rhizobium of Indonesia. In Risalah Lakakarya Penelitian Penanbatan Nitrogen Secara Hayate pada Kacang Kacangan pp. 1-29. Bogor, Indonesia: Central Research Institute for Food Crops.
Pulver, E.L., Brockmann, F. & Wein, H.C. 1982 Nodulation of soybean cultivars with Rhizobium spp. and their response to inoculation with R. japonicum. Crop Science 22, 1085-1070.
Pulver, E.L., Kueneman, E.A. & Rao, R. 1984 Identification of promiscuous nodulating soybeans efficient in nitrogen fixation. Crop Science 25, 660-663.
Rao, R., Thottappilly, G. & Ayanaba, A. 1981 Studies on the persistence of introduced strains of Rhizobium japonicum in soils during fallow and the e.ects on soybean growth yield. In Biological Nitrogen Fixation Technology for Tropical Agriculture, eds. Graham, P.H. & Harris, S.C. pp. 209-315. CIAT Publication. ISBN 8-48920622-8.
Saginga, N., Dashiell, K., Okogun, J.A. & Thotappilly, G. 1997 Nitrogen fixation and N contribution by promiscuous nodulating soybeans in Southern Guinea Savana of Nigeria. Plant and Soil 195, 257-266.
Simanungkalit, R.D.M., Indrasumunar, A., Pratwai, E., Hastuti, R.D. & Roughley, R.J. 1995 Population dynamics of bradyrhizobia in latosol soil used for upland and lowland rice, soybean cropping system in west Java Indonesia. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 27, 625-628.
Somasegaran, P. & Hoben, H.J. 1985 Methods in Legume Rhizobium Technology. University of Hawaii, Project and MIRCEN, Department of Agronomy and Soil Science, Hawaii Institute of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources, College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources 128-138.
Somasegaran, R., Woolfenden, R. & Halliday, J. 1983 Sustainability of oven dried root nodules for Rhizobium strain identification by immunofluorescence and agglutination. Journal of Applied Bacteriology 55, 253-266.
Steel, R.G.D. & Torrie, J.H. 1960 Principles and Procedures and Statistics New York: McGrawHill.
Thies, J.E., Singleton, P.W. & Bohlool, B.B. 1991 Influence of the size of indigenous populations on establishment and symbiotic performance of introduced rhizobia on field grown legumes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 57, 16-28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okereke, G., Onochie, C., Onukwo, A. et al. Response of introduced Bradyrhizobium strains infectinga promiscuous soybean cultivar. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 16, 43–48 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008927327678
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008927327678