Abstract
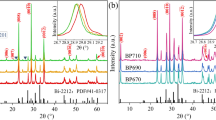
The effect of electron irradiation having the energy of 75, 100, and 200 keV on structural modifications of Bi-2212 superconducting samples has been studied. For the last energy, the irradiation time from zero to 150 min was used. At a constant energy of the electrons, the observed phenomena consist in the disappearance of the incommensurate unidimensional modulation, in the decreasing of spots' intensity and their elongation along the equivalent crystallographic axis a, and even spot splitting with the occurrence of double extra spots, with the increase of the irradiation time.
After electron irradiation with energy of 75 and 100 keV, the structural modifications lead to some spot patterns consisting of some planar lattices (in some cases a pseudo-tetragonal one) that are twisted on each other at different angles (8°, 13.6°, 19°, etc.) around the axis of the incident electron beam. For the irradiation at increased doses of thin microcrystals having reduced lateral dimensions, the electron diffraction spots were arranged in discrete or partial continuous Debye rings or continuous concentric Debye rings characteristic for the polycrystalline state.
After electron irradiation with energy of 200 keV, the effects of electron irradiation on Bi-2212 samples depend strongly on irradiation fluence rate and time and consisted in the following: disordering defects in the diffraction patterns (disappearance of some spots, spot intensity modification, streaks occurrence, spot elongation); alteration and disappearance of incommensurate structural modification; conversion of single crystal particle areas into polycrystalline material; and quasi-amorphization.
A simple approach based on the evaluation of the displacement yield of in-plane oxygen atoms vs. irradiation time for the different incident energy and electron fluence rates could explain the general trend of irradiation damage in HTS materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
G. Aldica, I. I. Geru, B. M. Puscasu, F. Constantinescu, P. Badica, J.Supercond. 9(3), 281 (1996).
S. K. Tolpygo, J.-Y. Lin, M. Gurvitch, S. T. Hou, J. M. Phillips, Phys.Rev. B 53(18), 12454 (1996).
S. K. Tolpygo, J.-Y. Lin, M. Gurvitch, S. T. Hou, J. M. Phillips, Phys.Rev. B 53(18), 12462 (1996).
A. Legris, F. Rullier-Albenque, E. Radeva, P. Lejay, J.Phys (France) 3, 1605 (1993).
J. Giapitzakis, D. M. Ginsberg, M. A. Kirk, S. Ockers, Phys. Rev. B 50, 15 967 (1994).
G. Aldica, A. Crisan, M. Velter-Stefanescu, S. Mandache, J.Mat.Sci. 32, 1195 (1997).
S. Mandache, A. Crisan, G. Aldica, S. Popa, J.Supercond. 10(3), 211 (1997).
M. Wang, G. Xiong, X. Tang, Z. Hong, Physica C 210, 113 (1993).
A. E. Hughes, D. Pooley, J.Phys. C 4, 1963 (1971).
C. H. Chen, D. J. Werder, S. H. Liou, H. S. Chen, M. Hong, Phys.Rev. B 37, 9834 (1988).
S. N. Basu, T. E. Mitchell, M. Nastasi, J.Appl.Phys. 69, 3167 (1991).
B. D. Weaver, E. M. Jackson, G. P. Summers, E. A. Burke, Phys.Rev. B 46, 1134 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aldica, G., Vasiliu, F., Geru, I.I. et al. The Effect of Electron Beam Irradiation on Electron Diffraction Patterns of Bi-Sr-Ca-Cu-O High- Tc Superconductors. Journal of Superconductivity 13, 623–631 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007889204595
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007889204595