Abstract
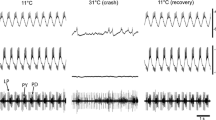
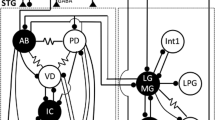
The extent to which individual neural networks can producephase-constant motor patterns as cycle frequency is altered has notbeen studied extensively. I investigated this issue in thewell-defined, rhythmic pyloric neural network. When pyloric cyclefrequency is altered three- to fivefold, pyloric inter-neuronaldelays shift by hundreds to thousands of msec, and all pyloricpattern elements show strong phase maintenance. The experimentalparadigm used is unlikely to activate exogenous inputs to thenetwork, and these delay changes are thus likely to arise fromphase-compensatory mechanisms intrinsic to the network. Pyloricinter-neuronal delays depend on the time constants of the network‘ssynapses and of the membrane properties of its neurons. The observeddelay shifts thus suggest that, in response to changes in overallcycle frequency, these constants vary so as to maintain patternphasing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott LF, Hooper SL, Kepler T, Marder E (1990) Oscillating networks: Modeling the pyloric circuit of the stomatogastric ganglion. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neuronal Networks. IEEE, Ann Arbor, MI. pp. I175–I180.
Arbas EA, Calabrese RL (1984) Rate modification in the heartbeat central pattern generator of the medicinal leech. J. Comp. Physiol. A.155:783–794.
Bal T, Nagy F, Moulins M (1988) The pyloric central pattern generator in crustacea: A set of conditional neuronal oscillators. J. Comp. Physiol. A.163:715–727.
Beltz B, Eisen JS, Flamm R, Harris-Warrick R, Hooper SL, Marder E (1984) Serotonergic innervation and modulation of the stomatogastric ganglion of three decapod crustaceans (Homarus americanus, Cancer irroratus, and Panulirus interruptus). J. Exp. Biol. 109:35–54.
Blitz DM, Christie AE, Marder E, Nusbaum MP (1995) Distribution and effects of tachykinin-like peptides in the stomatogastric nervous system of the crab, Cancer borealis. J. Comp. Neurol. 354:282–294.
Cazalets JR, Nagy F, Moulins M (1990) Suppressive control of the crustacean pyloric network by a pair of identified interneurons. I. Modulation of the motor pattern. J. Neurosci.10:448–457.
Christie AE, Baldwin D, Turrigiano G, Graubard K, Marder E (1995) Immunocytochemical localization of multiple cholecystokininlike peptides in the stomatogastric nervous system of the crab, Cancer borealis. J. Exp. Biol.198:263–271.
Cohen AH, Ermentrout GB, Kiemel T, Kopell N, Sigvardt KA, Williams TL (1992) Modelling of intersegmental coordination in the lamprey central pattern generator for locomotion. Trends Neurosci.15:434–438.
Coleman MJ, Nusbaum MP, Cournil I, Claiborne BJ (1992) Distribution of modulatory inputs to the stomatogastric ganglion of the crab, Cancer borealis. J. Comp. Neurol.325:581–594.
Coleman MJ, Nusbaum MP(1994) Functional consequences of compartmentalization of synaptic input. J. Neurosci.14:6544–6552.
DiCaprio RA, Jordan G, Hampton T (1997) Maintenance of motor pattern phase relationships in the ventilatory system of the crab. J. Exp. Biol.200:963–974.
Eisen JS, Marder E (1982) Mechanisms underlying pattern generation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion as determined by selective inactivation of identified neurons. III. Synaptic connections of electrically coupled pyloric neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 48:1392–1415.
Eisen JS, Marder E (1984) A mechanism for the production of phase shifts in a pattern generator. J. Neurophysiol.51:1375–1393.
Flamm RE, Harris-Warrick RM (1986) Aminergic modulation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion. I. Effects on motor pattern and activity of neurons within the pyloric circuit. J. Neurophysiol. 55:847–865.
Friesen WO, Pearce RA (1993) Mechanisms of intersegmental coordination in leech locomotion. Semin. Neurosci.5:41–47.
Golowasch J, Marder E (1992) Ionic currents of the lateral pyloric neuron of the stomatogastric ganglion of the crab. J. Neurophysiol. 67:318–331.
Grillner S (1981) Control of locomotion in bipeds, tetrapods, and fish. In: UB Brooks, ed. Handbook of Physiology: The Nervous System (section 1)—Motor Control. American Physiological Society. Bethesda, MD. pp. 1179–1236.
Grillner S, Wallén P (1985) Central pattern generators for locomotion, with special reference to vertebrates. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 8:233–261.
Harris-Warrick RM, Marder E, Selverston AI, Moulins M (1992) Dynamic Biological Networks: The Stomatogastric Nervous System. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Harris-Warrick RM, Coniglio LM, Barazangi N, Guckenheimer J, Gueron S (1995) Dopamine modulation of transient potassium current evokes phase shifts in a central pattern generator network. J. Neurosci.15:342–358.
Hartline DK (1979) Pattern generation in the lobster (Panulirus) stomatogastric ganglion. II. Pyloric network simulation. Biol. Cybern. 33:223–236.
Hooper SL (1993) Cellular properties underlying phase and duty cycle regulation in the lobster pyloric network (Abstract). Soc. Neurosci. Abstr.19:996.
Hooper SL, Marder E (1987) Modulation of the lobster pyloric rhythm by the peptide, proctolin. J. Neurosci.7:2097–2112.
Hooper SL, Moulins M, Nonnotte L (1990) Sensory input induces long-lasting changes in the output of the lobster pyloric network. J. Neurophysiol.64:1555–1573.
Johnson BR, Peck JH, Harris-Warrick RM (1995) Distributed amine modulation of graded chemical transmission in the pyloric network of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J. Neurophysiol. 74:437–451.
Katz PS, Harris-Warrick RM (1989) Serotonergic/cholinergic muscle receptor cells in the crab stomatogastric nervous system. II. Rapid nicotinic and prolonged modulatory effects on neurons in the stomatogastric ganglion. J. Neurophysiol.62:571–581.
Kopell N, Ermentrout GB (1986) Symmetry and phaselocking in chains of weakly coupled oscillators. Comm. Pure. Appl. Math. 39:623–660.
Marder E, Hooper SL, Siwicki KK (1986) Modulatory action and distribution of the neuropeptide proctolin in the crustacean stomatogastric nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol.243:454–467.
McClellan AD, Sigvardt KA(1988) Features of entrainment of spinal pattern generators for locomotor activity in the lamprey spinal cord.J. Neurosci.8:133–145.
McCormick DA, Huguenard JR (1992) A model of the electrophysiological properties of thalamocortical relay neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 68:1384–1400.
Meyrand P. Moulins M (1986) Myogenic oscillatory activity in the pyloric rhythmic motor system of crustacea. J. Comp. Physiol. A 158:489–503.
Meyrand P, Marder E (1991) Matching neural and muscle oscillators: Control by FMRFamide-like peptides. J. Neurosci.11:1150–1161.
Miller JP, Selverston AI (1982a) Mechanisms underlying pattern generation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion as determined by selective inactivation of identified neurons. II. Oscillatory properties of pyloric neurons. J. Neurophysiol.48:1378–1391.
Miller JP, Selverston AI (1982b) Mechanisms underlying pattern generation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion as determined by selective inactivation of identified neurons. IV. Network properties of pyloric system. J. Neurophysiol.48:1416–1432.
Morris LG, Hooper SL (1994) Dorsal dilator muscles in Panulirus may express both pyloric and gastric mill motor patterns (Abstract). Soc. Neurosci. Abstr.20:1413.
Moulins M, Nagy F (1983) Control of integration by extrinsic inputs in the crustacean pyloric circuit. J. Physiol, Paris78:739–748.
Nagy F, Dickinson PS (1983) Control of a central pattern generator by an identified modulatory interneurone in crustacea. I. Modulation of the pyloric motor output. J. Exp. Biol.105:33–58.
Nagy F, Cardi P (1994) A rhythmic modulatory gating system in the stomatogastric nervous system of Homarus gammarus. II. Modulatory control of the pyloric CPG. J. Neurophysiol.71:2490–2502.
Norris BJ, Coleman MJ, Nusbaum MP (1996) Pyloric motor pattern modification by a newly identified projection neuron in the crab stomatogastric nervous system. J. Neurophysiol.75:97–108.
Nusbaum MP, Marder E (1989) A modulatory proctolin-containing neuron (MPN). II. State-dependent modulation of rhythmic motor activity. J. Neurosci.9:1600–1607.
Nusbaum MP, Weimann JM, Golowasch J, Marder E (1992) Presynaptic control of modulatory fibers by their neural network targets. J. Neurosci.12:2706–2714.
Rand RH, Cohen AH, Holmes PJ (1988) Systems of coupled oscillators as models of central pattern generators. In: AH Cohen, S Rossignol, S Grillner, eds. Neural Control of Rhythmic Movements in Vertebrates. Wiley, New York, NY. pp. 333–368.
Raper JA(1979) Nonimpulse-mediated synaptic transmission during the generation of a cyclic motor program. Science205:304–306.
Rezer E, Moulins M(1983) Expression of the crustacean pyloric pattern generator in the intact animal. J. Comp. Physiol. A153:17–28.
Russell DF (1979) CNS control of pattern generators in the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. Brain Res.177:598–602.
Russell DF, Hartline DK (1982) Slow active potentials and bursting motor patterns in pyloric network of the lobster, Panulirus interruptus. J. Neurophysiol.48:914–937.
Selverston AI, Russell DF, Miller JP, King DG (1976) The stomatogastric nervous system: Structure and function of a small neural network. Prog. Neurobiol.7:215–290.
Skiebe P, Schneider H (1994) Allatostatin peptides in the crab stomatogastric nervous system: Inhibition of the pyloric motor pattern and distribution of allatostatin-like immunoreactivity. J. Exp. Biol.194:195–208.
Stein PSG (1976) Mechanisms of interlimb phase control. In: RM Herman, S Grillner, PSG Stein, DG Stuart, eds. Neural Control of Locomotion. Plenum Press, New York, NY. pp.465–487.
Tierney AJ, Harris-Warrick RM (1992) Physiological role of the transient potassium current in the pyloric circuit of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J. Neurophysiol.67:599–609.
Turrigiano GG, Selverston AI (1989) Cholecystokinin-like peptide is a modulator of a crustacean central pattern generator. J. Neurosci. 9:2486–2501.
Weimann JM, Marder E, Evans B, Calabrese RL (1993) The effects of SDRNFLRFNH 2 and TNRNFLRFNH 2 on the motor patterns of the stomatogastric ganglion of the crab, Cancer borealis. J. Exp. Biol.181:1–26.
Williams TL (1992) Phase coupling by synaptic spread in chains of coupled neuronal oscillators. Science258:662–665.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hooper, S.L. Phase Maintenance in the Pyloric Pattern of the Lobster (Panulirus interruptus) Stomatogastric Ganglion. J Comput Neurosci 4, 191–205 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008822218061
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008822218061