Abstract
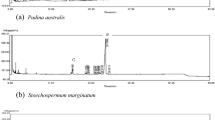
Fatty acid compositions of twelve algal species from two different classes were determined. Three Chlorophyta species (Acetabularia calyculus, Cladophora sericoides and Dictyosphaeria cavernosa) and nine Phaeophyta species (Colpomenia sinuosa, Cystoseria trinodis, Dictyota cervicornis, Hormophysa triquetra, Padina gymnospora, Sargassum binderi, S. boveanum, S. denticulatum and S. heteromorpha) were investigated. Thirty-four fatty acids were identified. Myristic, palmitic, oleic, linoleic, eicosodienic and lignoceric acids were predominant in all examined algal species. Branched saturated fatty acids were also found in all investigated species except Cladophora serricoides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heiba HI, Al-Nagdy SA, Rizk AM, Durgham MM (1993). The amino acid composition of some common marine algae from Qatar (Arabian Gulf). Qatar Uni Sci J 13(2): 219-225.
Balasubramanyan RH, Rangaswami H (1972). Algae as poultry feed. Madaras Agr J 59(7): 379-390.
Miura A (1975). Prophyra cultivation in Japan, pp. 273-304, in Tokida J, Hirose H (eds.), Advances of phycology in Japan. The Hague: Dr W Junk Publishers.
Nisizawa K, Nada H, Kikuchi R, Watanabe T (1987). The main seaweed foods in Japan. Hydrobiologia 151-152: 5-29.
Tseng CK (1981). Marine phytoculture in China. Proc Int Sea Weed Symposium 10: 123-125.
Mumford, TF, Miura A (1984). Prophyra as food. Tokyo University of Fisheries, Japan.
Chapman VJ, Chapman DJ (1980) Seaweeds and their uses, 3rd edn., pp. 88-89, 98-147. London: Chapman and Hall.
Nelson WA (1984). Prophyra (Karengo) biology uses and harvesting. MAF Information Services, New Zealand.
Kumar HD, Singh NH (1976). A textbook of algae. New Delhi: Affil East West Press, 216 pp.
Phol P, Zurheid F (1979). In: Hoppe HA, Leving T, Tanaka Y (eds.), Marine algae in pharmaceutical science. Berlin/New York: Walter de Gruyter, pp. 473-523.
Bremer HJ, Schweiger HG, Schweiger E (1962). Free amino acid content of nucleate and anucleate Acetabularia. Biochem Biophys Acta 56: 380-382.
Tkachenko FP, Koval VT (1990). Biochemical composition of dominent benthic seaweeds in the Black Sea. Gidrobiol Zh 26(5): 33-36.
Atay D (1967). Influence of season on the niacin and biotin contents of Cystoseira barbatafrom the Black Sea. Yearbook Fac Agr, Univ Ankara 7: 85-94.
Hasni S, Hussain M (1986). Determination of macro and micronutrients of a few marine algae found at the Karachi coast. J Pharm (Univ Karachi) 5(1): 29-36.
Yu JY, Lee KY, Kim SH (1975). Nutritive value and utilization of powdered seaweeds. Hanguk Yongyang Hakhoe chi 8(1): 15-37.
Dave MJ, Parekh RG, Grag SK, Mehta DJ (1979). Preparation of seaweed meal for the feeding of farm animal. Salt Res Ind 15(2): 34-38.
Ratan R, Pantayak BC, Bhatia DR (1979). A note on the utilisation of seaweed-meal (Sargassum) in concentrate mixture of cross bred hoggets. Indian J Anim Sci 49: 140- 142.
Naidu KA, Tewari A, Joshi HV, Viswanah S, Ramesh HP, Rao SV (1993). Evaluation of nutritional quality and food safety of seaweeds of India. J Food Saf 13(2): 77-90.
Behairy AKA, ElSayed MM (1983). Biochemical composition of some marine brown algae from Jeddah coast, Saudi Arabia. Indian J Mar Sci 12: 200-201.
Yunev OA, Markova (1979). Extraction of steroids with hypocholesterolemic effect from marine brown algae. Ekol Morsk Org, Mater Vses Nauchno-Tekh Konf 74-78.
Rizk AM, Al-Easa, HSS, Kornprobst JM, eds. The phytochemistry of the macro-algae of the Arabian Gulf (in press).
Attaway DH, Zaborsky OR, eds (1983). Marine biotechnology, Vol. 1: Pharmaceutical and bioactive natural products.
Bongiorni L, Pietra F (1995). Marine natural products for industrial applications. Chemistry and industry 54-58.
Fleurance J, Kaas R (1995). Les algues marines: une source meconnue de proteines vegetales. Equinox 56: 12-17.
Heiba HI (1989). Fatty acid composition of eleven algae from the coastal zones of Qatar. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 39: 401-405.
Aknin M, Dogberi K, Samb A, Kornprobst JM, Gaydou EM, Miralles J (1992). Fatty acid and sterol composition of eight brown algae from the Senegalese coast. Comp Biochem Physiol 102B(4): 841-843.
Aknin M, Moellet-Nzaou R, Cisse E, Kornprobst JM, Gaydoudou EM, Samb A, Miralles J (1992). Fatty acid composition of twelve species of Chlorophyceae from the Senegalese coast. Phytochemistry 31(8): 2739-2741.
Araki S, Sakurai T, Omata T, Kawaguchi A, Murata N (1986). Lipid and fatty acid composition in the red alga Porphyra yessonsis. Jap J Physiol 34: 94-100.
Gillan FT, Hogg RW, Diew EA (1984). The sterol and fatty acid composition of seven tropical sea grasses from the North Queensland Australia. Phytochemistry 23: 2817- 2821.
Jamieson GR, Reid EH (1972). The component fatty acids of some marine algal lipids. Phytochemistry 11: 1423-1432.
Khotimchenko SV (1991). Fatty acid composition of seven Sargassumspecies. Phytochemistry 30(8): 2639-2641.
Miyazawa M, Uematsu T, Kameoka H (1982).Wax composition of Sargassum fulvellum. Phytochemistry 21(7): 1788-1791.
Nicols PD, Volkman JK, Johns RB (1983). Sterols and fatty acids of the unicellular alga FCRG 51. Phytochemistry 22(6): 1447-1452.
Takagi T, Asahi M, Itabashi Y (1985). Fatty acid composition of twelve algae from Japanese waters. Yukagaku 34(12): 1008-1012.
Napoli LD, Magno S, Mayo L, Novellino E (1982). Sterol composition of some Mediterranean green algae. Phytochemistry 21: 1993-1994.
Round FE (1973). The biology of algae. London: Edward Arnold.
Volkman JK, Smith DJ, Eglinton G, Forsboig TEV, Corner EDS (1981). Sterol and fatty acid composition of four marine haptophycean algae. J Mar Assoc 61(2): 509-527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heiba, H.I., Al-Easa, H.S. & Rizk, AF.M. Fatty acid composition of twelve algae from the coastal zones of Qatar. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 51, 27–34 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007980227542
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007980227542