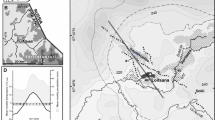
Abstract
Recent environmental change research in Lake Baikal is introduced together with an overview of several interrelated papers published concurrently in this issue of Journal of Paleolimnology. Five themes are tackled by analysis of recent Baikal sediment cores, dating, geochemistry, particulate pollutants, magnetism and diatoms. The concurrent papers focus on the first four themes in some detail and summary results of diatom analysis (from Mackay et al., 1998) are given here. Taken together these studies provide a time-space framework for recent environmental change in Lake Baikal not previously available.
There are significant shifts in species composition of the endemic planktonic diatom assemblages in uppermost sediments collected from throughout the lake. However, these changes usually precede the sediment record of low level but widespread contamination by industrial products. The most clear sign of industrial contamination is the presence of particles from fossil fuel combustion in sediment post dating the 1930s.
Although evidence for widespread biostratigraphic changes by pollution is lacking, radionuclide, diatom, lithostratigraphic and magnetic stratigraphies indicate two main features, (i) it is possible to make stratigraphic correlations within and between basins using recent sediment cores, (ii) that turbidite deposits, from several to tens of cm thick, are frequently encountered in recent sediments.
Turbidite deposits occur in 210Pb dated and pre-210Pb sediment core sections and are undoubtedly a major macro-disturbance feature in many deep water locations in Lake Baikal. If profiles are to be used as direct proxy records of climate variability, then screening of cores for turbidites is a pre-requisite for quality assurance in future paleoenvironmental studies.
On-going international research including Swiss, Russian and British joint paleoenvironmental studies on the distribution and biological formation of recent sediments will hopefully lead to better interpretation of Holocene and pre-Holocene sediment records in Lake Baikal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleby, P. G., R. J. Flower, A. W. Mackay & N. L. Rose, 1998. Paleolimnological assessment of recent environmental change in Lake Baikal: sediment chronology. J. Paleolimnol. 20: 119–133.
Battarbee, R. W., 1991. Recent paleolimnology and diatom-based environmental reconstruction. In: L. C. K. Shane & E. J. Cushing (eds), Quaternary Landscapes. University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis: 129–174.
BDP-93 Baikal Drilling Project Members, 1997. Preliminary results of the first scientific drilling on Lake Baikal, Buguldieka site, southeastern Siberia. Quaternary International 37: 3–17.
Bowmaker, J. K., V. I. Govardovskii, S. A. Shukolyukov, L.V. Zuela, D. M. Hunt, V. G. Sideleva & O. G. Smirnova, 1993. Visual pigments and the photic environment: the cottoid fish of Lake Baikal. Vision Research 34: 591–605.
Boxshall, G. A., T. D. Evstigneeva & P. F. Clark, 1993. A new interstitial cyclopoid copepod from a sandy beach on the western shore of Lake Baikal, Siberia. Hydrobiologia 268: 99–107.
Boyle, J. F., A. W. Mackay, N. L. Rose, R. J. Flower & P. G. Appleby, 1998. Sediment heavy metal records in Lake Baikal: natural and anthropogenic sources. J. Paleolimnol. 20: 135–150.
Bradbury, J. P. & V. K. Dieterich-Rurup, 1993. Holocene diatom paleolimnology of Elk Lake, Minnesota. In: J. P. Bradbury & W. E. Dean (eds), Elk Lake Minnesota: Evidence for rapid Climate Change in the NorthCentral United States: 215–238. Special Paper 276. US Geological Survey, Denver.
Bradbury, J. P., Y. V. Bezrukova, G. P. Chernyaeva, S. M. Colman, G. Khursevich, J. W. King & Ye. V. Likhoshway, 1994. A synthesis of postglacial diatom records from Lake Baikal. J. Paleolimnol. 10: 213–252.
Callender, E. & L. Granina, 1997. Geochemical mass balances of major elements in Lake Baikal. Limnol. Oceanogr. 42: 148–155.
Colman, S. M., J. A. Peck, E. B. Karabanov, S. J. Carter, J. W. King & D. F. Williams, 1995. Continental climate response to orbital forcing: The diatom paleoproductivity record from Lake Baikal. Nature 378: 769–771.
Colman, S. M., G. A. Jones, R. Meyer, J. W. King, J. A. Peck & W. H. Orem, 1996. AMS radiocarbon analyses from Lake Baikal, Siberia: challenges of dating sediments from a large, oligotrophic lake. Quaternary Science Reviews 15: 669–684.
Dearing, J. A., 1992. Sediment yield and sources in a welsh upland lake catchment during the past 800 years. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 17: 1–22.
Dearing, J.A., J. F. Boyle, P. G. Appleby, A. W. Mackay & R. J. Flower, 1998. Magnetic properties of recent sediments in Lake Baikal, Siberia. J. Paleolimnol. 20: 163–173.
Dienes, L., 1969. Locational factors and locational developments in the Soviet chemical industry.Research Paper No. 119, 1–264 pp. University of Chicago.
Edgington, D. N., J. V. Klump, J. A, Robbins, Y. S. Kusner, V. D. Pampoura & I. V. Sandimirov, 1991. Sedimentation rates, residence times and radionuclide inventories in Lake Baikal from 137Cs and 210Pb in sediment cores. Nature 350: 601–604.
Edlund, M. B., E. F. Stoermer & C. H. Pilskaln, 1995. Siliceous microfossil succession in the recent history of two basins in lake Baikal, Siberia. J. Paleolimnol. 14: 165–184.
Fedorova, V. A., 1975. Diatom algae in bottom sediments. In: Dynamics of the lake Baikal Depression. Transactions of the Limnological Institute 21: 83–87 (in Russian).
Flower, R. J., 1993a. Diatom preservation: experiments and observations on dissolution and breakage in modern and fossil material. Hydrobiologia 269/270: 473–484.
Flower, R. J., 1993b. A taxonomic reevaluation of endemic Cyclotella taxa in Lake Baikal, Siberia. Nova Hedwigia, Beih. 106: 203–220.
Flower, R. J., A.W. Mackay, N. L. Rose, J. L. Boyle, J. A. Dearing, P. G. Appleby, A. E. Kuzmina & L. Z. Granina, 1995a. Sedimentary records of recent environmental change in lake Baikal, Siberia. The Holocene 5: 323–327.
Flower, R. J., D. T. Monteith, A. W. Mackay, J. M. Chambers, 1995b. The design and performance of a new box corer for collecting undisturbed samples of soft subaquatic sediments. J. Paleolimnol. 14: 101–111.
Flower, R. J., S. V. Politov, B. Rippey, N. L. Rose, P. G. Appleby & A. C. Stevenson, 1997. Sedimentary records of the extent and impact of atmospheric contamination from a remote Siberian highland lake. The Holocene 7: 161–173.
Flower, R. J., D. Ryves, R. W. Battarbee, J. Mueller & M. Sturm, 1998. Lake Baikal: some aspects of current research. Minutes of a workshop held during the 7th International Symposium on Palaeolimnology, Heiligkrueztal, Germany. 28th August 2nd September. J. Paleolimonol., in press.
Galazii, M. J., 1982. The ecosystem of Lake Baikal and problems of environmental protection. Soviet Geography 22: 217–225.
Galazii, M., 1991. Lake Baikal reprieved. Endeavour 15: 13–17.
Grachev, M., V. P. Kumarev, L. V. Mamaev, V. L. Zorin, N. N. Baranova, G. Denikina, S. I. Belikov, E. A. Petrov, R. S. Kolesnik, A. M. Dorofeev, V. N. Beim, F. G. Kudelin, F. Magieva & V. N. Sidorov, 1989. Distemper virus in Baikal seals. Nature 338: 209.
Grachev, M., 1994. Formation of the Lake Baikal International Centre for Ecological Research. Ecol. Int. Bull. 21: 75–88.
Grachev, M., Ye. V. Likhoshway, S. M. Colman & A. E. Kuzmina, 1996. Measurement of the diatom sedimentation flux in Lake Baikal by means of automatic traps. Doklady Acad. Science 350: 87–91 (in Russian).
Grachev, M., Ye. V. Likhoshway, S. S. Vorobyova, O. M. Khylystov, E. V. Bezrukova, E. V. Veinberg, E. L. Goldberg, L. Z. Granina, E. G. Kornakova, F. I. Lazo, O. V. Levina, P. P. Letunova, P. V. Otiniv, V. V. Pirog, M. A. Fedorin, V. A. Zolotaryov & V. A. Kravchinsky, 1997. Signals of the paleoclimates of Upper Pleistocene in the sediments of Lake Baikal. Geologia i geofizka, in press.
Granina, L. Z., 1991.Vertical profiles of iron and manganese concentrations in Lake Baikal pore waters. Geokhimiya 10: 1493–1500.
Goldberg, E. D., V. F. Hodge, J. J. Griffin, M. Koide & D. N. Edgington, 1981. Impact of fossil fuel combustion on the sediments of Lake Michigan. Envir. Sci. Technol. 15: 466–471.
Green, J. & G. Koslova, 1992. Carotenoids, photoprotection and foodweb links in Lake Baikal. Freshwat. Biol. 28: 49–58.
Julius, M. L., E. F. Stoermer, S. M. Colman & T. C. Moore, 1997. A preliminary investigation of siliceous microfossil succession in late Quaternary sediments from Lake Baikal, Siberia. J. Paleolimnol. 18: 187–204.
Kozhov, M., 1963. Lake Baikal and its Life. Monographiae Biologicae XI. Junk. The Hague.
Lees, J. A., R. J. Flower & P. G. Appleby, 1998a. Mineral magnetic and physical properties of surficial sediments and onshore samples from the southern basin of Lake Baikal, Siberia. J. Paleolimnol. 20: 175–186.
Lees, J. A., R. J. Flower, D. Ryves, E. G. Vologina & M. Sturm, 1998b. Identifying sedimentation patterns in lake Baikal using whole core and surface scanning magnetic susceptibility. J. Paleolimnol. 20: 187–202.
Likhoshway, Y. V., 1994. Diatom algae in palaeoclimate reconstructions. In: Baikal as a Natural Laboratory for Global Change, Pt. 2 (Abstracts), p. 25. INTAS – Russian Academy of Sciences, Siberian Branch, Irkutsk.
Mackay, A. W., R. J. Flower & R. W. Battarbee, 1996. Stratigraphical evidence of environmental change in Lake Baikal associated with recent changes in climate. Environmental Change Research Centre, Research Report No. 19, 166 pp.
Mackay, A. W., R. J. Flower, A. E. Kuzmina, L. Z. Granina, N. L. Rose, P. G. Appleby, J. F. Boyle & R. W. Battarbee, 1998. Diatom succession trends in recent sediments from Lake Baikal and their relationship to pollution and to climate change. Phil. Trans. R. Soc., Lond., in press.
Massey-tewart, J., 1991. Lake Baikal: on the brink. IUCN Envir. Res. Ser. 2: 3–36.
Mote, V. L., 1974. Air Pollution in the Soviet Union. In: I. Volges (ed.), Environmental Deterioration in the Soviet Union: 24–55. Preager Publishers, New York, 168 pp.
Oldfield, F., C. Barnosky, E. B. Leopold & J. P. Smith, 1983. Mineral magnetic studies of lake sediments. Hydrobiologia 103: 37–44.
Pampoura, V. D., M. I. Kuzmin, A. N. Gvozdkov, V. S. Antipin & I. S. Lomonosov, 1993. Geochemistry of recent sediments in Lake Baikal. Rus. Geol. Geophys. 34: 52–59.
Peck, J. A., J. W. King, S. M. Colman & V. Kravchinski, 1994. A rock magnetic record from Lake Baikal, Siberia: Evidence for Late-Quaternary climate change. Earth Planet. Lett. 122: 221–238.
Petrova, Z. I. & V. I. Levitsky, 1984. Petrology and geochemistry of granulite complexes of the Baikal area. Novosibirsk, Nauka, 200 pp.
Popovskaya, G. & A. Kuzmina, 1988. Ecological Problems of the Baikal Region, Pt. 2. (Abstracts). State Committee on Public Education, Hydrobiological Society, USSR Academy of Sciences, Irkutsk.
Pryde, P. R., 1972. Conservation in the Soviet Union. Cambridge University Press, 299 pp.
Renberg, I. & M. Wik, 1985. Soot particle counting in recent lake sediments: an indirect dating method. Ecol. Bull. 37: 53–57.
Rippey, B., R. J. Murphy & S. W. Kyle, 1982. Anthropogenically derived changes in the sedimentary flux ofmg, Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, Hg, Pb & P in Lough Neagh, Northern Ireland. Envir. Sci. Technol. 16: 23–30.
Rose, N. L. & S. Juggins, 1994. A spatial relationship between carbonaceous particles in lake sediments and sulphur deposition. Atmos. Envir. 28: 177–183.
Rose, N. L., 1995. Carbonaceous particle record in lake sediments from the Arctic and other remote areas of the Northern Hemisphere. Science of the Total Environment 160/161: 487–496.
Rose, N. L., P.G. Appleby, J. F. Boyle, A.W. Mackay & R. J. Flower, 1998. The spatial and temporal distribution of fossil-fuel derived pollutants in the sediment record of Lake Baikal, eastern Siberia. J. Paleolimnol. 20: 151–162.
Shimaraev, M. N., V. I. Verbolov, N. G. Granin & P. P. Sherstyankin, 1994. In: M. N. Shimaraev & S. Okuda (eds), Physical Limnology of Lake Baikal: A Review. Baikal International Center for Ecological Research. Report No. 2, Irkutsk Okayama.
Sorokovnikova, L. M., V. N. Cinukovich, V. V. Drukker, T. G. Potemkina, O. G. Netsvetaeva & V. A. Afanaseva, 1994. Peculiarities of the ecological situation of the Selenga River during flood. In: Baikal as a Natural Laboratory for Global Change, Pt. 3 (Abstracts). p. 91. INTAS – Russian Academy of Sciences, Siberian Branch, Irkutsk.
Sturm, M., V. Matta, M. Schurter, A. Zwyssig, E. G. Vologina, O. V. Levina, R. Gnatovsky, R. J. Flower, D. Ryves, J. A. Lees & D. H. Jewson, 1987. Recent sedimentation in Lake Baikal. Results of high resolution trap and short core research. 7th International Symposium on Palaeolimnology, Heiligkrueztal, Germany. 28th August – 2nd September. Abstract Volume, Wuerzberger Geographische Manuscripte 41: 213–214.
Thompson, R. & F. Oldfield, 1986. Environmental Magnetism. Allen & Unwin, London.
Zumbrunnen, C., 1974. Lake Baikal controversy, a serious water pollution threat or a turning point in Soviet environmental conservation. In: I. Volges (ed.), Environmental Deterioration in the Soviet Union: 80–122. Preager Publishers, New York, 168 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flower, R. Paleolimnology and recent environmental change in Lake Baikal: an introduction and overview of interrelated concurrent studies. Journal of Paleolimnology 20, 107–117 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008047614619
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008047614619