Abstract
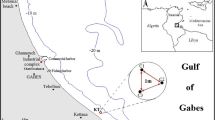
The concentrations of metals (Mn, Pb, Fe, Zn, Cu, Cd,Co, Ni, Cr, Na, K, Ca, Mg) were determined in thegreen alga Ulva rigida, in the sediment andseawater of Thermaikos Gulf (Greece) during monthlysamplings in 1994–1995. This Gulf is the recipientof domestic and industrial effluents. Pb, Fe, Cu, Coand Cr concentrations in U. rigida at the studyarea were higher than those 13 years earlier andapparently came from different sources than those forZn, Cd and Ni. The relative abundance of metals inthe alga decreased in the order: Mg > Na > K >Ca > Pb > Fe > Mn > Zn > Cr, Cu > Ni >Co > Cd. Only Cu concentrations in the alga fromKalochori and Cd ones from Viamyl showed significantseasonal changes. Cu and Cd concentrations ingeneral followed the same pattern of variation, withminimum values in winter-spring. This pattern isdiscussed in relation to growth dynamics and tissueage. Only Pb concentrations in the alga showed asignificant positive correlation with concentrationsin the seawater. There were both positive andnegative correlations among some metals in the alga. It is concluded that U. rigida can be used as anindicator species, especially for Pb.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brix H, Lyngby JE (1983) The distribution of some metallic elements in eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) and sediment in the Limfjord, Denmark. Estuar. coast. Shelf Sci. 16: 455-467.
Brix H, Lyngby JE, Schierup HH (1983) Eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) as an indicator organism of trace metals in Limfjord, Denmark. Mar. envir. Res. 8: 165-181.
Catsiki VA, Papathanassiou E (1993) The use of the chlorophyte Ulva lactuca (L.) as indicator organism of metal pollution. In: Proceedings of Cost-48 Symposium of Sub Group III. Macroalgae, Eutrophication and Trace Metal Cycling in Estuaries and Lagoons. Thessaloniki, Greece, 93-105.
Collins MB (1981) Sediment yield studies of headwater catchments in Sussex, S-E. England. Earth Surface Processes 13: 25-36.
Diamantopoulos E, Deligiannis A, Ziogouk, Kozlakidou S, Stylianou I, Bagiatis (1989). Quantitative feature of the Sewage of Thessaloniki. 6th Seminar for protection of the environment. Aquatic Recipients, Thessaloniki, Greece: 129-137.
Diannelidis B-E, Delivopoulos SG (1999) Ultrastructural effects of heavy metals on the epidermal cells of Dictyota spiralis (Mont.) Hamel (Dictyotales, Phaeophyta). Int. J. Algae 1(3): 21-30.
Djingova R, Kuleff I, Arpadjan S, Voulgaropoulos A, Sawidis T, Alexandrov S (1987) Neutron activation and atomic absorption analysis of Ulva lactuca and Gracilaria verrucosa from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Toxicol. Envir. Chem. 15: 149-158.
Ganoulis J, Krestenitis J (1982) Choix du site optimum d'evacuàtion des eaux usées dans une région côtière. Societé Hydrotechnique de France, 17 Journeés de J 'Hydraulique.
Güven KC, Topcuo-Glu S, Kut D, Esen N, Erenturk N, Saygi N, Cevher E, Guvener B, Ozturk B (1992) Metal uptake by Black sea algae. Bot. mar. 35: 337-340.
Haritonidis S (1978) Contribution to the research of marine macrophyceae (Chloro-, Phaeo-and Rhodophyceae) of Thermaikos Gulf. PhD Thesis, Univ. Thessaloniki, Greece, 175 pp. (inGreek).
Haritonidis S (1993) Introduction into eutrophication problems and metal distribution in Greek lagoons. In: Proceedings of COST-48 Symposium of SubGroup III. Macroalgae, Eutrophication and Trace Metal Cycling in Estuaries and Lagoons. Thessaloniki, Greece, 24-26 September, 154-163.
Haritonidis S, Malea P (1995) Seasonal and local variation of Cr, Ni and Co concentrations in Ulva rigida C. Agardh and Enteromorpha linza (Linnaeus) from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Envir. Pollut. 89: 319-327.
Haritonidis S, Malea P (1999a) Bioaccumulation of metals by the green alga Ulva rigida from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Envir. Pollut. 104: 365-372.
Haritonidis S, Malea P (1999b) Seasonal and local variation of metals in seawater treated by different methods and in sediment of Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Obelia 25: 89-109.
Ho YB (1987) Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta, Ulvales) in Hong Kong intertidal waters-its nitrogen and phosphorus contents and its use as a bioindicator of eutrophication. Asian. Mar. Biol. 4: 97-102.
Ho YB (1990) Ulva lactuca as bioindicator of metal contamination in interdal waters in Hong Kong. Hydrobiologia 203: 73-81.
Hortung H, Kress N, Friedlander M (1992) Trace element concentrations intertidal algae collected along the Mediterranean shore. Israel Fresen. Envir. Bull. 1: 84-89.
Karez CS, Magalhaes VF, Pfeiffer WC, Amado Fillo GM (1994) Trace metal accumulation by algae in Sepetiba Bay, Brazil. Envir. Pollut. 83: 351-356.
Malea P, Haritonidis S (1995) Local distribution and seasonal variation of Fe, Pb, Zn, Cu, Cd, Na, K, Ca and Mg concentrations in the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Aschers. in the Antikyra Gulf, Greece. P.S.Z.N.I. mar. Ecol. 16: 41-56.
Malea P, Haritonidis S (1999a) Metal content in Enteromorpha linza (Linnaeus) in Thermaikos Gulf (Greece). Hydrobiologia 394: 103-112.
Malea P, Haritonidis S (1999b) Seasonal accumulation of metals by red alga Gracilaria verrucosa (Huds.) Papenf. from Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. J. appl. Phycol. 11: 503-509.
Malea P, Haritonidis S, Stratis I (1994) Bioaccumulation of metals by Rhodophyta species at Antikyra Gulf (Greece) near an aluminium factory. Bot. mar. 37: 505-513.
Malea P, Haritonidis S, Kevrekidis T (1995) Metal content of some green and brown seaweeds from Antikyra Gulf (Greece). Hydrobiologia 310: 19-31.
Marcantonatos G (1990) Treatment and Disposal of AquaticWastes, Sewage, Industrial Effluents, Animal Residue. Athens, 738 pp.
Munda IM, Hundnik V (1991) Trace metal content in some seaweeds from the Northern Adriatic. Bot. mar. 34: 241-249.
Orfanidis SE, Lazaridou E, Seferlis E, Haritonidis S (1994) Eutrophication and the abundance of seaweeds in the biotope of Agia Triada, Gulf of Thessaloniki. In: Proceedings 5th National l. Symp. Oceanogr. Fish. 1: 67-70.
Pulich WM (1980) Heavy metal accumulation by selected Halodule wrightii Asch. populations in the Corpus Christi Bay area. Mar. Sci. Univ. Tex. 23: 89-100.
Sawidis Th, Voulgaropoulos AN (1986) Seasonal bioaccumulation of iron, cobalt and copper in marine algae from Thermaikos Gulf of the Northern Aegean Sea, Greece. Mar. envir. Res. 19: 39-47.
Shiber JG (1980) Trace metals with seasonal considerations in coastal algae and molluscs from Beirut, Lebanon. Hydrobiologia 69: 147-162.
Shiber J, Washburn E (1978) Lead, mercury and certain nutrient elements in Ulva lactuca (Linnaeus) from Ras Beirut, Lebanon. Hydrobiologia 61: 187-192.
Talbot V, Chegwidden A (1982) Cadmium and other heavy metal concentrations in selected biota from Cockburn Sound, western Australia, Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 33: 779-788.
Wahbeh M (1984) Levels of Zn, Mn, Mg, Fe and Cd in three species of seagrasses from Aqaba (Jordan). Aquat. Bot. 20: 179-183.
Wahbeh MI, Mahasneh DM, Mahasneh I (1985) Concentrations of zinc, manganese, copper, cadmium, magnesium and iron in ten species of algae and seawater from Aqaba, Jordan. Mar. envir. Res. 16: 98-102.
Wong MH, Kwok TT, Ho KC (1982) Heavy metal in Ulva lactuca collected within Tolo Harbour and almost landlocked sea. Hydrobiologia 16: 223-230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malea, P., Haritonidis, S. Use of the green alga Ulva rigida C. Agardh as an indicator species to reassess metal pollution in the Thermaikos Gulf, Greece, after 13 years. Journal of Applied Phycology 12, 169–176 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008136320459
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008136320459