Abstract
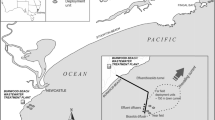
A critical examination of an aquatic environment adjacent to the discharge from an unbleached kraft pulp and paper mill (UBKM) was conducted in 1995. The assessment involved sampling of sediments, water, benthic macroinvertebrates, and fish collected 1.6 km upstream from the mill, at the mill's outlet, and 2.5 km downstream. Field-collected blue catfish (Ictalurus furcatus) and bluegill sunfish (Lepomis macrochisus) exposed to site sediments in the laboratory showed no significant within-organism adverse effects as measured by EROD activity, benzo[a]pyrene hydroxylase activity, CYP1A content, DNA damage, condition factor, organ indices, differential blood cell counts, and histopathology, though DNA strand breaks increased at the most downstream site. No aqueous or sediment toxicity was observed using Ceriodapnia dubia and Pimephales promelas or Hyalella azteca and Chironomus tentans, respectively. Embryos of the mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) were evaluated for reproductive potential following laboratory exposures of adult mosquitofish to river sediments and water for 90 days. No significant adverse reproductive effects were observed immediately below the BKME discharge site. Analyses of field-collected benthic macroinvertebrate samples revealed no significant effects in terms of taxa, taxa richness, and other measures of their status. Using a comprehensive suite of within-organism, whole-organism, and community level endpoints, our study demonstrates that this effluent, discharged following secondary treatment from an UBKM, had no significant adverse impacts on the receiving aquatic ecosystem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1992). Cited in text, but not in references.
Adams, S.M., Crumby, W.D., Greeley, M.S. Jr., Shugart, L.R. and Saylor, C.F. (1992). Responses of fish populations and communities to pulp mill effluents: A holistic assessment. Ecotoxicol. and Environ. Saf. 24, 347-60.
Ahtianinen, J., Nakari, T. and Silvonen, J. (1996). Toxicity of TCF and ECF pulp bleaching effluents assessed by biological toxicity tests. In M.R. Servos, K.R. Munkittrick, J.H. Carey, and G.J. Van der Kraak (eds) Environmental Fate and Effects of Pulp and Paper Mill Effluents, pp. 33-40. St Lucie Press.
American Public Health Association. (1992). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste-water. 18th ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C.
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). (1991). Standard Guide for Conducting Sediment Toxicity Tests with Freshwater Invertebrates. E 1383-90, Philadelphia, PA.
Andersson, T., Forlin, L., Hardig, J. and Larsson, A. (1988). Physiological disturbances in fish living in coastal water polluted with bleached kraft pulp mill effluents. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 45, 1525-36.
Blaylock, B.G. (1969). The fecundity of a Gambusia affinis population exposed to chronic environmental radiation. Radiat. Res. 37, 108-17.
Blaylock, B.G. and Frank, M.L. (1980). Effects of chronic low-level irradiation on Gambusia affinis. In Egami, N. (eds) Radiation Effects on Aquatic Organisms, pp. 81-90. Baltimore, MD: University Park Press.
Bradford, M.M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248-54.
Deardorff, T.L., Renard, J.J. and Phillips, R.B. (2000) in press. An environmental assessment before and after conversion of a bleached kraft mill to elemental-chlorine-free bleaching. In V. Turosky (eds) Chlorine and Chlorine Compounds in the Paper Industry. Chelsea, Michigan: Ann Arbor Press.
Environmental Protection Agency. (1977). Suspended and Dissolved Solids Effects on Freshwater Biota. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. EPA-600/3-77-042. p. 33 Gov. Printing Office, Corvallis, Oregon 97330.
EPA, (1977) Cited in text.
Freeman, S.E., and Thompson, B.D. (1990). Quantitation of ultraviolet radiation-induced cyclobutyl pyrimidine dimers in DNA by video and photographic densitometry. Anal. Biochem. 186, 222-8.
Gillespie, W.B. Jr., Rodgers, J.H. Jr. and Crossland, N.O. (1996). Effects of a nonionic surfactant (C14-15AE-7) on aquatic invertebrates in outdoor stream mesocosms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 1418-22.
Hawkins, W.E., Walker, W.W. and Overstreet, R.M. (1995). Carcinogenicity tests using aquarium fish. In Rand, G.M. (eds) Fundamentals of Aquatic Toxicology, pp. 421-46. Washington, DC: Taylor & Francis.
Hodson, P.V., Maj, M.K., Efler, S., Burnison, B.K., Van Heiningen, A.R.P., Girard, R. and Carey, J.H. in press (1996). MFO induction in fish by spent cooking liquors from kraft pulp mills. Environ. Toxicol. Chem.
Huuskonen, S. and Lindstrom-Seppa, P. (1995). Hepatic cytochrome P4501A and other biotransformation activities in perch (Perca fluviatilis): the effects of unbleached pulp mill effluents. Aquat. Toxicol. 31, 27-41.
Kloepper-Sams, P.J., Swanson, S.M., Marchant, T., Schryer, R. and Owens, J.W. (1994). Exposure of fish to biologically treated bleached-kraft effluent. 1) Biochemical, physiological and pathological assessment of rocky mountain whitefish (Prosopium williamsoni) and longnose sucker (Catastomus catostomus). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 13, 1469-82.
Kovacs, T.G., Gibbons, J.S., Tremblay, L.A., O'Conner, B.I., Martel, P.H. and Voss, R.H. (1995). The effects of a secondary-treated bleached kraft pulp mill effluent on aquatic organisms as assessed by short-term and long-term laboratory tests. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 31, 7-22.
Kurelec, B. (1990). The genotoxic disease syndrome. PNAS. 78, 1237-40.
Lindstrom-Seppa, P. and Oikari, A. (1990). Biotransformation activities of feral fish in waters receiving bleached pulp mill effluents. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 9, 1415-24.
McCarthy, J.F. and Shugart, L.R. (1990). Biological markers of environmental contamination. In McCarthy, J.F. and Shugart, L.R. (eds) Biomarkers of Environmental Contamination. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
Munkittrick, K.R., Portt, C.B., Van Der Kraak, G.J., Smith I.R. and Rodosh, D.A. (1991). Impact of bleached-kraft mill effluent on population characteristics, liver MFO activity, and serum steroid levels of a Lake Superior (Catostomus commersoni) population. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 48, 1371-80.
Munkittrick, K.R., McMaster, M.E., Portt, C.B., Van Der Kraak, G.J., Smith I.R. and Dixon D.G. (1992). Changes in maturity, plasma sex steroid levels, hepatic mixed-function oxygenase activity, and the presence of external lesions in lake whitefish (Coregonus clupeaformis) exposed to bleached kraft mill effluent. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 49, 1560-9.
Munkittrick, K.R., and Van Der Kraak, G.J. (1994). Receiving water environmental effects associated with discharges from Ontario Pulp Mills. Pulp and Paper Canada 5, 57-9.
Nebeker, A.V., Cairns, M.A., Gastatter, J.H., Malueg, K.W., Schuytema, G.S. and Krawczyk, D.F. (1984). Biological methods for determining toxicity of contaminated freshwater sediments to invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 3, 617-30.
Nieuwkoop, P.D. and Faber, J. (1994). Normal Table of Xenopus Laevis (Daudin). p. 15. New York: Garland Publishing, Inc.
Owens, J.W. (1991). The hazard assessment of pulp and paper effluents in the aquatic environment: a review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 10, 1511-1540.
Pesonen, M. and Andersson, T. (1992). Toxic effects of bleached and unbleached paper mill effluents in primary cultures of rainbow trout hepatocytes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 24, 63-71.
Pielou, E.C. (1975). Ecological Diversity, New York: Wiley.
Prough, R.A., Burke, M.D. and Mayer, R.T. (1978). Direct fluorometric methods for measuring mixed-function-oxidase activity. Methods Enzymol. 52, 372-7.
Rosa-Molinar, E. and Williams, C.S. (1984). Notes on fecundity of an arrhenoid population of mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis holbrooki). Northeast Gulf Sci. 7, 121-5.
Sambrook, J., Fritsh, E.F. and Maniatus, T. (1989). Molecular cloning, Book 1. Section 1.25 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Schlenk, D. and Buhler, D.R. (1988). Cytochrome P-450 and Phase II activities in the gumboot chiton Cryptochiton stelleri. Aquat. Toxicol. 13, 167-82.
Schlenk, D., Ronis, M.J.J., Miranda, C. and Buhler, D.R. (1995). Effects of 2-methylisoborneol (MIB), and ethanol on the expression and activity of cytochrome P450s from the channel catfish. J. Fish Biol. 46, 282-91.
Shugart, L.R., D'surney, S.J., Gettys-Hull, C. and Greeley, M.S. (1991). Biological (molecular and cellular) markers of toxicity. ORNL/TM, Oak Ridge: Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
Theodorakis, C.W., D'surney, S.J., Bickham, J.W., Lyne, T.B., Bradley, B.P., Hawkins, W.E., Farkas, W.L., McCarty, J.F. and Shugart, L.R. (1992). Sequential expression of biomarkers in bluegill sunfish exposed to contaminated sediment. Ecotoxicology 1, 45-73.
Theodorakis, C.W., D'surney, S.J. and Shugart, L.R. (1994). Detection of genotoxic insult as DNA strand breaks in fish blood cells by agarose gel electrophoresis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 13, 1023-31.
Todd, J.C. and Sanford, A.H. (1969). Clinical diagnosis by laboratory methods. 14th Ed. Davidsohn and Henry, (eds) W.B. Saunders and Co.
Van Den Heuval, M.R., Munkittrick, K.R., Van Der Kraak, G.J., Servos, M.R. and Dixon, D.G. (1995). Hepatic 7-ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity, plasma steroid hormone concentrations, and liver bioassay-derived 2,3,7,8-TCDD toxic equivalent concentrations in wild white sucker (Catostomus commersoni) caged in bleached kraft pulp mill effluent. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 52, 1339-50.
Weber, C.I. and Peltier, W.H. (1989). Short-Term Methods for Estimating the Chronic Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Water to Freshwater Organisms. EPA/600/4-89/001.
Zar, J.H. (1984). Biostatistical Analysis, 2nd ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felder, D., D'Surney, S., Rodgers, J. et al. A Comprehensive Environmental Assessment of a Receiving Aquatic System Near an Unbleached Kraft Mill. Ecotoxicology 7, 313–324 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008826129356
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008826129356