Abstract
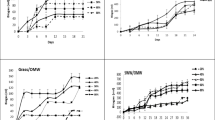
Combined anaerobic digestion of oil mill effluent(OME) together with manure, household waste (HHW) orsewage sludge was investigated. In batch experimentsit was shown that OME could be degraded into biogaswhen codigested with manure. In codigestion with HHWor sewage sludge, OME dilution with water (1:5) wasrequired in order to degrade it. Using continuouslystirred lab-scale reactors it was shown thatcodigestion of OME with manure (50:50 and 75:25 OMEto manure ratios) was successful with a theoreticalOME utilization of 75% and with approx. 87%reduction of the lipids content in OME. An OMEutilization of approx. 55%, and lipid reduction of73% was reached in codigestion with HHW (50:50 and75:25 OME to HHW ratios). The results showed thatthe high buffering capacity contained in manure,together with the content of several essentialnutrients, make it possible to degrade OME withoutprevious dilution, without addition of externalalkalinity and without addition of external nitrogensource.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahring BK (1995) Methanogenesis in thermophilic biogas reactors. Ant. van Leeuw. 67: 91–102
Ahring BK, Angelidaki I & Johansen K (1992) Anaerobic treatment of manure together with organic industrial waste. Water Sci. Technol. 7: 311–318
Ahring BK, Angelidaki I & Johansen K (1992) Co-digestion of organic solid waste, manure and organic industrial waste. Waste Management International K.J. Thimé-Kozmiensky (Eds.) EF-Verlag für Energie-und Umwelttechnik GmbH 1: 661–666
Angelidaki I, Petersen S & Ahring BK (1990) Effect of lipids on thermophilic anaerobic digestion and reduction of lipid inhibition upon addition of bentonite. Appl.Microbiol. Biotechnol. 33: 469–472
Aveni A (1984) Biogas recovery from olive oil mill wastewater by anaerobic digestion. In: Rreffero GL, Ferranti MP & Naveau H (Eds) Anaerobic digestion and carbohydrate hydrolysis of waste (pp 489–491). Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, Essex
Beccari M, Bonemazzi F, Majone M & Riccardi C (1996) Interactions between acidogenesis and methanogenesis in the anaerobic treatment of olive oil mill effluents. Wat. Res. 1: 183–189
Boari G, Brunetti A, Passino R & Rozzi A (1984) Anaerobic digestion of olive oil mill wastewaters. Agricul. Wastes 10: 161–175
Boari G, Mancini IM & Trulli E (1984) Anaerobic digestion of olive oil mill effluent pretreated and stored in household waste sanitary landfills. Wat. Sci. Technol. 28: 27–34
Bryant MP & Robinson IM (1961) Studies on nitrogen requirements of some ruminal cellulolytic bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. 9: 96–103
Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE & Trussel RR (1985) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C.
Hashimoto AG (1983) Conversion of straw-manure mixtures to methane at mesophilic and thermophilic temperatures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 15: 185–200
Hendriksen HV, Larsen S & Ahring BK (1992) Influence of supplemental carbon source on anaerobic dechlorination of pentachlorophenol in granular sludge. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 365–370
McCarty, 1964. Anaerobic waste treatment fundamentals III. Public works 95: 91–94
Morelli A, Rindone B, Andreoni V, Villa M, Sordini C & Balice V (1990) Fatty acids monitoring in the anaerobic depuration of olive mill wastewaters. Biological Wast. 32: 253–263
Sørensen AH (1996) Microbial characterization of methanogenic reactors. Ph. D. Thesis. Copenhagen, Denmark
Schink B (1988) Principles and limits of anaerobic degradation: Environmental and technological aspects. In: Zehnder AJB (Ed) Biology of anaerobic microorganisms. Chapter 14. A Wiley-Interscience Publication. John Wiley & Sons.
Tsonis SP & Grigoropoulos SG (1993) Anaerobic treatability of olive oil mill wastewater. Wat. Sci. Tech. 28: 34–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angelidaki, I., Ahring, B. Codigestion of olive oil mill wastewaters with manure, household waste or sewage sludge. Biodegradation 8, 221–226 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008284527096
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008284527096