Abstract
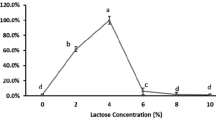
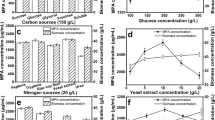
The fermentative production of rifamycin by Amycolatopsis mediterranei (MTCC17) has been studied. Both qualitative and quantitative aspects of the fermentation were determined by optimizing cultural conditions and medium design to improve the production of rifamycin. A pH value of 7.0, a temperature of 26°C, an aeration rate of 250rev/min for a 50ml volume, a level of inoculum of 10% grown aeration for 48h and a fermentation period of 11days were found to be optimum. Among the nitrogen sources, and culture conditions, peanut meal and aeration were found to be critical for rifamycin production respectively. The above mentioned exercise increased the yields of rifamycin from 350mg/l to 2000mg/l.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonowitz, Y. & Demain, A.L. 1980 Thoughts on secondary metabolism. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 1, 5–9.
Alena, C. 1985 Preparation of media. In Biotechnology, eds Rehm, H.-J. and Reed, G. Vol. 2, pp. 631–698. Weinheim: VCH.
Demain, A.L., Aharonowitz, A.R. & Martin, J.F. 1983 Metabolic control of secondary biosynthetic pathways. In Biochemistry and Genetic Regulation of Commercially Important Antibiotics, ed Vining, pp. 49–72. Reading, MA. Addison-wesley.
Demain, A.L., Kennal, Y.M. & Aharonowitz, Y. 1980 Carbon catabolite regulation of secondary metabolism. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 22,(Suppl. 1), 5–9.
Gresham, R. & Inamine, E. 1986 Nutritional improvement of processes. In Manual of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, eds Demain, A.L. & Solomon, N.A. pp. 41–48. Washington: American Society for Microbiology.
Hershbach, G.J.M., Vanderbeek, C.P. & Vandijk, P.W.M. 1984 The rifamycin properties, biosynthesis and fermentation. In Biotechnology of Industrial Antibiotics ed E.J. Vandemme pp. 45–140, New York: Marcel Dekker.
Indian Standard Pharmacopeia 1995 pp. 447–449.
Kluepfel, D., Lancini, G.C. & Sarton, G. 1965 Metabolism of barbital by Streptomyces mediterranei. Applied Microbiology 13, 600–604.
Lal, R., Khanna, M., Kaur, H., Srivastava, N., Tripathi, K.K. & Lal, S. 1995 Rifamycins, Strain improvement programme, CRC Critical Reviews of Microbiology 21, 19–30.
Lal, R. & Lal, S. 1994 Recent trends in rifamycin research. Bio-Essays 16, 211–216.
Louis, E. 1902 Oilcake & meal testing oils & fats. In Vegetable Fats and Oils, ed Andes, L.E. p. 300. London. Scott, Greenwood & Son.
Margalith, P. & Pagani, H. 1961a Rifomycin: XIII, fermentation and production of rifomycin complex. Applied Microbiology 9, 320–3245.
Margalith, P. & Pagani, H. 1961b Rifomycin: XIV Production of Rifomycin B. Applied Microbiology 9, 325–334.
Martin, J.F. & Demain, A.L. 1980 Control of antibiotic biosynthesis. Microbiological Reviews 44, 230–251.
Nunn, 1996 T.B. World, biggest killer, says WHO. SCRIP Pharmaceutical News.
Ronald, C. LI, Prem K. Narang, J.S., Cameron, W & Bianchine, J.R. 1997 Rifabutin absorption in the gut unaltered by concomitant administration of didenosine in AIDS patients. Antimicrobial Agent and Chemotherapy 41, 1566–1570.
Schupp, T., Hutter, R. & Hapwood, D.A. 1975 Genetic recombination in Nocardia mediterranei. Journal of Bacteriology, 121, 128–136.
Sensi, P. & Thiemann, J.E. 1967 Production of rifamycins. Progress in Industrial Microbiology 6, 21–59.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishna, P., Venkateswarlu, G. & Rao, L. Studies on fermentative production of rifamycin using Amycolatopsis mediterranei. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 14, 689–691 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008801302687
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008801302687