Abstract
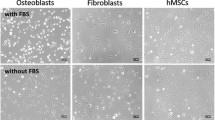
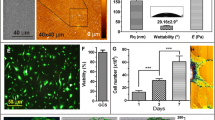
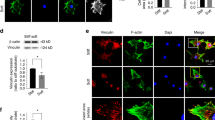
Primary bovine osteoblasts were used to study in-vitro effects of attachment on vinculin assembly in cells cultured on various artificial substrates. Materials coated with fibronectin and bovine serum albumin (BSA) as well as untreated materials (tissue culture polystyrene and Aclar foils) were chosen to investigate substrate-dependent proliferation during the first 3 days of culture. Proliferation was highest on fibronectin-coated substrates, followed by BSA-coated and untreated substrates. During the first 24 h of cultivation, cell attachment kinetics revealed no significant difference between the various substrates. After 24 h detachment rates obtained by calcium depletion with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid were highest on uncoated materials, followed by BSA- and fibronectin-coated substrates. Phase contrast microscopy revealed typical osteoblast morphology after cell adhesion for 24 h. The dynamic attachment process was concomitant with the reassembly of vinculin into streak-like focal contacts clustered on the ventral side of cells. The kinetics of vinculin reassembly were independent of the underlying coating. Thus, fibronectin coating of artificial substrates increased the attachment strength and proliferation rate of osteoblasts. While the reassembly of vinculin in focal contacts seems to be a prerequisite of osteoblast attachment in vitro, it does not seem to have profound effects on the subsequent cell behaviour on artificial substrates. © Chapman & Hall
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. P. Jennissen, in “Modern aspects of protein adsorption on biomaterials”, edited by Y. F. Missirlis and W. Lemm (Kluwer, Amsterdam, 1991) p. 63.
R. Bendori, D. Salomon and B. Geiger, EMBO J. 6 (1987) 2897.
M. J. Bissell and M. H. Barcellos-Hoff, J. Cell Sci. Suppl. 8 (1987) 327.
L. Masi, A. Franchi, M. Santucci, D. Danielli, L. Arganini, V. Giannone, L. Formigli, S. Benvenuti, A. Tanini, F. Beghe, M. Mian and M. L. Brandi, Calcif. Tissue Int. 51 (1992) 202.
J. B. Meigs and Y.-L. Wang, J. Cell Biol. 102 (1986) 1430.
S. Vukicevic, F. P. Luyten, H. K. Kleinman and A. H. Reddi, Cell 63 (1990) 437.
W. J. Grzesik and P. G. Robey, J. Bone Miner. Res. 9 (1994) 487.
K. Moller, U. Meyer, D. H. Szulczewski, H. Heide, B. Priessnitz and D. B. Jones, Cells Materials 4 (1994) 263.
S. J. Jones and A. Boyde, Scanning Electron Microsc. 2 (1979) 529.
M. A. Malik, D. A. Puleo, R. Bizios and R. H. Doremus, Biomaterials 13 (1992) 123.
D. A. Puleo and R. Bizios, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 26 (1992) 291.
Idem., Bone Miner. 18 (1992) 215.
W.-T. Chen and S. J. Singer, J. Cell Biol. 95 (1982) 205.
K. Burridge, K. Fath, T. Kelly, G. Nuckolls and C. Turner, Ann. Rev. Cell Biol. 4 (1988) 487.
B. Geiger, Z. Avnur, G. Rinnerthaler, H. Hinssen and V. J. Small, J. Cell Biol. 99 (1984) 835.
K. Burridge and J. R. Feramisco, Cell 19 (1980) 587.
J. J. Otto, Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 16 (1990) 1.
M. Samuels, R. M. Ezzeil, T. J. Cardozo, D. R. Critchley, J.-L. Coll and E. D. Adamson, J. Cell Biol. 121 (1993) 909.
D. B. Jones, H. Nolte, J. G. Scholuebbers, E. Turner and D. Veltel, Biomaterials 12 (1991) 101.
S. K. Akiyama, K. Nagata and K. M. Yamada, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1031 (1990).
S. M. Albelda and C. A. Buck, FASEB J. 4 (1990) 2868.
J. S. Bauer, C. L. Schreiner, F. G. Giancotti, E. Ruoslahti and R. L. Juliano, J. Cell Biol. 116 (1992) 477.
R. O. Hynes, Cell 48 (1987) 549.
E. Ruoslahti and M. D. Pierschbacher, Science 238 (1987) 491.
D. D. Schlaepfer, S. K. Hanks, T. Hunter and P. van der Geer, Nature 372 (1994) 786.
R. S. Carvalho, J. E. Scott, D. M. Suga and E. H. Yen, J. Bone Miner. Res. 9 (1994) 999.
A. Morla, Z. Zhang and E. Ruoslahti, Nature 367 (1994) 193.
M. A. Horton and J. Davies, J. Bone Miner. Res. 4 (1989) 803.
D. A. Puleo and R. Bizios, Bone 12 (1991) 271.
B. Geiger, Cell 18 (1979) 193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer, U., Meyer, T. & Jones, D.B. Attachment kinetics, proliferation rates and vinculin assembly of bovine osteoblasts cultured on different pre-coated artificial substrates. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 9, 301–307 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008894612021
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008894612021