Abstract
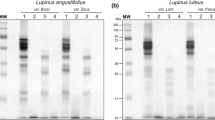
Seed globulins isolated from 58 accessions representing 12 Old World Lupinus species were studied using two techniques of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): reversed-phase (RP-HPLC) and ion-exchange (IE-HPLC). Differences in quantitative and qualitative composition of globulins between smooth-seeded and rough-seeded lupins appear to be significant. Each investigated species/subspecies is distinguished by its specific protein HPLC pattern of globulins. The number of globulin peaks recorded in particular species varied from four to eight. In total, 72 retention times of protein peaks were distinguished in the investigated taxa. Chromatographic data were subjected to statistical analysis using hierarchical UPGMA grouping of the examined taxa. Heterogeneous smooth-seeded lupins proved to be distantly related to rather homogeneous rough-seeded lupins except for the new species L. anatolicus. Within the rough-seeded lupins three subgroups are distinguished: (1) L. atlanticus, L. cosentinii and L. digitatus, (2) L. palaestinus and L. pilosus and (3) L. princei. The obtained data are discussed with reference to taxonomic relationships in the Old World lupins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainouche, A. & R.J. Bayer, 1996. Phytogenetic relationships among the OldWorld and New World Lupinus species (Fabaceae) based on internal transcribed spacers of nuclear ribosomal DNA. In: Proc. of the IXth Int. Lupin Conference, 11–16 May, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, Poster session abstracts, p. 5.
Ainouche, A., R. Greinwald, L. Witte & A. Huon, 1996. Seed alkaloid composition of Lupinus tassilicus Maire (Fabaceae: Genisteae) and comparison with its related rough seeded lupin species. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 4: 405–414.
Batey, I.L., 1994. HPLC ion-exchange chromatographic separations of cereal and legume proteins. In: Kruger, J.E. & J.A. Bietz (Eds.), High-performance Liquid Chromatography of Cereal and Legume Proteins, American Association of Cereals Chemists, St. Paul, MN, pp. 372–391.
Carstairs, S.A., B.J. Buirchell & W.A. Cowling, 1992. Chromosome number, size and interspecific crossing ability of three OldWorld lupins, Lupinus princei Harms, L. atlanticus Gladstones and L. digitatus Forskal, and implications for cytosystematic relationships among the rough-seeded lupins. J. Roy. Soc.West. Austral. 75: 83–88.
Cristofolini, G., 1989. A serological contribution to the systematics of the genus Lupinus (Fabaceae). Pl. Syst. Evol. 166:265–278.
Duranti, M.,P. Restani, M. Poniatowska & P. Cerletii, 1981. The seed globulins of Lupinus albus. Phytochemistry 20: 2071–2075.
Duranti, M., C. Gius & A. Scarafoni, 1995. Lectin-like activity of lupin seed conglutin, a glycoprotein previously referred to as a storage protein. J. Exp. Bot. 46: 725–728.
Esnault, M.A., A. Merceur & J. Citharel, 1991. Characterization of globulins of yellow lupin seeds. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 29: 573–583.
Ferreira, R.B., T.S. Melo & A.N. Teixeira, 1995. Catabolism of the seed storage proteins from Lupinus albus: fate of globulins during germination and seedling growth. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 22: 373–381.
Garcia, M.C., M. Torre, F. Laborda & M.L. Marina, 1997. Rapid separation of soybean globulins by reversed-phase highperformance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 758: 75–83.
Gillespie, J.M. & R.J. Blagrove, 1975. Variability in the proportion and type of subunits in lupin storage globulin. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 2: 29–39.
Gladstones, J.S., 1974. Lupins of the Mediterranean region and Africa. Dept. Agric. W. Austral., Tech. Bull. 26: 1–48.
Gladstones, J.S., 1984. Present situation and potential of Mediterranean/ African lupins for crop production. In: Proc. IIIrd Int. Lupin Congress, June 4–8, La Rochelle, France, pp. 18–37.
Gueguen, J. & P. Cerletti, 1994. Proteins of some legume seeds: soybean, pea, fababean and lupin. In: B.J.F. Hudson (Ed.), New and Developing Sources of Food Proteins, Vol.2, Chapman and Hall, London, pp. 145–193.
Gupta, S., B.J. Buirchell & W.A. Cowling, 1996. Interspecific reproductive barriers and genomic similarity among the rough-seeded Lupinus species. Plant Breeding 115: 123–127.
Huebner, F.R. & J.A. Bietz, 1994. RP-HPLC for varietal identi-fication in cereals and legumes. In: Kruger, J.E. & J.A. Bietz (Eds.), High-performance Liquid Chromatography of Cereal and Legume Proteins, American Association of Cereals Chemists, St. Paul, MN, pp. 97–120.
Käss, E. & M. Wink, 1997. Molecular phylogeny and phylogeography of Lupinus (Leguminosae) inferred from nucleotide sequence of the rbcL gene and ITS 1+2 regions of rDNA. Plant Syst. Evol. 208: 139–167.
Ladizinsky, G. & Hymowitz, T., 1979. Seed protein electrophoresis in taxonomic and evolutionary studies. Theor. Appl. Genet. 54: 680–685.
Mossé, J. & J.C. Pernollet, 1983. Storage proteins of legume seeds. In: S.K. Arora (Ed.), Chemistry and Biochemistry of Legumes, Edward Arnold, London, pp. 111–193.
Nowacki, E., 1960. Systematics of Genisteae in the light of chemical analyses. Genet. Polon. 1: 119–143.
Pazy, B., U. Plitmann & C.C. Heyn, 1981. Genetic relationships between Lupinus pilosus and L. palaestinus (Fabaceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 137: 39–44.
Plitmann, U., 1981. Evolutionary history of the Old World lupines. Taxon 30: 430–437.
Plitmann, U. & C.C. Heyn, 1984. Old-World Lupinus: taxonomy, evolutionary relationships and links with New-World species. In: Proc. of IIIrd Int. Lupin Congress, June, 4–8, La Rochelle, France, pp. 55–66.
Pollard, N.J., C.W. Wrigley, F. Bekes, A. Aumatell & F. Mac-Richie, 1996. Distinction between genotypes of Lupinus species by dodecyl sulphate-gel electrophoresis and by capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 17: 221–223.
Przybylska, J., 1995. Some examples of the use of electrophoretic protein analysis in taxonomic investigations of leguminous plants. J. Appl. Genet. 36: 255–271.
Przybylska, J. & Z. Zimniak-Przybylska, 1995. Electrophoretic patterns of seed globulins in the Old-World Lupinus species. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 42: 69–75.
Salmanowicz, B.P., 1995. Comparative study of seed albumins in the Old-World Lupinus species (Fabaceae) by reversed-phase HPLC. Plant Syst. Evol. 195: 77–86.
Salmanowicz, B.P. & J. Przybylska, 1994. Electrophoretic patterns of seed albumins in the Old-World Lupinus species (Fabaceae): variation in the 2S albumin class. Plant Syst. Evol. 192: 67–78.
Swiecicki, W., 1985. Studies on the interspecific hybrid Lupinus hispanicus Boiss. et Reut. x Lupinus luteus L. Lupin Newslett. 8: 24–25.
S, W., W.K. S & B. Wolko, 1996. Lupinus anatolicus — a new lupin species of the Old World. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 43: 109–117.
Williams, C.A., A. Demissie & J.B. Harborne, 1983. Flavonoids as taxonomic markers in Old-World Lupinus species. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 11: 221–231.
Wink, M., C. Meissner & L. Witte, 1995. Patterns of quinolizidine alkaloids in 56 species of the genus Lupinus. Phytochemistry 38: 139–153.
Wolko, B. & N.F. Weeden, 1990. Relationships among lupin species as reflected by isozyme phenotype. Genet. Polon. 31: 189–197.
Zimniak-Przybylska, Z. & J. Przybylska, 1997. Electrophoretic globulin patterns in some New World Lupinus species. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 44: 57–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salmanowicz, B.P. Seed globulins in the Old World Lupinus species: Comparative study by HPLC. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 46, 409–417 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008608120931
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008608120931