Abstract
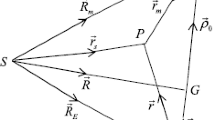
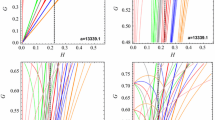
Eccentricity resonances between the secular motion of an Earth satellite's orbit and the longitudes of the Sun and the Moon are studied within a Hamiltonian framework. The problem is approximated in a traditional manner, with the Earth's potential including only the second zonal harmonic, and a Hill‐type approximation for perturbing bodies. For a family of 10 resonances, stable and unstable points are identified and libration widths are estimated. Numerical values are given for the maximum variation of eccentricity available at each resonance. The respective amplitudes of the perigee heights' librations range from 2 to 750 km. The resonances of the solar origin are generally stronger than their lunar counterparts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coffey, S. L., Deprit, A. and Deprit, E.: 1994, 'Frozen orbits for satellites close to an Earth-like planet', Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 59, 37-72.
Cook, G. E.: 1962, 'Luni-solar perturbations of the orbit of an Earth satellite', Geophys. J. 6, 271-291.
Garfinkel, B.: 1966, 'Formal solution in the problem of small divisors', Astron. J. 71, 657-669.
Giacaglia, G. E. O.: 1994, 'Third body perturbations on satellites', in: P. K. Seidelmann and B. Kaufman (eds.), Proceedings of the Artificial Satellite Theory Workshop held at the U.S. Naval Observatory November 8–9, 1993, U.S. Naval Observatory, Washington, 73-155.
Hough, M. E.: 1981, 'Sun-synchronous orbits near critical inclination', Celest. Mech. 25, 137-157.
Hughes, S.: 1980, 'Earth satellite orbits with resonant lunisolar perturbations, I. Resonances dependent only on inclination', Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 372, 243-264.
Hughes, S.: 1981, 'Earth satellite orbits with resonant lunisolar perturbations, II. Some resonances dependent on the semi-major axis, eccentricity and inclination', Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 375, 379-396.
Kaula, W. M.: 1962, 'Development of the lunar and solar disturbing functions for a close satellite', Astron. J. 67, 300-303.
Musen, P.: 1960, 'Contributions to the theory of satellite orbits', in: H. K. Bijl (ed), Space Research, North-Holland, New York, pp. 434-447.
Siebold, K. and Reynolds, R.: 1995, 'Lifetime reduction of a geosyncronous transfer orbit with the help of lunar-solar perturbations', Advances in Space Research 16(11), 155-161.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breiter, S. Lunisolar Apsidal Resonances at low Satellite Orbits. Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy 74, 253–274 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008379908163
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008379908163