Abstract
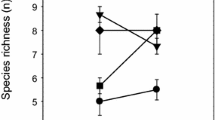
This study describes changes in species diversity and canopy cover in relation to variation in livestock grazing in a semi-arid area in Inner Mongolia, China. Canopy cover for each species was recorded 2 and 3 years after cessation of livestock grazing, as well as in an area with continued grazing. Total species richness, alpha diversity, beta diversity and canopy cover were analysed. Sixty species were recorded during the study; 25 of them were annuals. The total number of species was the same, 52, in the grazed and the protected area, but species richness and alpha diversity per plot were lower in the area protected from grazing. The beta diversity showed little difference between the protected area and the grazed control. The total canopy cover was highest in the protected area, but the cover of annuals was higher in the grazed area. In CA ordination, the difference between treatments increased with time of protection. However, in the short period covered by this study it was difficult to separate the effects of protection from grazing and fluctuation in weather conditions, particularly of precipitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon. (1990) SAS/STAT User's Guide, Version 6, 4th edn. Cary, NC: SAS Institute.
Backéus, I. (1993) Ecotone versus ecocline: vegetation zonation and dynamic around a small reservoir in Tanzania. J. Biogeogr 20, 209–18.
Belsky, A.J. (1992) Effects of grazing, competition, disturbance and fire on species composition and diversity in grassland communities. J. Veg. Sci. 3, 187–200.
Bowns, J. E. and Bagley, C. F. (1986) Vegetation responses to long-term sheep grazing on mountain ranges. J. Range Manage. 39, 431–4.
Chesson, P. and Huntly, N. (1989) Short-term instabilities and long-term community dynamics. Trends Ecol. Evol. 4, 293–8.
Clements, F. E. (1916) Plant succession: an analysis of the Development of Vegetation. Publication 242. Washington, D C: Carnegie Institute, Washington.
Collins, S. L. and Barber, S. C. (1985) Effects of disturbance on diversity in mixed-grass prairie. Vegetatio 64, 87–94.
Cramer, W. and Hytteborn, H. (1987) The separation of fluctuation and long term change in vegetation dynamics of a rising seashore. Vegetatio 69, 157–67.
DeAngelis, D. L. and Waterhouse, J. C. (1987) Equilibrium and non-equilibrium concept in ecological models. Ecol. Monogr. 57, 1–21.
Facelli, J. M. and D'Angela, E. (1990) Directionality, convergence, and rate of change during early succession in the Inland Pampa, Argentina. J. Veg. Sci. 1, 255–60.
Frost, P., Medina, E., Menaut, J.-C. et al. (1986) Responses of savannas to stress and disturbance. Biol. Int. Spec. Iss. 10.
Glenn-Lewin, D. C. and van der Maarel, E. (1992) Patterns and processes of vegetation dynamics. In Plant Succession-Theory and Prediction (D. Glenn-Lewin, R. K. Peet and T. T. Veblen, eds) pp. 11–59. London: Chapman and Hall.
Grime, J. P. (1979) Plant Strategies and Vegetation Processes. Chichester: Wiley.
Helle, T. and Aspi, J. (1983) Effects of winter grazing by reindeer on vegetation. Oikos 40, 337–43.
Hobbs, R. J. and Mooney, H. A. (1991) Effects of rainfall variability and gopher disturbance on serpentine annual grassland dynamics. Ecology 72, 59–68.
Huang, Z. H. (1982) Grassland improvement in the Ordos region. In Research Collection l, Institute of Desert Research (Z. D. Zhu, ed.) Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
Huston, M. (1993) Biological diversity, soils, and economics. Science 262, 1676–80.
Huston, M. (1994) Biological diversity: the coexistence of species on changing landscapes. Cambridge: Cambridge university press.
Karban, R. and Myers, J. M. (1989) Induced plant responses to herbivores. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst 20, 331–48.
Khinchin, A. I. (1957) Mathematical Foundations of Information Theory. New York: Dover.
Lavorel, S., Lepart, J., Debussche, M. et al. (1994) Small scale disturbances and the maintenance of species diversity in Mediterranean old fields. Oikos 70, 455–73.
Liu, Y. X. (1985) (ed.) Flora in desertis Republicae Populorum Sinarum. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
Madany, M. H. and West, N. E. (1983) Livestock grazing-fire regime interactions within montane forests of Zion National Park, Utah. Ecology 64, 661–7.
McCune, B. and Allen, T. F. H. (1985) Will similar forests develop on similar sites? Can. J. Bot. 63, 367–76.
McNaughton, S. J. (1983a) Compensatory plant growth as a response to herbivory. Oikos. 40, 329–36.
McNaughton, S. J. (1983b) Serengeti grassland ecology: the role of composite environmental factors and contingency in community organization. Ecol. Monogr. 53, 291–320.
McNaughton, S. J. (1994) Conservation goals and configuration of biodiversity. Syst. Conserv. Eval. 50, 41–62.
Milchunas, D. G. and Lauenroth, W. K. (1989) Three-dimensional distribution of plant biomass in relation to grazing and topography in the shortgrass steppe. Oikos 55, 82–86.
Milles, J. (1979) Vegetation Dynamics. London: Chapman and Hall
Minchin, P. R. (1987) An evaluation of the relative robustness of techniques for ecological ordination. Vegetatio 69, 89–107.
Mwalyosi, R. B. B. (1992) Influence of livestock grazing on range condition in south-west Masailand, Northern Tanzania. J. Appl. Ecol. 29, 581–8.
Økland, R. H. (1986) Rescaling of ecological gradients. I. Calculation of ecological distance between vegetation stands by means of their floristic composition. Nord. J. Bot. 6, 651–60.
Pandey, C. B. and Singh, J. S. (1991) Influence of grazing and soil conditions on secondary savanna vegetation in India. J. Veg. Sci. 2, 95–102.
Pielou, E. C. (1977) Mathematical Ecology. New York: Willey-Interscience.
Pitt, M. D. and Heady, H. F. (1978) Responses of annual vegetation to temperature and rainfall pattern in Northern California. Ecology 59, 336–50.
Raunkiaer, C. (1937) Plant Life Forms. Oxford: Clarendon.
Rusch, G. and Fernández-Palacios, J. M. (1995) The influence of spatial heterogeneity on regeneration by seed in a limestone grassland. J. Veg. Sci. 6, 417–26.
Shannon, C. E. and Weaver, W. (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. Urbana: University of Illinois Press.
Siegel, S. (1956) Nonparametric Statistics for the Behavioural Sciences. New York: MacGraw-Hill.
Skarpe, C. (1991) Impact of grazing in savanna ecosystems. Ambio 20, 351–6.
Skarpe, C. (1992) Dynamics of savanna ecosystems. J. Veg. Sci. 3, 293–300.
Smart N. O. E. Hatton, J. C. and Spence, D. H. N. (1985) The effect of long-term exclusion of large herbivores on vegetation in Murchsion Fall National Park, Uganda. Biol. Conserv. 33, 229–45.
Smith, R. S. and Rushton, S. P. (1994) The effects of grazing management on the vegetation of mesotrophic (meadow) grassland in Northern England. J. Appl. Ecol. 31, 14–24.
Sykes, M. T., van der Maarel, E., Peet, R. K. and Willems, J. H. (1994) High species mobility in species-rich plant communities: an intercontinental comparison. Folia Geobat. Phytotax. 29, 439–48.
ter Braak, C. J. F. (1987) CANOCO-a FORTRAN Program for Canonical Community Ordination by (Partial) (Detrended) (Canonical) Correspondence Analysis (Version 2.0) Wageningen: TNO Institute of Applied Computer Science.
ter Braak, C. J. F. (1990) Update notes: CANOCO version 3.10. Wageningen: TNO Institute of Applied Computed Science.
van der Maarel, E. (1993) Some remarks on disturbance and its relations to diversity and stability. J. Veg. Sci. 4, 733–6.
van der Maarel, E. and Sykes, M. T. (1993) Small-scale plant species turnover in a limestone grassland: the carousel model and some comments on the niche concept. J. Veg. Sci. 4, 179–88.
Walker, B. H. (1987) A general model of savanna structure and function. In Determinants of Tropical Savannas (B. H. Walker, ed.) France: ICSU Press.
Walker, M. D. Webber, P. J., Arnold, E. H. and Ebert-May, D. (1994) Effects of interannual climate variation on aboveground phytomass in alpine vegetation. Ecology 75, 393–408.
Werger, M. J. A. (1974) Environment destruction in southern Africa: the role of overgrazing and trampling. In Vegetation Science and Environmental Protection (A. Miyawaki and R. Tüxen, R. eds) pp. 301–5. Tokyo: Maruzen.
Westoby, M. (1980) Elements of a theory of vegetation dynamics in arid rangelands. Isr. J. Bot. 28, 169–94.
Whittaker, R. H. (1975) Communities and Ecosystems, 2nd edn. New York: Macmillan.
Zhang, W. (1992) Succession and recovery of overgrazed pasture vegetation under exclosure in Naiman banner. J. Arid Env. 6, 74–84. (in Chinese).
Zhang, W. and Skarpe, C. (1995) Small scale species dynamics in semi-arid steppe vegetation, China. J. Veg. Sci. 6, 583–92.
Zhang, W. and Skarpe, C. (1996) Small scale vegetation dynamics in semi-arid steppe, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Arid Env. 34, 421–39.
Zhu, Z. and Liu, S. (1981) The Desertification Process and its Control in Northern China. Beijing: Forestry Press (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W. Changes in species diversity and canopy cover in steppe vegetation in Inner Mongolia under protection from grazing. Biodiversity and Conservation 7, 1365–1381 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008852017493
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008852017493