Abstract
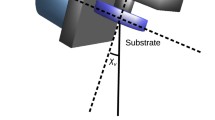
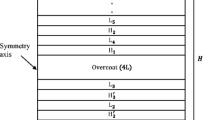
The CEA/DAM megajoule-class pulsed Nd:glass laser devoted to Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF) research will require 240 cavity-end mirrors. The approved laser design necessitates 42-cm × 46-cm × 9-cm highly-reflective (HR)-coated substrates representing more than 50 m2 of coated area. Prototypes of these dielectric mirrors were prepared with interference quaterwave stacks of SiO2 and ZrO2-PVP (PolyVinylPyrrolidone) thin films starting from sol-gel colloidal suspensions (sols). Low refractive index material was based on nanosized silica particles and high refractive index coating solution was made of a composite system. The colloidal/polymeric ratio in the composite system has been optimized regarding refractive index value, laser damage threshold and chemical interactions have been studied using FT-IR spectroscopy. A deposition technique so-called “Laminar Flow Coating” (LFC) has been associated to sol-gel chemistry for HR laser damage-resistant sol-gel coating development. This novel coating method confirmed its main advantages compared to dipping or spinning processes: coating large flat square substrates at room temperature with small solution consumption, good thickness uniformity, weak edge-effects, induced stress-free coating, good optical properties and laser damage resistance fulfilling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.G. Floch, P.F. Belleville, and J.J. Priotton et al., Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 74(10–12) (1995).
H.G. Floch and P.F. Belleville, Procédé de fabrication de couches minces présentant des propriétés optiques, French Patent 92 08524, 1992, assigned to CEA.
P.F. Belleville and H.G. Floch, in 24th Boulder Damage Symposium Proceedings (SPIE, 1992), Vol. 1848, p. 290.
W. Stüober et al., J. Colloid Interface Sci. 26, 62 (1968).
F.M. Fowkes, in Advances in Ceramics, Vol. 21: Ceramic Powder Science, edited by G.L. Messing et al. (American Ceramic Society Proc., 1989), p. 411.
H.G. Floch and P.F. Belleville, Matériau Composite à Indice de Réfraction Élevé, Procédé de Fabrication de ce Matériau Composite et Matériau Optiquement Actif Comprenant ce Matériau Composite, French Patent 93 08762, 1993, assigned to CEA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belleville, P., Bonnin, C. & Priotton, JJ. Room-Temperature Mirror Preparation Using Sol-Gel Chemistry and Laminar-Flow Coating Technique. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 19, 223–226 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008788322168
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008788322168